Flink 系列文章
1、Flink 部署、概念介绍、source、transformation、sink使用示例、四大基石介绍和示例等系列综合文章链接
13、Flink 的table api与sql的基本概念、通用api介绍及入门示例
14、Flink 的table api与sql之数据类型: 内置数据类型以及它们的属性
15、Flink 的table api与sql之流式概念-详解的介绍了动态表、时间属性配置(如何处理更新结果)、时态表、流上的join、流上的确定性以及查询配置
20、Flink SQL之SQL Client: 不用编写代码就可以尝试 Flink SQL,可以直接提交 SQL 任务到集群上
22、Flink 的table api与sql之创建表的DDL
30、Flink SQL之SQL 客户端(通过kafka和filesystem的例子介绍了配置文件使用-表、视图等)
本文介绍了flink cli的启动、使用以及通过创建kafka、filesystem等例子介绍了配置文件的使用,同时也简单的介绍了视图、临时表等内容。
本文依赖环境是flink、kafka环境可用,flink的版本是1.13.5、jdk8.
一、SQL客户端
Flink 的 Table & SQL API 可以处理 SQL 语言编写的查询语句,但是这些查询需要嵌入用 Java 或 Scala 编写的表程序中。此外,这些程序在提交到集群前需要用构建工具打包。这或多或少限制了 Java/Scala 程序员对 Flink 的使用。
SQL 客户端 的目的是提供一种简单的方式来编写、调试和提交表程序到 Flink 集群上,而无需写一行 Java 或 Scala 代码。SQL 客户端命令行界面(CLI) 能够在命令行中检索和可视化分布式应用中实时产生的结果。
部署请参考:1、Flink1.12.7或1.13.5详细介绍及本地安装部署、验证 和 2、Flink1.13.5二种部署方式(Standalone、Standalone HA )、四种提交任务方式(前两种及session和per-job)验证详细步骤
1、启动 SQL 客户端命令行界面
SQL Client 脚本也位于 Flink 的 bin 目录中。将来,用户可以通过启动嵌入式 standalone 进程或通过连接到远程 SQL 客户端网关来启动 SQL 客户端命令行界面。目前仅支持 embedded 模式。可以通过以下方式启动 CLI:
#启动flink sql客户端
./bin/sql-client.sh embedded -d 配置文件
#或
./bin/sql-client.sh embedded
#或
./bin/sql-client.sh
#注意:需要使用部署flink集群的用户启动
[alanchan@server1 bin]$ sql-client.sh embedded
SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/local/flink-1.13.5/lib/log4j-slf4j-impl-2.16.0.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/local/bigdata/hadoop-3.1.4/share/hadoop/common/lib/slf4j-log4j12-1.7.25.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLoggerFactory]
No default environment specified.
Searching for '/usr/local/flink-1.13.5/conf/sql-client-defaults.yaml'...not found.
Command history file path: /home/alanchan/.flink-sql-history
▒▓██▓██▒
▓████▒▒█▓▒▓███▓▒
▓███▓░░ ▒▒▒▓██▒ ▒
░██▒ ▒▒▓▓█▓▓▒░ ▒████
██▒ ░▒▓███▒ ▒█▒█▒
░▓█ ███ ▓░▒██
▓█ ▒▒▒▒▒▓██▓░▒░▓▓█
█░ █ ▒▒░ ███▓▓█ ▒█▒▒▒
████░ ▒▓█▓ ██▒▒▒ ▓███▒
░▒█▓▓██ ▓█▒ ▓█▒▓██▓ ░█░
▓░▒▓████▒ ██ ▒█ █▓░▒█▒░▒█▒
███▓░██▓ ▓█ █ █▓ ▒▓█▓▓█▒
░██▓ ░█░ █ █▒ ▒█████▓▒ ██▓░▒
███░ ░ █░ ▓ ░█ █████▒░░ ░█░▓ ▓░
██▓█ ▒▒▓▒ ▓███████▓░ ▒█▒ ▒▓ ▓██▓
▒██▓ ▓█ █▓█ ░▒█████▓▓▒░ ██▒▒ █ ▒ ▓█▒
▓█▓ ▓█ ██▓ ░▓▓▓▓▓▓▓▒ ▒██▓ ░█▒
▓█ █ ▓███▓▒░ ░▓▓▓███▓ ░▒░ ▓█
██▓ ██▒ ░▒▓▓███▓▓▓▓▓██████▓▒ ▓███ █
▓███▒ ███ ░▓▓▒░░ ░▓████▓░ ░▒▓▒ █▓
█▓▒▒▓▓██ ░▒▒░░░▒▒▒▒▓██▓░ █▓
██ ▓░▒█ ▓▓▓▓▒░░ ▒█▓ ▒▓▓██▓ ▓▒ ▒▒▓
▓█▓ ▓▒█ █▓░ ░▒▓▓██▒ ░▓█▒ ▒▒▒░▒▒▓█████▒
██░ ▓█▒█▒ ▒▓▓▒ ▓█ █░ ░░░░ ░█▒
▓█ ▒█▓ ░ █░ ▒█ █▓
█▓ ██ █░ ▓▓ ▒█▓▓▓▒█░
█▓ ░▓██░ ▓▒ ▓█▓▒░░░▒▓█░ ▒█
██ ▓█▓░ ▒ ░▒█▒██▒ ▓▓
▓█▒ ▒█▓▒░ ▒▒ █▒█▓▒▒░░▒██
░██▒ ▒▓▓▒ ▓██▓▒█▒ ░▓▓▓▓▒█▓
░▓██▒ ▓░ ▒█▓█ ░░▒▒▒
▒▓▓▓▓▓▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒░░▓▓ ▓░▒█░
______ _ _ _ _____ ____ _ _____ _ _ _ BETA
| ____| (_) | | / ____|/ __ | | / ____| (_) | |
| |__ | |_ _ __ | | __ | (___ | | | | | | | | |_ ___ _ __ | |_
| __| | | | '_ | |/ / \___ | | | | | | | | | |/ _ '_ | __|
| | | | | | | | < ____) | |__| | |____ | |____| | | __/ | | | |_
|_| |_|_|_| |_|_|_ |_____/ __________| _____|_|_|___|_| |_|__|
Welcome! Enter 'HELP;' to list all available commands. 'QUIT;' to exit.
Flink SQL> select 1;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
默认情况下,SQL 客户端将从 ./conf/sql-client-defaults.yaml 中读取配置。有关环境配置文件结构的更多信息,请参见本文配置部分。
2、执行 SQL 查询
命令行界面启动后,你可以使用 HELP 命令列出所有可用的 SQL 语句。输入第一条 SQL 查询语句并按 Enter 键执行,可以验证你的设置及集群连接是否正确:
Flink SQL> show databases;
+------------------+
| database name |
+------------------+
| default_database |
+------------------+
1 row in set
Flink SQL> use default_database;
[INFO] Execute statement succeed.
Flink SQL> show tables;
Empty set
Flink SQL> SELECT 'Hello World';
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
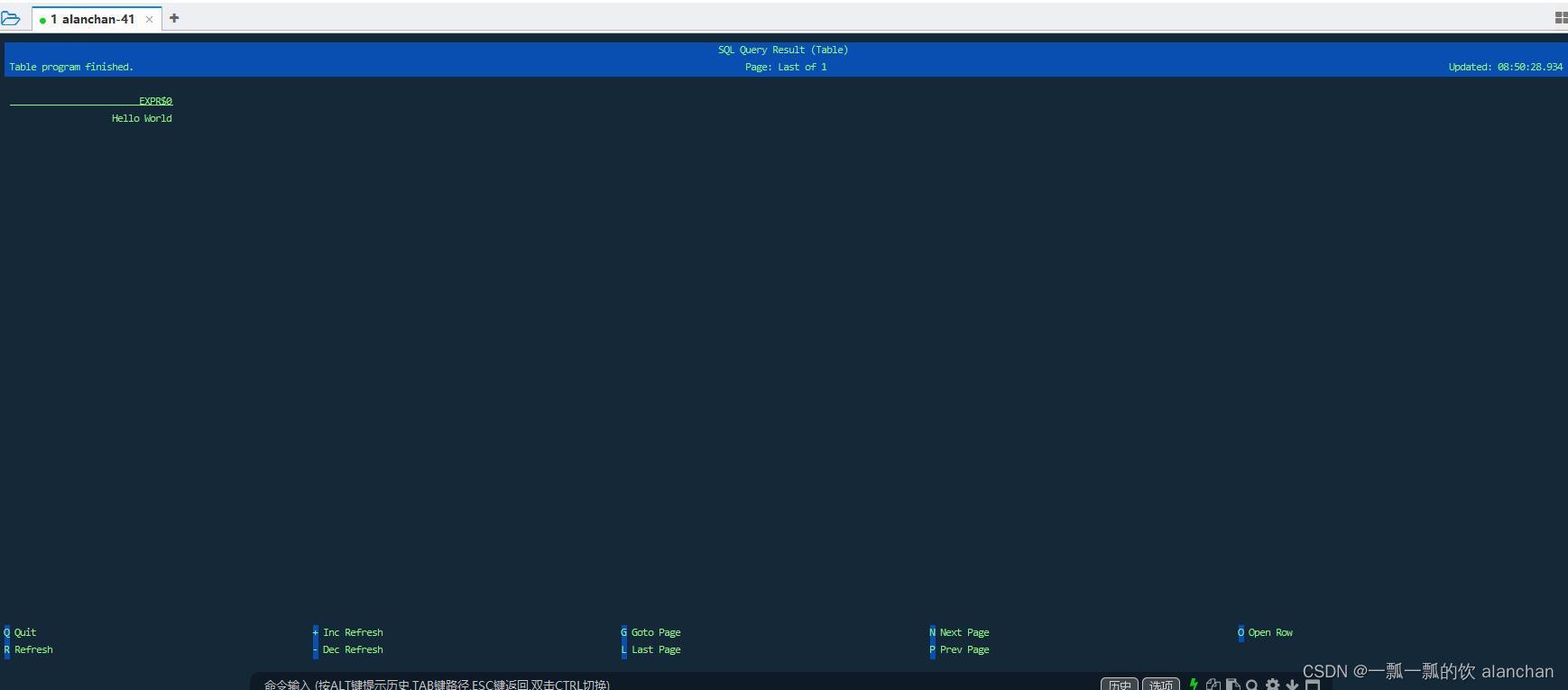
该查询不需要 table source,并且只产生一行结果。CLI 将从集群中检索结果并将其可视化。按 Q 键退出结果视图。
CLI 为维护和可视化结果提供三种模式。
- 表格模式(table mode)在内存中实体化结果,并将结果用规则的分页表格可视化展示出来。执行如下命令启用:
SET execution.result-mode=table;
Flink SQL> SET execution.result-mode=table;
[WARNING] The specified key 'execution.result-mode' is deprecated. Please use 'sql-client.execution.result-mode' instead.
[INFO] Session property has been set.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
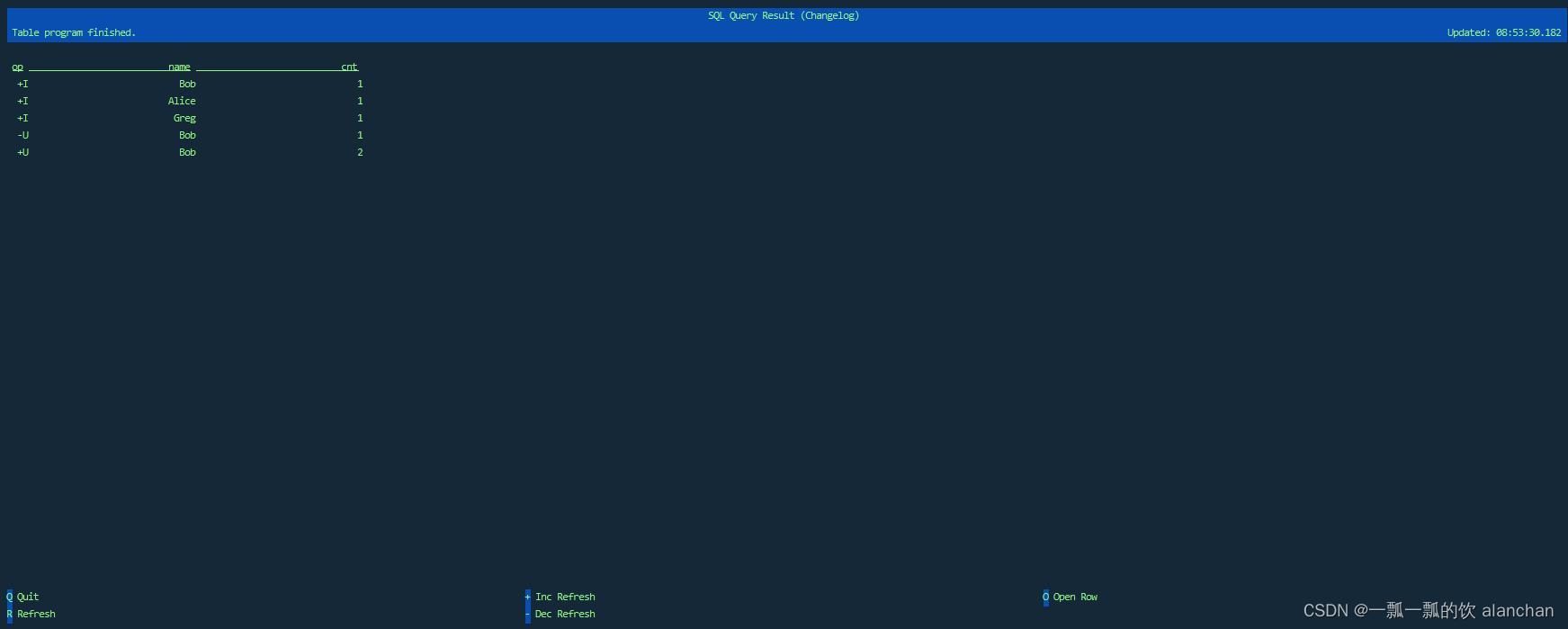
- 变更日志模式(changelog mode)不会实体化和可视化结果,而是由插入(+)和撤销(-)组成的持续查询产生结果流。
SET execution.result-mode=changelog;
Flink SQL> SET execution.result-mode=changelog;
[WARNING] The specified key 'execution.result-mode' is deprecated. Please use 'sql-client.execution.result-mode' instead.
[INFO] Session property has been set.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
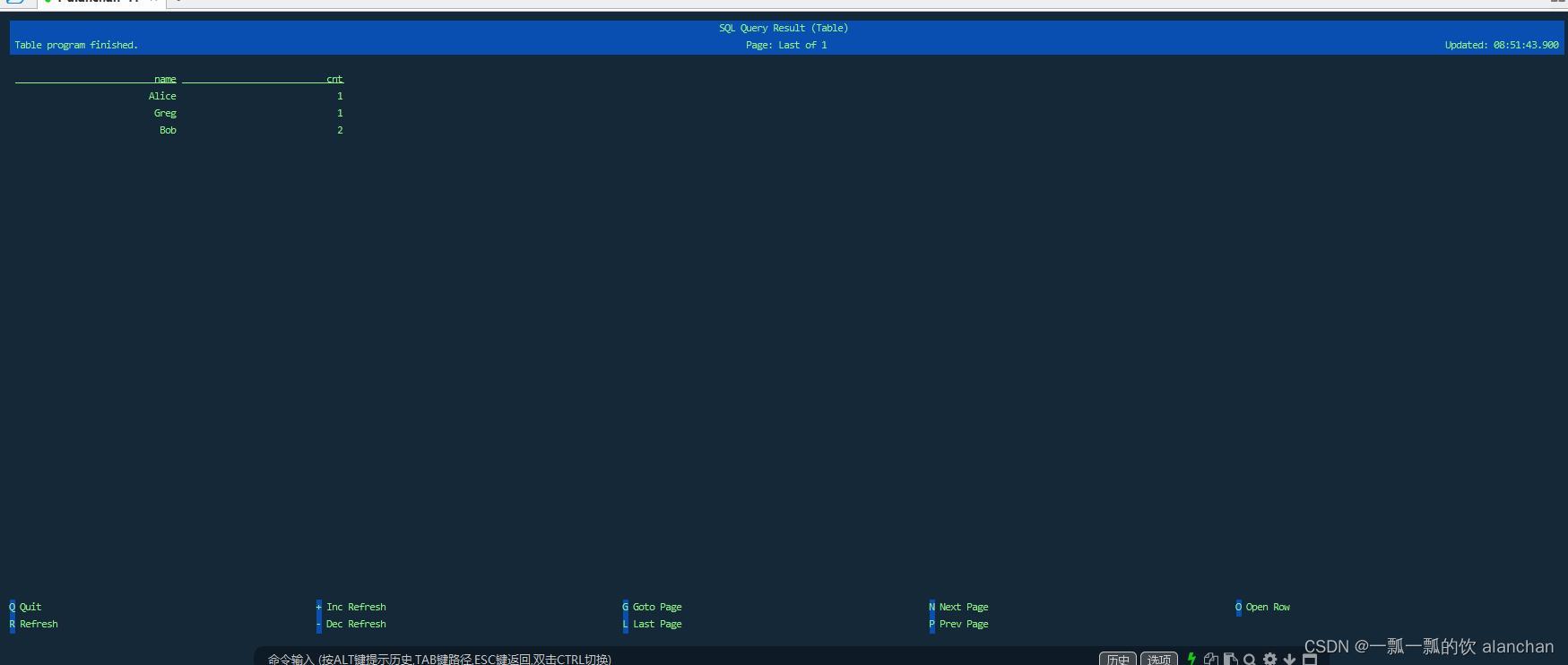
- Tableau模式(tableau mode)更接近传统的数据库,会将执行的结果以制表的形式直接打在屏幕之上。具体显示的内容会取决于作业 执行模式的不同(execution.type):
SET execution.result-mode=tableau;
Flink SQL> SET execution.result-mode=tableau;
[WARNING] The specified key 'execution.result-mode' is deprecated. Please use 'sql-client.execution.result-mode' instead.
[INFO] Session property has been set.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注意当你使用这个模式运行一个流式查询的时候,Flink 会将结果持续的打印在当前的屏幕之上。如果这个流式查询的输入是有限的数据集, 那么Flink在处理完所有的数据之后,会自动的停止作业,同时屏幕上的打印也会相应的停止。如果你想提前结束这个查询,那么可以直接使用 CTRL-C 按键,这个会停掉作业同时停止屏幕上的打印。
你可以用如下查询来查看三种结果模式的运行情况:
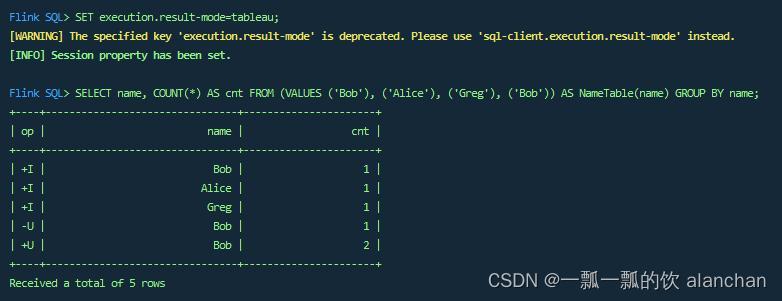
SELECT name, COUNT(*) AS cnt FROM (VALUES ('Bob'), ('Alice'), ('Greg'), ('Bob')) AS NameTable(name) GROUP BY name;
- 1
- 2
此查询执行一个有限字数示例:
变更日志模式 下,看到的结果应该类似于:
表格模式 下,可视化结果表将不断更新,直到表程序以如下内容结束:
Tableau模式 下,如果这个查询以流的方式执行,那么将显示以下内容:
如果这个查询以批的方式执行,显示的内容如下:
±------±----+
| name | cnt |
±------±----+
| Alice | 1 |
| Bob | 2 |
| Greg | 1 |
±------±----+
3 rows in set
这几种结果模式在 SQL 查询的原型设计过程中都非常有用。这些模式的结果都存储在 SQL 客户端 的 Java 堆内存中。为了保持 CLI 界面及时响应,变更日志模式仅显示最近的 1000 个更改。表格模式支持浏览更大的结果,这些结果仅受可用主内存和配置的最大行数(max-table-result-rows)的限制。
在批处理环境下执行的查询只能用表格模式或者Tableau模式进行检索。
定义查询语句后,可以将其作为长时间运行的独立 Flink 作业提交给集群。为此,其目标系统需要使用 INSERT INTO 语句指定存储结果。配置部分解释如何声明读取数据的 table source,写入数据的 sink 以及配置其他表程序属性的方法。
3、配置
SQL 客户端启动时可以添加 CLI 选项,具体如下。
./bin/sql-client.sh embedded --help
Mode "embedded" submits Flink jobs from the local machine.
Syntax: embedded [OPTIONS]
"embedded" mode options:
-d,--defaults <environment file> The environment properties with which every new session is initialized.
Properties might be overwritten by session properties.
-e,--environment <environment file> The environment properties to be imported into the session. It might
overwrite default environment properties.
-h,--help Show the help message with descriptions of all options.
-hist,--history <History file path> The file which you want to save the command history into. If not
specified, we will auto-generate one under your user's home directory.
-j,--jar A JAR file to be imported into the
session. The file might contain
user-defined classes needed for the
execution of statements such as
functions, table sources, or sinks.
Can be used multiple times.
-l,--library A JAR file directory with which every
new session is initialized. The files
might contain user-defined classes
needed for the execution of
statements such as functions, table
sources, or sinks. Can be used
multiple times.
-pyarch,--pyArchives Add python archive files for job. The
archive files will be extracted to
the working directory of python UDF
worker. Currently only zip-format is
supported. For each archive file, a
target directory be specified. If the
target directory name is specified,
the archive file will be extracted to
a name can directory with the
specified name. Otherwise, the
archive file will be extracted to a
directory with the same name of the
archive file. The files uploaded via
this option are accessible via
relative path. ' #' could be used as
the separator of the archive file
path and the target directory name.
Comma (',') could be used as the
separator to specify multiple archive
files. This option can be used to
upload the virtual environment, the
data files used in Python UDF (e.g.:
--pyArchives
file:///tmp/py37.zip,file:///tmp/data
.zip#data --pyExecutable
py37.zip/py37/bin/python). The data
files could be accessed in Python
UDF, e.g.: f = open('data/data.txt',
'r').
-pyexec,--pyExecutable <arg> Specify the path of the python
interpreter used to execute the
python UDF worker (e.g.:
--pyExecutable
/usr/local/bin/python3). The python
UDF worker depends on Python 3.5+,
Apache Beam (version == 2.23.0), Pip
(version >= 7.1.0) and SetupTools
(version >= 37.0.0). Please ensure
that the specified environment meets
the above requirements.
-pyfs,--pyFiles <pythonFiles> Attach custom python files for job.
These files will be added to the
PYTHONPATH of both the local client
and the remote python UDF worker. The
standard python resource file
suffixes such as .py/.egg/.zip or
directory are all supported. Comma
(',') could be used as the separator
to specify multiple files (e.g.:
--pyFiles
file:///tmp/myresource.zip,hdfs:///$n
amenode_address/myresource2.zip).
-pyreq,--pyRequirements <arg> Specify a requirements.txt file which
defines the third-party dependencies.
These dependencies will be installed
and added to the PYTHONPATH of the
python UDF worker. A directory which
contains the installation packages of
these dependencies could be specified
optionally. Use '#' as the separator
if the optional parameter exists
(e.g.: --pyRequirements
file:///tmp/requirements.txt#file:///
tmp/cached_dir).
-s,--session <session identifier> The identifier for a session.
'default' is the default identifier.
-u,--update <SQL update statement> Experimental (for testing only!):
Instructs the SQL Client to
immediately execute the given update
statement after starting up. The
process is shut down after the
statement has been submitted to the
cluster and returns an appropriate
return code. Currently, this feature
is only supported for INSERT INTO
statements that declare the target
sink table.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
1、环境配置文件
1、flink cli配置文件说明如下
默认情况下,SQL 客户端将从 ./conf/sql-client-defaults.yaml 中读取配置。
SQL 查询执行前需要配置相关环境变量。环境配置文件 定义了 catalog、table sources、table sinks、用户自定义函数和其他执行或部署所需属性。
每个环境配置文件是常规的 YAML 文件,例子如下。
tables:
- name: Users_Testing_alanchan
type: source-table
update-mode: append
connector:
type: filesystem
path: "/usr/local/bigdata/testdata/flink/users.csv"
format:
type: csv
fields:
- name: u_id
data-type: INT
- name: u_name
data-type: VARCHAR
- name: u_age
data-type: INT
- name: u_balance
data-type: DOUBLE
line-delimiter: "
"
comment-prefix: "#"
schema:
- name: u_id
data-type: INT
- name: u_name
data-type: VARCHAR
- name: u_age
data-type: INT
- name: u_balance
data-type: DOUBLE
- name: Users_Testing_alanchan_View
type: view
query: "SELECT u_id,u_name,u_age FROM Users_Testing_alanchan"
# 定义用户自定义函数
# functions:
# - name: myUDF
# from: class
# class: foo.bar.AggregateUDF
# constructor:
# - 7.6
# - false
# 定义 catalogs
# catalogs:
# - name: catalog_1
# type: hive
# property-version: 1
# hive-conf-dir: ...
# - name: catalog_2
# type: hive
# property-version: 1
# default-database: mydb2
# hive-conf-dir: ...
# 改变表程序基本的执行行为属性。
execution:
planner: blink # 可选: 'blink' (默认)或 'old'
type: streaming # 必选:执行模式为 'batch' 或 'streaming'
result-mode: table # 必选:'table' 或 'changelog'
max-table-result-rows: 1000000 # 可选:'table' 模式下可维护的最大行数(默认为 1000000,小于 1 则表示无限制)
time-characteristic: event-time # 可选: 'processing-time' 或 'event-time' (默认)
parallelism: 1 # 可选:Flink 的并行数量(默认为 1)
periodic-watermarks-interval: 200 # 可选:周期性 watermarks 的间隔时间(默认 200 ms)
max-parallelism: 16 # 可选:Flink 的最大并行数量(默认 128)
min-idle-state-retention: 0 # 可选:表程序的最小空闲状态时间
max-idle-state-retention: 0 # 可选:表程序的最大空闲状态时间
current-catalog: default_catalog # 可选:当前会话 catalog 的名称(默认为 'default_catalog')
current-database: default_database # 可选:当前 catalog 的当前数据库名称(默认为当前 catalog 的默认数据库)
restart-strategy: # 可选:重启策略(restart-strategy)
type: fallback # 默认情况下“回退”到全局重启策略
# 用于调整和调优表程序的配置选项。
# 在专用的”配置”页面上可以找到完整的选项列表及其默认值。
configuration:
table.optimizer.join-reorder-enabled: true
table.exec.spill-compression.enabled: true
table.exec.spill-compression.block-size: 128kb
# 描述表程序提交集群的属性。
deployment:
response-timeout: 5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
上述配置:
- 定义一个从 CSV 文件中读取的 table source Users_Testing_alanchan 所需的环境,
- 定义了一个视图 Users_Testing_alanchan_View ,该视图是用 SQL 查询声明的虚拟表,
- 定义了一个用户自定义函数 myUDF,该函数可以使用类名和两个构造函数参数进行实例化,已注释掉
- 连接到两个 Hive catalogs 并用 catalog_1 来作为当前目录,用 mydb1 来作为该目录的当前数据库,已注释掉
- streaming 模式下用 blink planner 来运行时间特征为 event-time 和并行度为 1 的语句,
- 在 table 结果模式下运行试探性的(exploratory)的查询,
- 并通过配置选项对联结(join)重排序和溢出进行一些计划调整。
重新启动flink cli,内容如下:
- users.csv文件内容
需要将该文件放在flink集群中的每台机器上
1,alan,18,20
2,alanchan,19,30
3,alanchanchn,20,40
4,alan_chan,25,60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- flink cli查询
查询表和视图
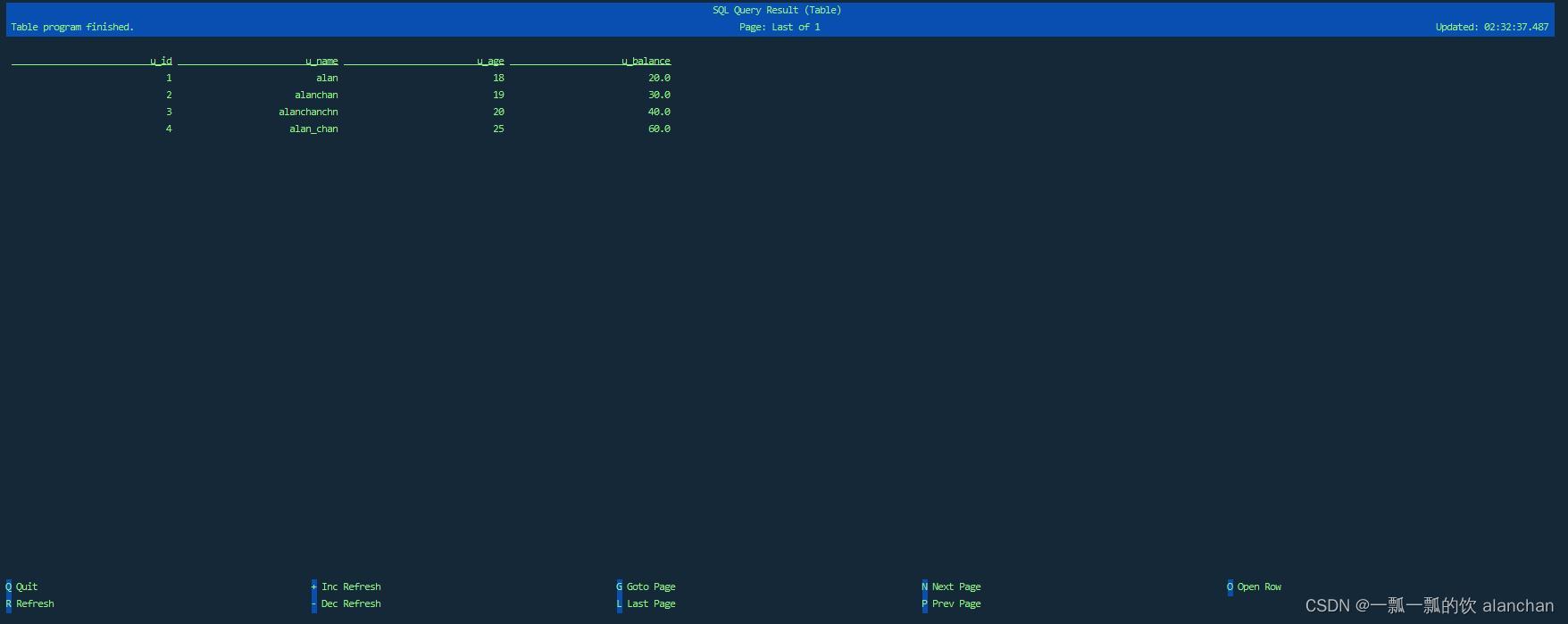
Flink SQL> select * from Users_Testing_alanchan ;
- 1
- 2
- 表显示如下
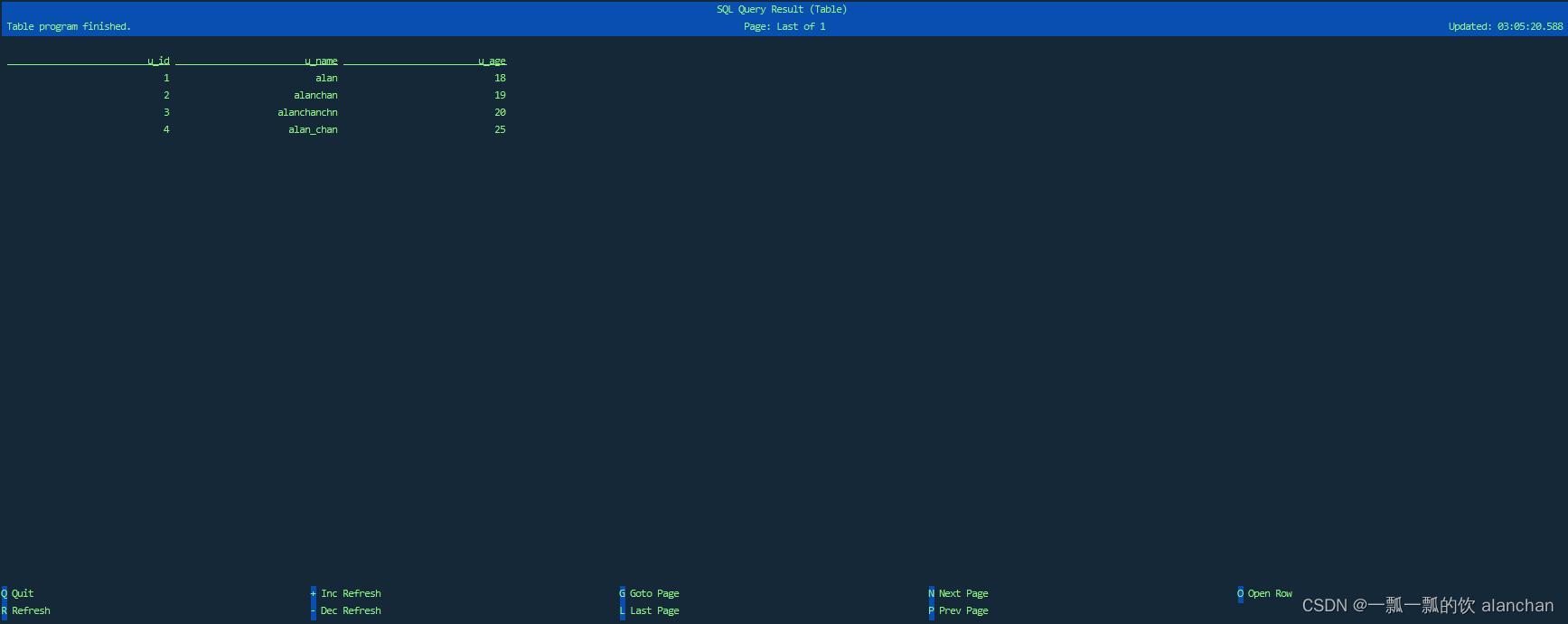
- 视图显示如下
Flink SQL> select * from Users_Testing_alanchan_View;
- 1
- 2
根据使用情况,配置可以被拆分为多个文件。因此,一般情况下(用 --defaults 指定默认环境配置文件)以及基于每个会话(用 --environment 指定会话环境配置文件)来创建环境配置文件。每个 CLI 会话均会被属于 session 属性的默认属性初始化。例如,默认环境配置文件可以指定在每个会话中都可用于查询的所有 table source,而会话环境配置文件仅声明特定的状态保留时间和并行性。启动 CLI 应用程序时,默认环境配置文件和会话环境配置文件都可以被指定。如果未指定默认环境配置文件,则 SQL 客户端将在 Flink 的配置目录中搜索 ./conf/sql-client-defaults.yaml。
在 CLI 会话中设置的属性(如 SET 命令)优先级最高:
CLI commands > session environment file > defaults environment file
2、重启策略(Restart Strategies)
重启策略控制 Flink 作业失败时的重启方式。与 Flink 集群的全局重启策略相似,更细精度的重启配置可以在环境配置文件中声明。
Flink 支持以下策略:
execution:
# 退回到 flink-conf.yaml 中定义的全局策略
restart-strategy:
type: fallback
# 作业直接失败并且不尝试重启
restart-strategy:
type: none
# 最多重启作业的给定次数
restart-strategy:
type: fixed-delay
attempts: 3 # 作业被宣告失败前的重试次数(默认:Integer.MAX_VALUE)
delay: 10000 # 重试之间的间隔时间,以毫秒为单位(默认:10 秒)
# 只要不超过每个时间间隔的最大故障数就继续尝试
restart-strategy:
type: failure-rate
max-failures-per-interval: 1 # 每个间隔重试的最大次数(默认:1)
failure-rate-interval: 60000 # 监测失败率的间隔时间,以毫秒为单位
delay: 10000 # 重试之间的间隔时间,以毫秒为单位(默认:10 秒)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
2)、依赖
SQL 客户端不要求用 Maven 或者 SBT 设置 Java 项目。相反,你可以以常规的 JAR 包给集群提交依赖项。你也可以分别(用 --jar)指定每一个 JAR 包或者(用 --library)定义整个 library 依赖库。为连接扩展系统(如 Apache Kafka)和相应的数据格式(如 JSON),Flink提供了开箱即用型 JAR 捆绑包(ready-to-use JAR bundles)。这些 JAR 包各个发行版都可以从 Maven 中央库中下载到。
更多的关于外部连接系统示例参考:
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及FileSystem示例(1)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Elasticsearch示例(2)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache Kafka示例(3)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及JDBC示例(4)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache HBase示例(5)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache Hive示例(6)
如下例子展示了从 Apache Kafka 中读取 csv 文件并作为 table source 的环境配置文件。
# kafka表
tables:
- name: Test_Flink_Kafka_Source_SQL
type: source-table
update-mode: append
connector:
property-version: 1
type: kafka
version: "universal"
topic: t_kafkasource_testing
startup-mode: earliest-offset
properties:
bootstrap.servers: "192.168.10.41:9092,192.168.10.42:9092,192.168.10.43:9092"
group.id: flink_alan_kafka
format:
property-version: 1
type: csv
schema: "ROW"
schema:
- name: t_id
data-type: BIGINT
- name: t_name
data-type: STRING
- name: t_balance
data-type: DOUBLE
- name: t_age
data-type: INT
- name: rowTime
data-type: TIMESTAMP(3)
rowtime:
timestamps:
type: "from-field"
from: "t_insert_time"
watermarks:
type: "periodic-bounded"
delay: "60000"
- name: procTime
data-type: TIMESTAMP(3)
proctime: true
# 改变表程序基本的执行行为属性。
execution:
planner: blink # 可选: 'blink' (默认)或 'old'
type: streaming # 必选:执行模式为 'batch' 或 'streaming'
result-mode: table # 必选:'table' 或 'changelog'
max-table-result-rows: 1000000 # 可选:'table' 模式下可维护的最大行数(默认为 1000000,小于 1 则表示无限制)
time-characteristic: event-time # 可选: 'processing-time' 或 'event-time' (默认)
parallelism: 1 # 可选:Flink 的并行数量(默认为 1)
periodic-watermarks-interval: 200 # 可选:周期性 watermarks 的间隔时间(默认 200 ms)
max-parallelism: 16 # 可选:Flink 的最大并行数量(默认 128)
min-idle-state-retention: 0 # 可选:表程序的最小空闲状态时间
max-idle-state-retention: 0 # 可选:表程序的最大空闲状态时间
current-catalog: default_catalog # 可选:当前会话 catalog 的名称(默认为 'default_catalog')
current-database: default_database # 可选:当前 catalog 的当前数据库名称(默认为当前 catalog 的默认数据库)
restart-strategy: # 可选:重启策略(restart-strategy)
type: fallback # 默认情况下“回退”到全局重启策略
# 用于调整和调优表程序的配置选项。
# 在专用的”配置”页面上可以找到完整的选项列表及其默认值。
configuration:
table.optimizer.join-reorder-enabled: true
table.exec.spill-compression.enabled: true
table.exec.spill-compression.block-size: 128kb
# 描述表程序提交集群的属性。
deployment:
response-timeout: 5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
运行上面的配置需要在flink的lib文件夹下增加关于kafka的依赖包,上述例子中增加了如下包
本文的依赖环境是flink 1.13.5
flink-sql-connector-kafka_2.11-1.13.5.jar
# 要重启集群
- 1
- 2
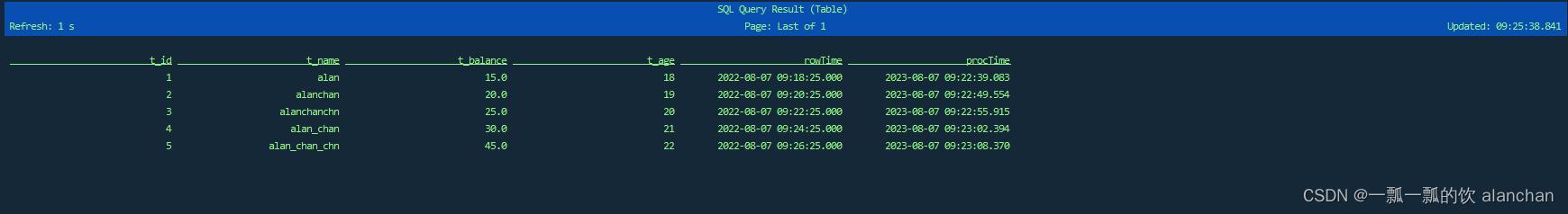
Test_Flink_Kafka_Source_SQL 表的结果格式与绝大多数的 csv 格式相似。此外,它还添加了 rowtime 属性 rowTime 和 processing-time 属性 procTime。
connector 和 format 都允许定义属性版本(当前版本为 1 )以便将来向后兼容。
- 验证
# kafka主题操作
kafka-topics.sh --delete --topic t_kafkasource_testing --bootstrap-server server1:9092
kafka-topics.sh --create --bootstrap-server server1:9092 --topic t_kafkasource_testing --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1
kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list server1:9092 --topic t_kafkasource_testing
# 测试数据
1,alan,15,18,2022-08-07 09:18:25
2,alanchan,20,19,2022-08-07 09:20:25
3,alanchanchn,25,20,2022-08-07 09:22:25
4,alan_chan,30,21,2022-08-07 09:24:25
5,alan_chan_chn,45,22,2022-08-07 09:26:25
# kafka客户端操作
[alanchan@server2 bin]$ kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list server1:9092 --topic t_kafkasource_testing
>1,alan,15,18,2022-08-07 09:18:25
>2,alanchan,20,19,2022-08-07 09:20:25
>3,alanchanchn,25,20,2022-08-07 09:22:25
>4,alan_chan,30,21,2022-08-07 09:24:25
>5,alan_chan_chn,45,22,2022-08-07 09:26:25
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 查询结果
3)、自定义函数(User-defined Functions)
SQL 客户端允许用户创建用户自定义的函数来进行 SQL 查询。当前,这些自定义函数仅限于 Java/Scala 编写的类以及 Python 文件。
为提供 Java/Scala 的自定义函数,你首先需要实现和编译函数类,该函数继承自 ScalarFunction、 AggregateFunction 或 TableFunction(19、Flink 的table api与sql之内置函数: Table API 和 SQL 中的内置函数)。一个或多个函数可以打包到 SQL 客户端的 JAR 依赖中。
所有函数在被调用之前,必须在环境配置文件中提前声明。functions 列表中每个函数类都必须指定
- 用来注册函数的 name,
- 函数的来源 from(目前仅限于 class(Java/Scala UDF),
Java/Scala UDF 必须指定:
- 声明了全限定名的函数类 class 以及用于实例化的 constructor 参数的可选列表。
functions:
- name: java_udf # required: name of the function
from: class # required: source of the function
class: ... # required: fully qualified class name of the function
constructor: # optional: constructor parameters of the function class
- ... # optional: a literal parameter with implicit type
- class: ... # optional: full class name of the parameter
constructor: # optional: constructor parameters of the parameter's class
- type: ... # optional: type of the literal parameter
value: ... # optional: value of the literal parameter
- name: python_udf # required: name of the function
from: python # required: source of the function
fully-qualified-name: ... # required: fully qualified class name of the function
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
对于 Java/Scala UDF,要确保函数类指定的构造参数顺序和类型都要严格匹配。
1、构造函数参数
根据用户自定义函数可知,在用到 SQL 语句中之前,有必要将构造参数匹配对应的类型。
如上述示例所示,当声明一个用户自定义函数时,可以使用构造参数来配置相应的类,有以下三种方式:
- 隐式类型的文本值:SQL 客户端将自动根据文本推导对应的类型。目前,只支持 BOOLEAN、INT、 DOUBLE 和 VARCHAR 。
如果自动推导的类型与期望不符(例如,你需要 VARCHAR 类型的 false),可以改用显式类型。
- true # -> BOOLEAN (case sensitive)
- 42 # -> INT
- 1234.222 # -> DOUBLE
- foo # -> VARCHAR
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 显式类型的文本值:为保证类型安全,需明确声明 type 和 value 属性的参数。
- type: DECIMAL
value: 11111111111111111
- 1
- 2
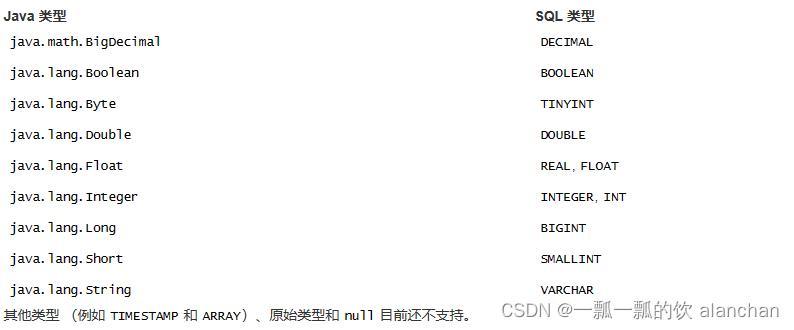
下表列出支持的 Java 参数类型和与之相对应的 SQL 类型。
- (嵌套)类实例:除了文本值外,还可以通过指定构造参数的 class 和 constructor 属性来创建(嵌套)类实例。这个过程可以递归执行,直到最后的构造参数是用文本值来描述的。
- class: foo.bar.paramClass
constructor:
- StarryName
- class: java.lang.Integer
constructor:
- class: java.lang.String
constructor:
- type: VARCHAR
value: 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4、Catalogs
Catalogs 可以由 YAML 属性集合定义,并且在 SQL 客户端启动之前自动注册到运行环境中。
用户可以指定在 SQL CLI 中哪些 catalog 要被作为当前的 catalog,以及哪个数据库的 catalog 可以用于当前数据库。
catalogs:
- name: catalog_1
type: hive
property-version: 1
default-database: mydb2
hive-conf-dir: >
- name: catalog_2
type: hive
property-version: 1
hive-conf-dir: >
execution:
...
current-catalog: catalog_1
current-database: mydb1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
更多关于 catalog 的内容,参考 24、Flink 的table api与sql之Catalogs。
5、分离的 SQL 查询
为定义端到端的 SQL 管道,SQL 的 INSERT INTO 语句可以向 Flink 集群提交长时间运行的分离查询。查询产生的结果输出到除 SQL 客户端外的扩展系统中。这样可以应对更高的并发和更多的数据。CLI 自身在提交后不对分离查询做任何控制。
INSERT INTO MyTableSink SELECT * FROM MyTableSource
- 1
sink MyTableSink 必须在环境配置文件中声明。查看更多关于 Flink 支持的外部系统及其配置信息,参见
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及FileSystem示例(1)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Elasticsearch示例(2)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache Kafka示例(3)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及JDBC示例(4)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache HBase示例(5)
16、Flink 的table api与sql之连接外部系统: 读写外部系统的连接器和格式以及Apache Hive示例(6)
如下展示 Apache Kafka 的 sink 示例。
CREATE TABLE Table_Sink_Kafka (
t_id BIGINT,
t_name STRING,
t_balance DOUBLE,
t_age INT,
t_insert_time TIMESTAMP(3)
) WITH (
'connector' = 'kafka',
'topic' = 't_kafka_sink_flink',
'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset',
'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '192.168.10.41:9092,192.168.10.42:9092,192.168.10.43:9092',
'format' = 'csv'
);
Flink SQL> CREATE TABLE Table_Sink_Kafka (
> t_id BIGINT,
> t_name STRING,
> t_balance DOUBLE,
> t_age INT,
> t_insert_time TIMESTAMP(3)
> ) WITH (
> 'connector' = 'kafka',
> 'topic' = 't_kafka_sink_flink',
> 'scan.startup.mode' = 'earliest-offset',
> 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '192.168.10.41:9092,192.168.10.42:9092,192.168.10.43:9092',
> 'format' = 'csv'
> );
[INFO] Execute statement succeed.
Flink SQL> select * from Test_Flink_Kafka_Source_SQL;
[INFO] Result retrieval cancelled.
-- 查询结果如下
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
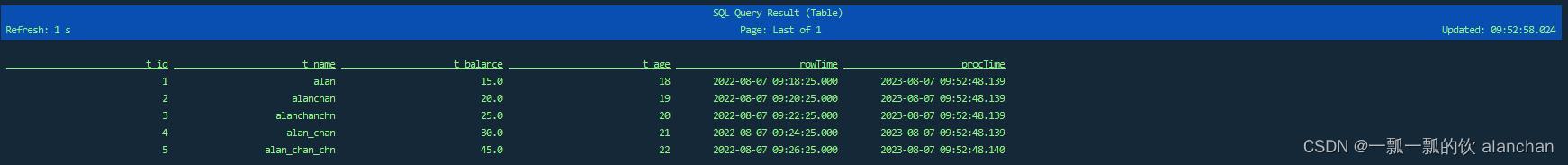
SQL 客户端要确保语句成功提交到集群上。一旦提交查询,CLI 将展示关于 Flink 作业的相关信息。
Flink SQL> INSERT INTO Table_Sink_Kafka SELECT t_id,t_name,t_balance,t_age,rowTime FROM Test_Flink_Kafka_Source_SQL;
[INFO] Submitting SQL update statement to the cluster...
[INFO] SQL update statement has been successfully submitted to the cluster:
Job ID: 40769216d90fa12fd0696e8e0a6dec2d
Flink SQL> select * from Table_Sink_Kafka;
-- 插入后的数据如下
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
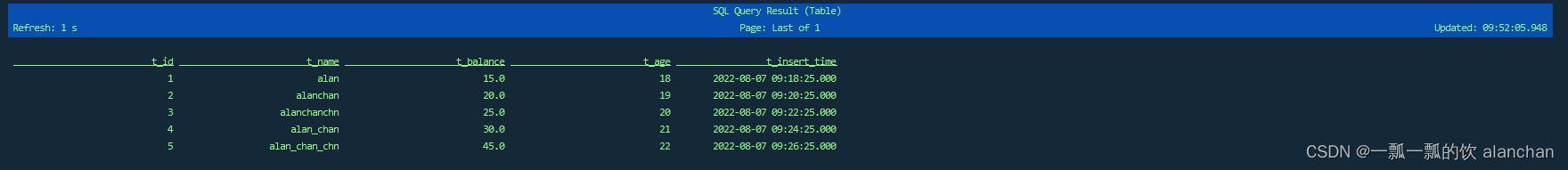
提交后,SQL 客户端不追踪正在运行的 Flink 作业状态。提交后可以关闭 CLI 进程,并且不会影响分离的查询。Flink 的重启策略负责容错。取消查询可以用 Flink 的 web 接口、命令行或 REST API 。
6、SQL 视图
视图是一张虚拟表,允许通过 SQL 查询来定义。视图的定义会被立即解析与验证。然而,提交常规 INSERT INTO 或 SELECT 语句后不会立即执行,在访问视图时才会真正执行。
视图可以用环境配置文件或者 CLI 会话来定义。
下例展示如何在一个文件里定义多张视图。视图注册的顺序和定义它们的环境配置文件一致。支持诸如 视图 A 依赖视图 B ,视图 B 依赖视图 C 的引用链。
tables:
# filesystem表
- name: Users_Testing_view_alanchan
type: source-table
update-mode: append
connector:
type: filesystem
path: "/usr/local/bigdata/testdata/flink/users.csv"
format:
type: csv
fields:
- name: u_id
data-type: INT
- name: u_name
data-type: VARCHAR
- name: u_age
data-type: INT
- name: u_balance
data-type: DOUBLE
line-delimiter: "
"
comment-prefix: "#"
schema:
- name: u_id
data-type: INT
- name: u_name
data-type: VARCHAR
- name: u_age
data-type: INT
- name: u_balance
data-type: DOUBLE
- name: Users_Testing_alanchan_View1
type: view
query: "SELECT u_id,u_name,u_age FROM Users_Testing_view_alanchan"
- name: Users_Testing_alanchan_View2
type: view
query: "SELECT u_id,u_name,u_balance FROM Users_Testing_view_alanchan"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
相较于 table soruce 和 sink,会话环境配置文件中定义的视图具有最高优先级。
-验证
Flink SQL> select * from Users_Testing_view_alanchan;
Flink SQL> select * from Users_Testing_alanchan_View2;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

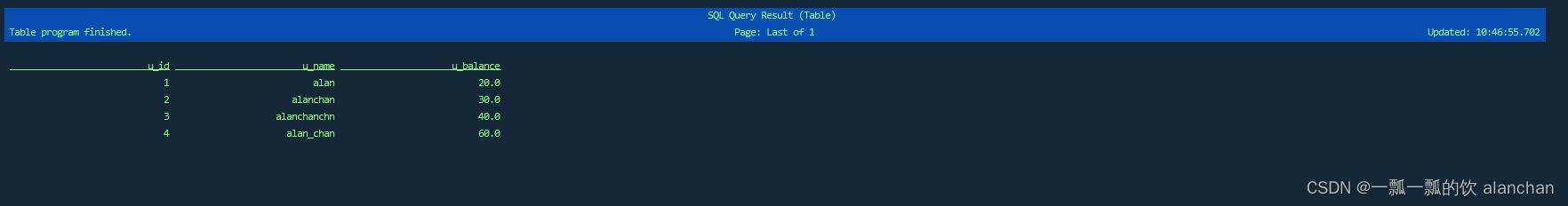
视图还可以在 CLI 会话中用 CREATE VIEW 语句来创建:
CREATE VIEW MyNewView AS select u_name from Users_Testing_view_alanchan;
Flink SQL> select * from MyNewView;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
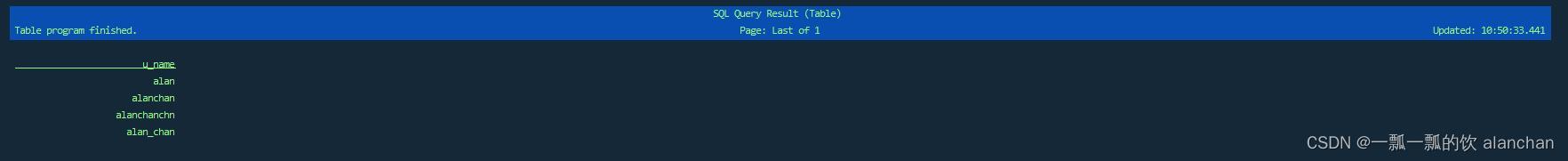
视图能在 CLI 会话中创建,也能用 DROP VIEW 语句删除:
Flink SQL> DROP VIEW MyNewView;
[INFO] Execute statement succeed.
Flink SQL> show tables;
+------------------------------+
| table name |
+------------------------------+
| Users_Testing_alanchan_View1 |
| Users_Testing_alanchan_View2 |
| Users_Testing_view_alanchan |
+------------------------------+
3 rows in set
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
CLI 中视图的定义仅限于上述语法。将来版本会支持定义视图结构以及在表名中加入转义的空格。
7、临时表(Temporal Table)
临时表是在变化的历史记录表上的(参数化)视图,该视图在某个特定时间点返回表的内容。这对于在特定的时间戳将一张表的内容联结另一张表是非常有用的。更多信息见15、Flink 的table api与sql之流式概念-详解的介绍了动态表、时间属性配置(如何处理更新结果)、时态表、流上的join、流上的确定性以及查询配置页面。
下例展示如何定义一张临时表 SourceTemporalTable:
tables:
# 定义包含对临时表的更新的 table source (或视图)
- name: HistorySource
type: source-table
update-mode: append
connector: # ...
format: # ...
schema:
- name: integerField
data-type: INT
- name: stringField
data-type: STRING
- name: rowtimeField
data-type: TIMESTAMP(3)
rowtime:
timestamps:
type: from-field
from: rowtimeField
watermarks:
type: from-source
# 在具有时间属性和主键的变化历史记录表上定义临时表
- name: SourceTemporalTable
type: temporal-table
history-table: HistorySource
primary-key: integerField
time-attribute: rowtimeField # could also be a proctime field
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
如例子中所示,table source,视图和临时表的定义可以相互混合。它们按照在环境配置文件中定义的顺序进行注册。例如,临时表可以引用一个视图,该视图依赖于另一个视图或 table source。
8、局限与未来
当前的 SQL 客户端仅支持嵌入式模式。在1.17版本后提供基于 REST 的 SQL 客户端网关(Gateway) 的功能。
以上,介绍了flink cli的启动、使用以及通过创建kafka、filesystem等例子介绍了配置文件的使用,同时也简单的介绍了视图、临时表等内容。


评论记录:
回复评论: