一、首先安装Live555
1、下载源码
由于不能apt-get install,所以先官网下载源码。http://www.live555.com/liveMedia/
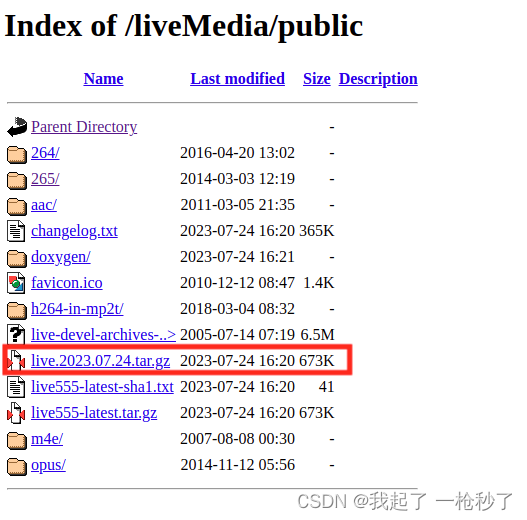
解压 tar -zxvf live.2023.07.24.tar.gz
安装可以看这篇博文前部
live555server环境搭建
OpenSSL必须安装
2、生成makefile
安装时如果直接在arm板子上装,生成makefile时就直接写
~/live$ ./genMakefiles linux
# 查看Makefile
~/live$ cat Makefile
##### Change the following for your environment:
COMPILE_OPTS = $(INCLUDES) -I/usr/local/include -I. -O2 -DSOCKLEN_T=socklen_t -D_LARGEFILE_SOURCE=1 -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64
C = c
C_COMPILER = cc
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
不能写成armlinux
~/live$ ./genMakefiles armlinux
# 查看Makefile
~/live$ cat Makefile
##### Change the following for your environment:
CROSS_COMPILE?= arm-elf-
COMPILE_OPTS = $(INCLUDES) -I/usr/local/include -I. -O2 -DSOCKLEN_T=socklen_t -DNO_SSTREAM=1 -D_LARGEFILE_SOURCE=1 -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64
C = c
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
如果选成了armlinux,这样make的时候用的就是交叉编译工具链,仅适用于从x86机器上给arm机器编译。
3、make
make时基本都会遇到test问题
编辑一下这个文件 /live/BasicUsageEnvironment/BasicTaskScheduler.cpp(190行左右)
if (fTriggersAwaitingHandling[i].test()) {
# 将上面这行改为
if (fTriggersAwaitingHandling[i].test_and_set()) {
- 1
- 2
- 3
4、sudo make install
编好了再运行sudo make install之后,就会把头文件放到 /usr/local/include 中,库文件放到 /usr/local/lib 中,不需要添加环境变量。
5、编译
编译demo的时候,在makefile中增加-I和-L就行。
例
文件名:
test_live555.cpp
编译指令:
g++ -I/usr/local/include -I/usr/local/include/groupsock -I/usr/local/include/UsageEnvironment -L/usr/local/lib test_live555.cpp -o test_live555 -lliveMedia -lBasicUsageEnvironment -lgroupsock -lUsageEnvironment -lssl -lcrypto
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-lliveMedia -lBasicUsageEnvironment -lgroupsock -lUsageEnvironment 是live555的
-lssl -lcrypto 是OpenSSL的
二、运行demo
我们既然是要做rtsp推流,demo在 live/testProgs/testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp 中,这个demo功能就是读取本地视频,然后启动RTSP推流服务器。
make的时候已经编译好了,我们可以直接运行。
不过我删减了一些,得自己编译了。拷到test_live555.cpp中,写一个makefile:
#include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
CC = g++
CFLAGS = -I/usr/local/include -I/usr/local/include/groupsock -I/usr/local/include/UsageEnvironment
LDFLAGS = -L/usr/local/lib
LIBS = -lliveMedia -lBasicUsageEnvironment -lgroupsock -lUsageEnvironment -lssl -lcrypto
TARGET = test_live555
all: $(TARGET)
$(TARGET): test_live555.cpp
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) $< -o $@ $(LIBS)
clean:
rm -f $(TARGET)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
(删干净了其他格式,只留了.264的,不然太乱)随便拷了一个.264文件过来,运行后打印如下:
$ ./test_live555
"h264ESVideoTest" stream, from the file "test.264"
Play this stream using the URL "rtsp://192.168.1.149:8554/h264ESVideoTest"
(We use port 8000 for optional RTSP-over-HTTP tunneling.)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
这时就代表,已经开始推流了,用vlc输入这个url就可以拉了
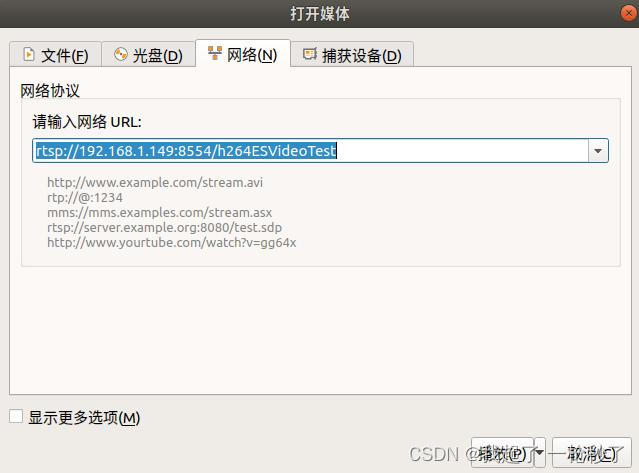
拉流时可以看到程序打印
MultiFramedRTPSink::afterGettingFrame1(): The input frame data was too large for our buffer size (60972). 55319 bytes of trailing data was dropped! Correct this by increasing "OutPacketBuffer::maxSize" to at least 115319, *before* creating this 'RTPSink'. (Current value is 60000.)
MultiFramedRTPSink::afterGettingFrame1(): The input frame data was too large for our buffer size (60972). 55319 bytes of trailing data was dropped! Correct this by increasing "OutPacketBuffer::maxSize" to at least 115319, *before* creating this 'RTPSink'. (Current value is 60000.)
MultiFramedRTPSink::afterGettingFrame1(): The input frame data was too large for our buffer size (60972). 9383 bytes of trailing data was dropped! Correct this by increasing "OutPacketBuffer::maxSize" to at least 69383, *before* creating this 'RTPSink'. (Current value is 60000.)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
同时也可以抓包看到RTSP相关网络包

三、问题
live555似乎无法对RTSP推理地址进行定制。除非改源码。

源码GroupsockHelper.cpp可见
ipv4AddressBits ourIPv4Address(UsageEnvironment& env) {
if (ReceivingInterfaceAddr != INADDR_ANY) {
// Hack: If we were told to receive on a specific interface address, then
// define this to be our ip address:
_ourIPv4Address = ReceivingInterfaceAddr;
}
if (!_weHaveAnIPv4Address) {
getOurIPAddresses(env);
}
return _ourIPv4Address;
}
...
void getOurIPAddresses(UsageEnvironment& env) {
// We use two methods to (try to) get our IP addresses.
// First, we use "getifaddrs()". But if that doesn't work
// (or if "getifaddrs()" is not defined), then we use an alternative (more old-fashioned)
// mechanism: First get our host name, then try resolving this host name.
struct sockaddr_storage foundIPv4Address = nullAddress(AF_INET);
struct sockaddr_storage foundIPv6Address = nullAddress(AF_INET6);
Boolean getifaddrsWorks = False; // until we learn otherwise
#ifndef NO_GETIFADDRS
struct ifaddrs* ifap;
if (getifaddrs(&ifap) == 0) {
// Look through all interfaces:
for (struct ifaddrs* p = ifap; p != NULL; p = p->ifa_next) {
// Ignore an interface if it's not up, or is a loopback interface:
if ((p->ifa_flags&IFF_UP) == 0 || (p->ifa_flags&IFF_LOOPBACK) != 0) continue;
// Also ignore the interface if the address is considered 'bad' for us:
if (p->ifa_addr == NULL || isBadAddressForUs(*p->ifa_addr)) continue;
// We take the first IPv4 and first IPv6 addresses:
if (p->ifa_addr->sa_family == AF_INET && addressIsNull(foundIPv4Address)) {
copyAddress(foundIPv4Address, p->ifa_addr);
getifaddrsWorks = True;
} else if (p->ifa_addr->sa_family == AF_INET6 && addressIsNull(foundIPv6Address)) {
copyAddress(foundIPv6Address, p->ifa_addr);
getifaddrsWorks = True;
}
}
freeifaddrs(ifap);
}
...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
在获取IP时
for (struct ifaddrs* p = ifap; p != NULL; p = p->ifa_next) {
- 1
ifap中有所有网卡的信息,但是
if (p->ifa_addr->sa_family == AF_INET && addressIsNull(foundIPv4Address)) {
- 1
这句只拿了第一个符合要求的ip。只要变量foundIPv4Address中有结果,就不会再要了。所以只能获取到一个ip,返回到上层的_ourIPv4Address中,拼接到RTSP服务器url前面。


评论记录:
回复评论: