上次讲了常用的接口:今天就来进行模拟实现啦
1.基本结构与文件规划
- list.h头文件:包含类的全部(函数的声明与定义)
- reverseIterator.h文件:进行反向迭代器的实现
- test.cpp源文件:进行调用test函数,测试和完善功能
基本结构:
#pragma once
namespace MyList
{
// List的节点类
template
struct ListNode
{
ListNode* _prev;
ListNode* _next;
T _data;
ListNode(const T& x=T())
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{}
};
//List的迭代器类
template
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode Node;
typedef ListIterator Self;
Node* _node;
ListIterator(Node* node)//构造函数
:_node(node)
{}
ListIterator(const Self& l)//拷贝构造函数
:_node(l._node)
{}
T& operator*();
T* operator->();
Self& operator++();
Self operator++(int);
Self& operator--();
Self& operator--(int);
bool operator!=(const Self& l);
bool operator==(const Self& l);
};
//list类
template
class list
{
typedef ListNode Node;//默认是private 不给外面用
public:
typedef ListIterator iterator;
typedef ListIterator const_iterator;
//构造函数
list();
list(int n, const T& value = T());
template
list(Iterator first, Iterator last);
//析构
~list();
// List Iterator
iterator begin();
iterator end();
const_iterator begin();
const_iterator end();
// List Capacity
size_t size()const;
bool empty()const;
// List Access
T& front();
const T& front()const;
T& back();
const T& back()const;
// List Modify
void push_back(const T& val) { insert(end(), val); }
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val);
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos);
void clear();
void swap(list& l);
private:
Node* _head;
};
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
ListNode结构体:- 定义了链表的节点结构,包含了三个成员变量:前驱指针
_prev、后继指针_next和数据_data。 - 构造函数初始化了这些成员变量,允许在创建节点时指定初始值。
- 定义了链表的节点结构,包含了三个成员变量:前驱指针
ListIterator结构体:- 定义了链表的迭代器结构,包含了指向节点的指针
_node。 - 重载了一系列操作符,如
*、->、++、--、!=、==,以便于对链表进行遍历和操作。
- 定义了链表的迭代器结构,包含了指向节点的指针
list类:- 包含了迭代器的定义、构造函数、析构函数以及一系列的操作函数。
- 定义了两种迭代器类型:
iterator和const_iterator,分别用于可修改的迭代和只读的迭代。 - 实现了一系列的操作函数
2.空参构造函数(constructor)
list()
{
_head = new Node;//去调用Node的默认构造函数了
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;//带头双向循环链表是这样的
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
使用new:动态开辟+调用默认构造函数了
3.完善迭代器(iterator)(begin(),end())
这里为什么我们要把迭代器封装为一个类呢?明明之前模拟vector和string时,就直接typedef了
之前模拟
vector和string时,二者底层都是连续的,想要到下一个可以直接++;想要得到里面的数据可以直接*。但是现在对于
list是不行的,我们就需要重载各种运算符,但是底层又是一个指针(内置类型)不能重载,现在就只能封装进一个类里,就能重载了
//List的迭代器类
template
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode Node;
typedef ListIterator Self;
Node* _node;
ListIterator(Node* node)//构造函数
:_node(node)
{}
ListIterator(const Self& l)//拷贝构造函数
:_node(l._node)//这里是浅拷贝(写不写都行)
//新创建的迭代器和原迭代器指向相同的内存地址
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Self& operator++()//前置
{
_node = _node->_next;//自己要更新
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self s(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return s;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;//自己要更新
return *this;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self s(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return s;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return _node != l._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return _node == l._node;
}
};
//list类
template
class list
{
typedef ListNode Node;//默认是private 不给外面用
public:
typedef ListIterator iterator;
typedef ListIterator const_iterator;
//构造函数
list()
{
_head = new Node;//去调用Node的默认构造函数了
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;//带头双向循环链表是这样的
}
// List Iterator
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;//隐式类型转换(由单参构造函数支撑)
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
4.List Capacity(size(),empty())
// List Capacity
size_t size()const
{
size_t size = 0;
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
size++;
++it;
}
return size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return size() == 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
4.增删改查(push_back,pop_back,pop_front,push_front,insert,erase)
// List Modify
void push_back(const T& val) //尾插
{
insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back() //尾删
{
erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& val) //头插
{
insert(begin(), val);
}
void pop_front()//头删
{
erase(begin());
}
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(val);//创建新节点
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
prev->_next = cur;
return newnode;//隐式类型转换
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != _head);
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return next;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
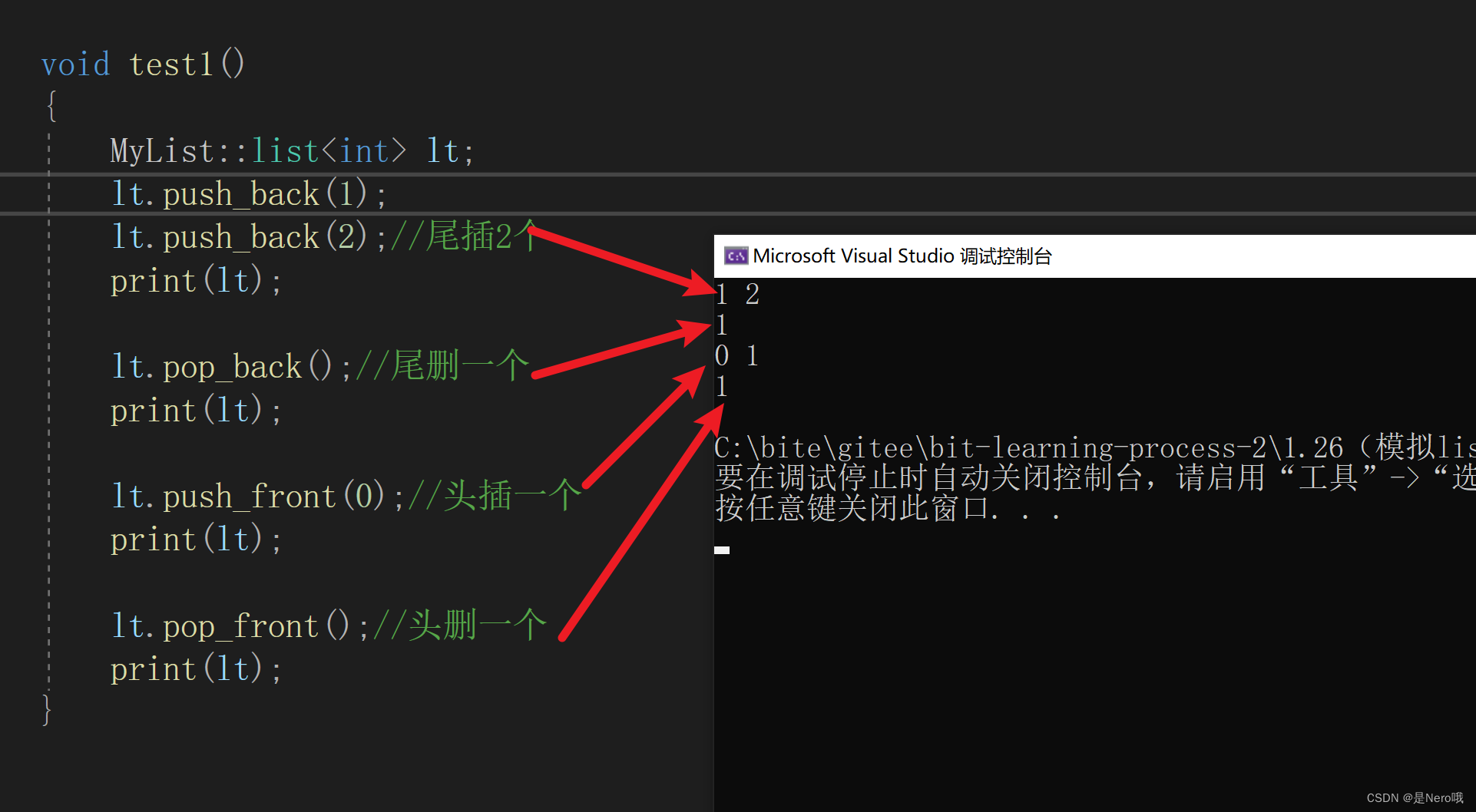
使用test1函数看功能是否正常
void print(MyList::list& lt)
{
list::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it; // 更新迭代器
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
MyList::list lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);//尾插2个
print(lt);
lt.pop_back();//尾删一个
print(lt);
lt.push_front(0);//头插一个
print(lt);
lt.pop_front();//头删一个
print(lt);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
6.clear()和swap()
void clear()
{
//删除除头结点(_head)以外的节点
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void swap(list& l)
{
std::swap(_head, l._head);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
7. 完善构造函数
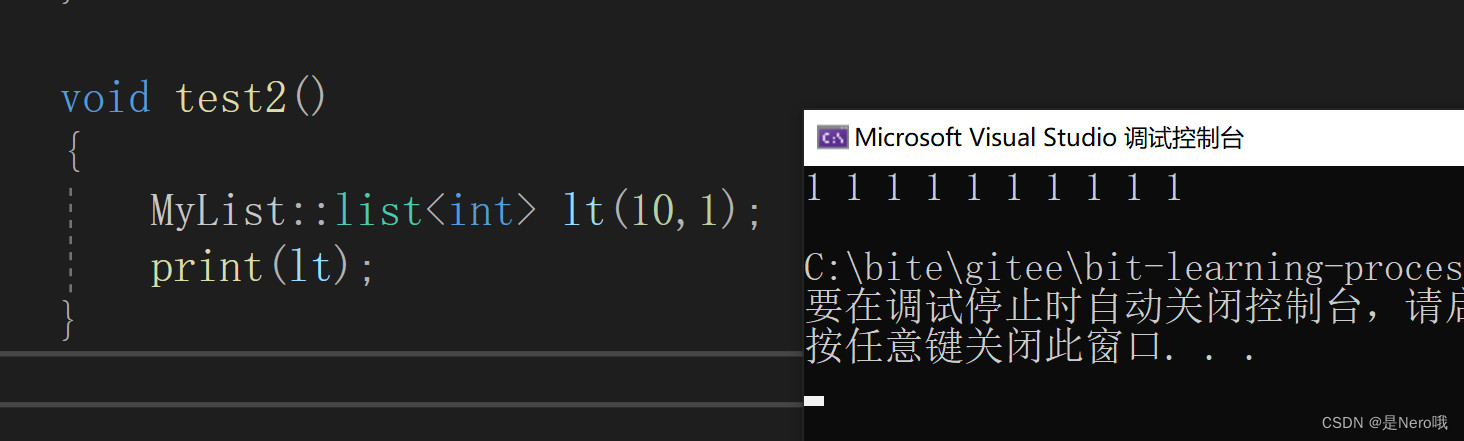
7.1list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type());
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
7.2利用迭代器进行构造
template
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
为什么使用模版:
因为可能使用其他类型的迭代器来进行初始化
7.3拷贝构造
list(const list& lt)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
iterator it = copy.begin();
while (it != copy.end())
{
push_back(*it);
it++;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
8.重载=
list& lt operator=(list lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注意这里的参数不是常量引用,而是按值传递的。这是因为在赋值操作符中我们会调用
swap函数,按值传递可以保证传入的参数会被复制一份,避免对原对象的修改。在函数体内,我们调用了swap函数,将当前对象和传入的对象进行内容交换,然后返回*this,即当前对象的引用。
9.析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
调用clear函数后,就只剩下头结点了
10.反向迭代器
我们再次使用封装的思想,封装一个反向迭代器进去
#pragma once
template
struct reserve_iterator
{
typedef reserve_iterator self;
iterator _it;
reserve_iterator(iterator it)
:_it(it)
{}
self& operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
--_it;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
++_it;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*()
{
iterator tmp = _it;
--tmp;
return *tmp;
}
Pre operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _it != s._it;
}
bool operator==(const self& s)
{
return _it == s._it;
}
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
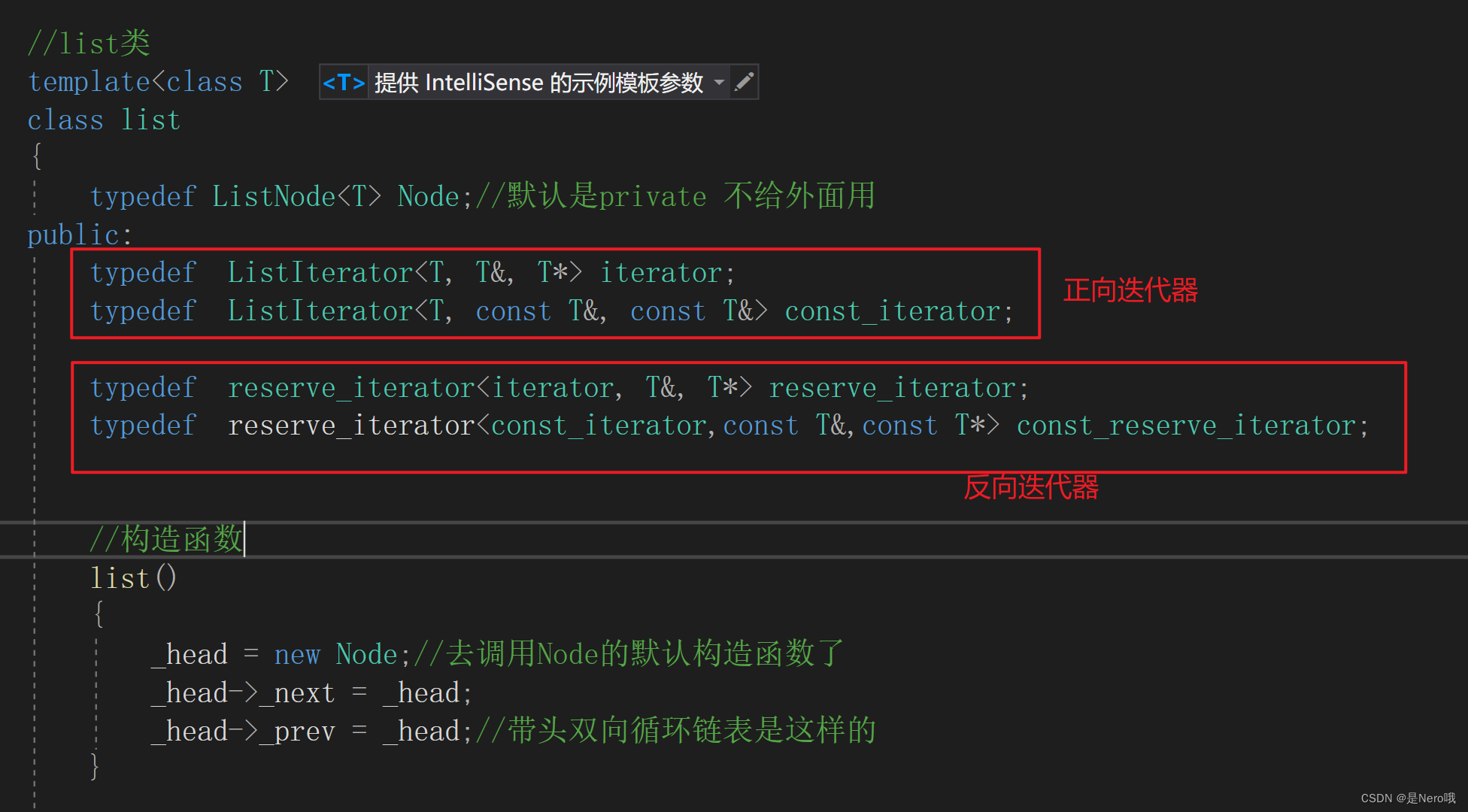
此时那list类里就是这样:
好啦,list的内容也结束啦,下次就是Stack和Queue了。感谢大家支持!!!


评论记录:
回复评论: