Transformers实战(二)快速入门文本相似度、检索式对话机器人
1、文本相似度
1.1 文本相似度简介
-
文本匹配是一个较为宽泛的概念,基本上只要涉及到两段文本之间关系的,都可以被看作是一种文本匹配的任务, -
只是在具体的场景下,不同的任务对匹配二字的定义可能是存在差异的,具体的任务场景包括文本相似度计算、问答匹配、对话匹配、文本推理等等,另外,如之前介绍的多项选择,本质上也是文本匹配
-
本次重点关注文本相似度任务,
即判断两段文本是不是表达了同样的语义 -
文本相似度本质上是一个分类任务。
| Sentence A | Sentence B | Label |
|---|---|---|
| 找一部小时候的动画片 | 求一部小时候的动画片。谢了 | 1 |
| 别急呀,我的朋友。 | 你一定要看我一下 | 0 |
| 明天多少度啊 | 明天气温多少度啊 | 1 |
| 可怕的事情终于发生 | 你到底想说什么? | 0 |
1.2 最直接的解决方案—交互策略
交互策略,就是输入句子对,对是否相似进行学习。
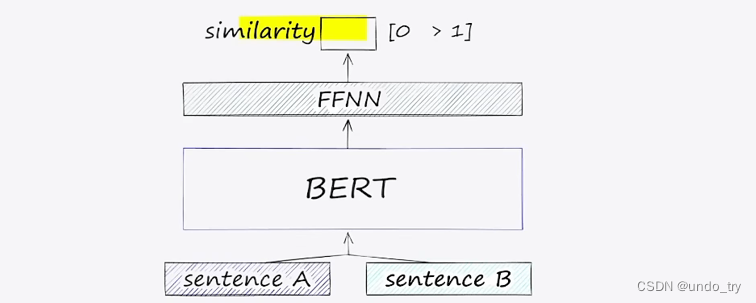
数据预处理方式如下:
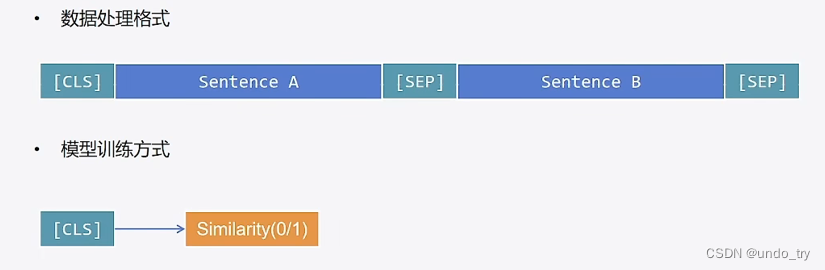
交互策略的实现比较简单,类似于情感分析。
1.2.1 数据集预处理
数据集:https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/SimCLUE/tree/main
预训练模型依然是哈工大开源的chinese-macbert-base
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, Trainer, TrainingArguments
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="./train_pair_1w.json", split="train")
dataset[0:2]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
{
'sentence1': ['找一部小时候的动画片',
'我不可能是一个有鉴赏能力的行家,小姐我把我的时间都花在书写上;象这样豪华的舞会,我还是头一次见到。'],
'sentence2': ['求一部小时候的动画片。谢了', '蜡烛没熄就好了,夜黑得瘆人,情绪压抑。'],
'label': ['1', '0']
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
# 划分数据集
datasets = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.2)
# tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("hfl/chinese-macbert-base")
# 离线加载
model_path = '/root/autodl-fs/models/chinese-macbert-base'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
def process_function(examples):
tokenized_examples = tokenizer(examples["sentence1"], examples["sentence2"], max_length=128, truncation=True)
tokenized_examples["labels"] = [float(label) for label in examples["label"]]
return tokenized_examples
tokenized_datasets = datasets.map(process_function, batched=True, remove_columns=datasets["train"].column_names)
tokenized_datasets
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['input_ids', 'token_type_ids', 'attention_mask', 'labels'],
num_rows: 8000
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['input_ids', 'token_type_ids', 'attention_mask', 'labels'],
num_rows: 2000
})
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
print(tokenized_datasets["train"][0])
- 1
{
'input_ids': [101, 1062, 4265, 1920, 782, 8024, 1963, 3362, 2769, 1762, 6878, 1168, 2600, 1385, 808, 1184, 6878, 1168, 4640, 2370, 7363, 678, 8024, 6929, 6421, 2582, 720, 1215, 8043, 102, 800, 2697, 6230, 2533, 800, 2190, 6821, 5439, 1928, 2094, 3683, 2190, 800, 1520, 1520, 6820, 779, 8024, 4507, 754, 800, 2190, 6821, 702, 782, 772, 4495, 4638, 3946, 2658, 679, 4881, 2544, 5010, 6629, 3341, 511, 102],
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
'labels': 0.0
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.2.2 加载模型、创建评估函数
import evaluate
# 离线加载模型
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_path, num_labels=1)
# 这里采用离线加载
accuracy_path = '/root/autodl-tmp/transformers-code/metrics/accuracy'
f1_path = '/root/autodl-tmp/transformers-code/metrics/f1'
acc_metric = evaluate.load(accuracy_path)
f1_metirc = evaluate.load(f1_path)
def eval_metric(eval_predict):
predictions, labels = eval_predict
predictions = [int(p > 0.5) for p in predictions]
labels = [int(l) for l in labels]
acc = acc_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
f1 = f1_metirc.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
acc.update(f1)
return acc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
1.2.3 创建TrainingArguments及Trainer
train_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="./cross_model", # 输出文件夹
per_device_train_batch_size=16, # 训练时的batch_size
per_device_eval_batch_size=16, # 验证时的batch_size
logging_steps=10, # log 打印的频率
evaluation_strategy="epoch", # 评估策略
save_strategy="epoch", # 保存策略
save_total_limit=3, # 最大保存数
learning_rate=2e-5, # 学习率
weight_decay=0.01, # weight_decay
metric_for_best_model="f1", # 设定评估指标
load_best_model_at_end=True) # 训练完成后加载最优模型
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
from transformers import DataCollatorWithPadding
trainer = Trainer(model=model,
args=train_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["test"],
data_collator=DataCollatorWithPadding(tokenizer=tokenizer),
compute_metrics=eval_metric)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
trainer.train()
- 1
1.2.4 模型预测
from transformers import pipeline
model.config.id2label = {0: "不相似", 1: "相似"}
pipe = pipeline("text-classification", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, device=0)
result = pipe({"text": "我喜欢北京", "text_pair": "天气怎样"}, function_to_apply="none")
result["label"] = "相似" if result["score"] > 0.5 else "不相似"
result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
{'label': '不相似', 'score': 0.054742373526096344}
- 1
1.3 基于向量匹配的解决方案
如果从多个文本中,找到最相似的文本,应该如何做呢?
基于交互策略,我们可以借鉴之前多项选择,用相同的处理方式(如下图)。
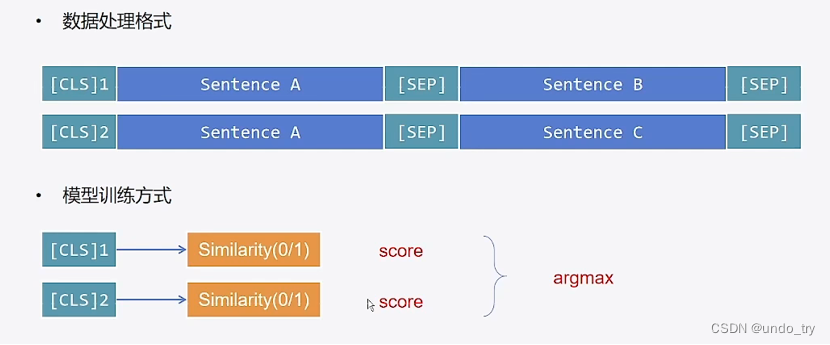
但是这样效率极低,因为每次都需要与全量数据进行模型推理,数据量较大时很难满足时延要求。
基于向量匹配的方案可以解决。
我们可以将候选文本经过训练好的模型进行向量化,然后存到向量数据库中(如faiss)。然后将问题也同样向量化,去向量库中进行向量匹配。(这也是检索式机器人的思路,我们将在检索机器人中,将本章节训练好的向量模型作为预训练模型,对文本进行向量化,并将向量集合存到faiss中,进行向量匹配,这里仅仅训练出向量模型。)
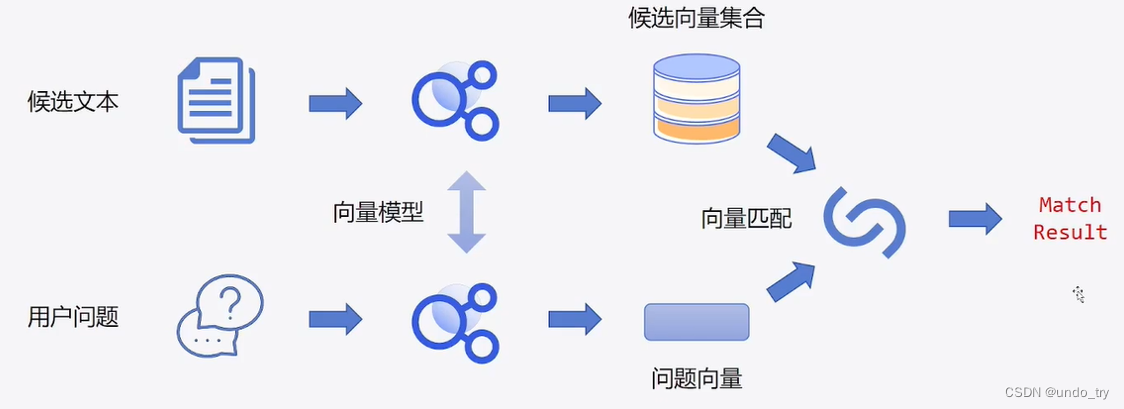
那么,这个向量模型该如何进行训练呢?
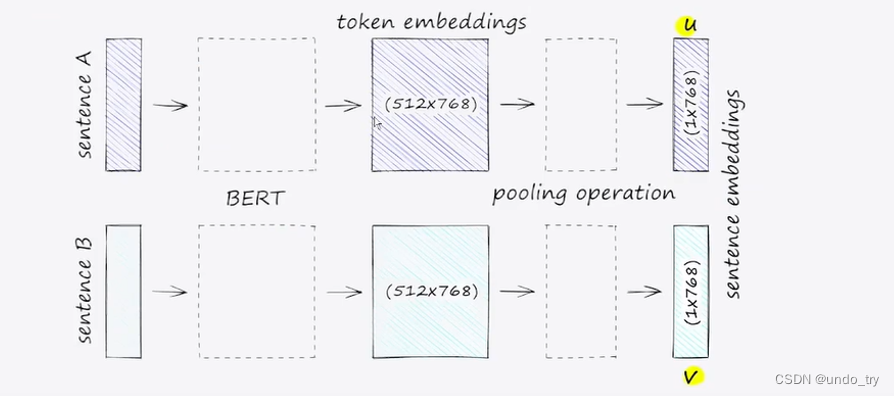
向量匹配训练,分别对句子进行编码,目标是让两个相似句子的相似度分数尽可能接近1。
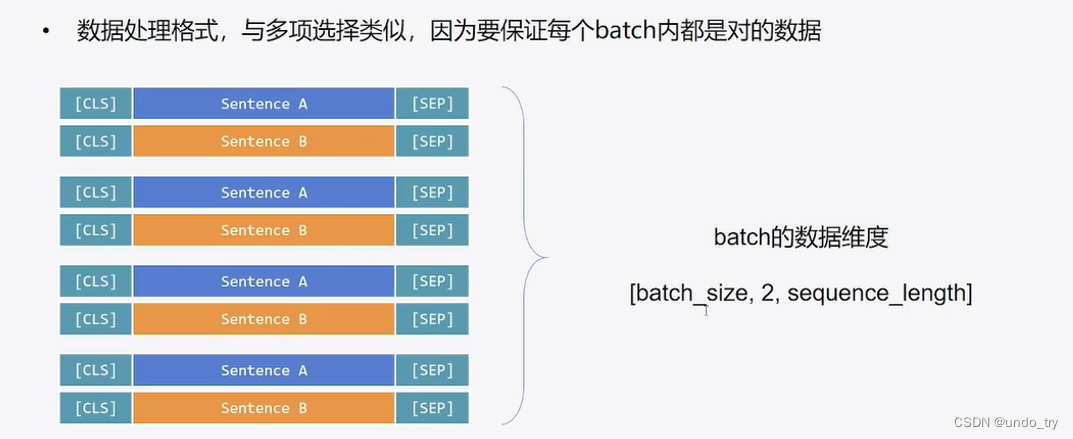
数据预处理与多项选择类似
注意:此时没有预定义模型,需要我们自己实现模型。
模型中的损失,我们可以用pytorch提供的余弦损失函数 torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss
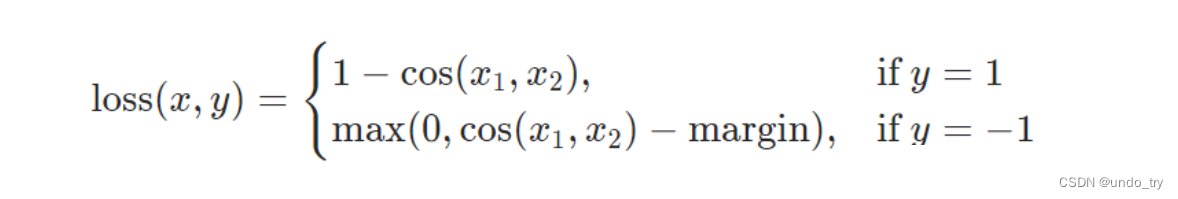
-
余弦损失函数,常常用于评估两个向量的相似性,两个向量的余弦值越高,则相似性越高。
-
x:包括x1和x2,即需要计算相似度的prediction和GT; -
y:相当于人为给定的flag,决定按哪种方式计算得到loss的结果。 -
注意:此时label应该为正负1
-
如果需要约束使x1和x2尽可能的相似,那么就使用
y=1,prediction和GT完全一致时,loss为0
input1 = torch.randn(100, 128)
input2 = torch.randn(100, 128)
cos = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(reduction='mean')
# # 需要初始化一个N维的1或-1
loss_flag = torch.ones([100])
output = cos(input1, input2, loss_flag)
print(output) # tensor(1.0003)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
1.3.1 数据预处理
数据集:https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/SimCLUE/tree/main
预训练模型依然是哈工大开源的chinese-macbert-base
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, Trainer, TrainingArguments
from datasets import load_dataset
import torch
# 离线加载数据
dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="./train_pair_1w.json", split="train")
# 数据集划分
datasets = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.2)
# 和多项选择相似的处理方式
model_path = '/root/autodl-fs/models/chinese-macbert-base'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
def process_function(examples):
sentences = []
labels = []
for sen1, sen2, label in zip(examples["sentence1"], examples["sentence2"], examples["label"]):
sentences.append(sen1)
sentences.append(sen2)
# 这里label处理为1和-1
labels.append(1 if int(label) == 1 else -1)
# input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids
tokenized_examples = tokenizer(sentences, max_length=128, truncation=True, padding="max_length")
tokenized_examples = {k: [v[i: i + 2] for i in range(0, len(v), 2)] for k, v in tokenized_examples.items()}
tokenized_examples["labels"] = labels
return tokenized_examples
tokenized_datasets = datasets.map(process_function, batched=True, remove_columns=datasets["train"].column_names)
tokenized_datasets
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['input_ids', 'token_type_ids', 'attention_mask', 'labels'],
num_rows: 8000
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['input_ids', 'token_type_ids', 'attention_mask', 'labels'],
num_rows: 2000
})
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
1.3.2 自定义训练模型
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassification, BertPreTrainedModel, BertModel
from typing import Optional
from transformers.configuration_utils import PretrainedConfig
from torch.nn import CosineSimilarity, CosineEmbeddingLoss
class DualModel(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: PretrainedConfig, *inputs, **kwargs):
super().__init__(config, *inputs, **kwargs)
self.bert = BertModel(config)
self.post_init()
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
token_type_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
):
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
# Step1 分别获取sentenceA 和 sentenceB的输入
senA_input_ids, senB_input_ids = input_ids[:, 0], input_ids[:, 1]
senA_attention_mask, senB_attention_mask = attention_mask[:, 0], attention_mask[:, 1]
senA_token_type_ids, senB_token_type_ids = token_type_ids[:, 0], token_type_ids[:, 1]
# Step2 分别获取sentenceA 和 sentenceB的向量表示
senA_outputs = self.bert(
senA_input_ids,
attention_mask=senA_attention_mask,
token_type_ids=senA_token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
senA_pooled_output = senA_outputs[1] # [batch, hidden]
senB_outputs = self.bert(
senB_input_ids,
attention_mask=senB_attention_mask,
token_type_ids=senB_token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
senB_pooled_output = senB_outputs[1] # [batch, hidden]
# step3 计算相似度
cos = CosineSimilarity()(senA_pooled_output, senB_pooled_output) # [batch, ]
# step4 计算loss
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss_fct = CosineEmbeddingLoss(0.3)
loss = loss_fct(senA_pooled_output, senB_pooled_output, labels)
output = (cos,)
return ((loss,) + output) if loss is not None else output
model = DualModel.from_pretrained(model_path)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
1.3.3 创建评估函数
import evaluate
# 这里采用离线加载
accuracy_path = '/root/autodl-tmp/transformers-code/metrics/accuracy'
f1_path = '/root/autodl-tmp/transformers-code/metrics/f1'
acc_metric = evaluate.load(accuracy_path)
f1_metirc = evaluate.load(f1_path)
def eval_metric(eval_predict):
predictions, labels = eval_predict
predictions = [int(p > 0.7) for p in predictions]
labels = [int(l > 0) for l in labels]
acc = acc_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
f1 = f1_metirc.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
acc.update(f1)
return acc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
1.3.4 创建TrainingArguments及Trainer
train_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="./dual_model", # 输出文件夹
per_device_train_batch_size=32, # 训练时的batch_size
per_device_eval_batch_size=32, # 验证时的batch_size
logging_steps=10, # log 打印的频率
evaluation_strategy="epoch", # 评估策略
save_strategy="epoch", # 保存策略
save_total_limit=3, # 最大保存数
learning_rate=2e-5, # 学习率
weight_decay=0.01, # weight_decay
metric_for_best_model="f1", # 设定评估指标
load_best_model_at_end=True) # 训练完成后加载最优模型
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
trainer = Trainer(model=model,
args=train_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["test"],
compute_metrics=eval_metric)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
trainer.train()
- 1
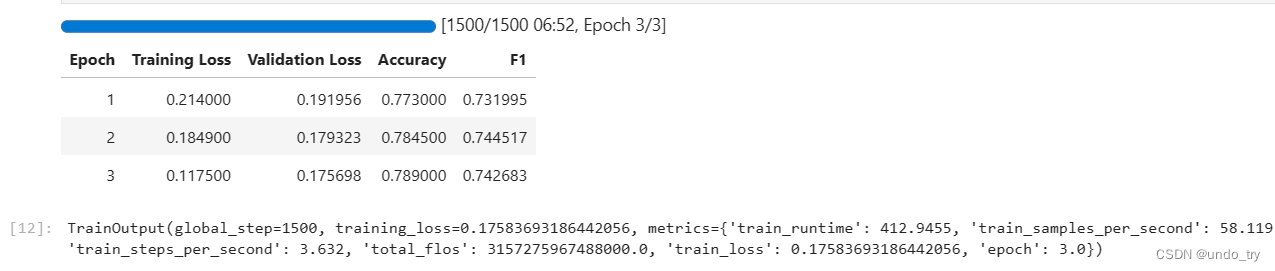
1.3.5 自定义pipeline实现模型评估
class SentenceSimilarityPipeline:
def __init__(self, model, tokenizer) -> None:
self.model = model.bert
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.device = model.device
def preprocess(self, senA, senB):
return self.tokenizer([senA, senB], max_length=128, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
def predict(self, inputs):
inputs = {k: v.to(self.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
return self.model(**inputs)[1] # [2, 768]
def postprocess(self, logits):
cos = CosineSimilarity()(logits[None, 0, :], logits[None,1, :]).squeeze().cpu().item()
return cos
def __call__(self, senA, senB, return_vector=False):
inputs = self.preprocess(senA, senB)
logits = self.predict(inputs)
result = self.postprocess(logits)
if return_vector:
return result, logits
else:
return result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
pipe = SentenceSimilarityPipeline(model, tokenizer)
pipe("我喜欢北京", "明天不行", return_vector=True)
- 1
- 2
- 3
(0.4414671063423157,
tensor([[ 0.8044, -0.7820, 0.9974, ..., -0.6317, -0.9653, -0.4989],
[ 0.3756, 0.0484, 0.9767, ..., -0.9928, -0.9980, -0.5648]],
device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<TanhBackward0>))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注:文本向量化更加便捷有效的工具
- sentence-transformers
https://www.sbert.net/
- text2vec
https://github.com/shibing624/text2vec
- uniem
https://github.com/wangyuxinwhy/uniem
2、检索式对话机器人
2.1 检索式对话机器人简介
-
对话机器人在本质上是一个用来模拟人类对话或聊天的计算机程序,接收人类的自然语言作为输入并给出合适的回复
-
按照任务类型划分,对话机器人简单的可以划分为闲聊机器人、问答机器人、任务型对话机器人
-
按照答案产生的逻辑划分,对话机器人可以划分为检索式对话机器人和生成式对话机器人
如何实现基于检索的问答机器人?
QQ匹配策略
可以利用QQ匹配策略,即取最优结果的Q对应的Answer作为最终结果。
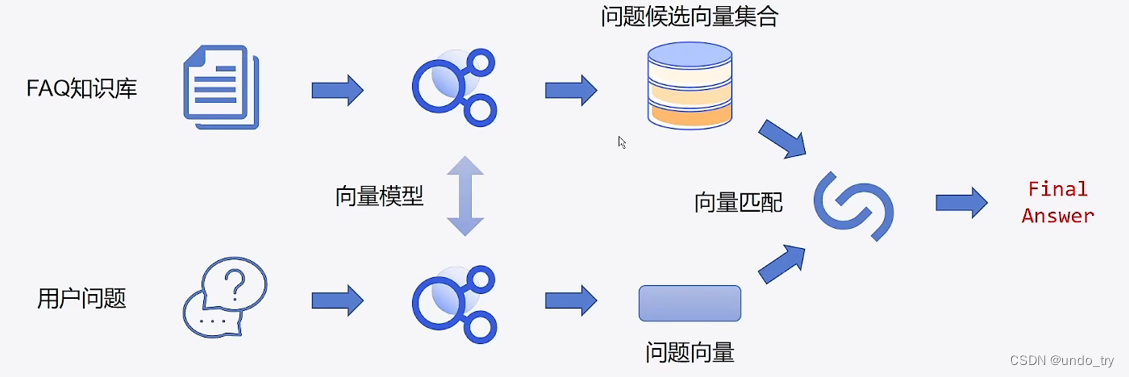
-
但是使用向量匹配的模型效果并不好,很难直接取到最优结果
-
因此引入基于交互策略模型。向量匹配模块又称为召回模块,交互策略的模块又称为排序模块
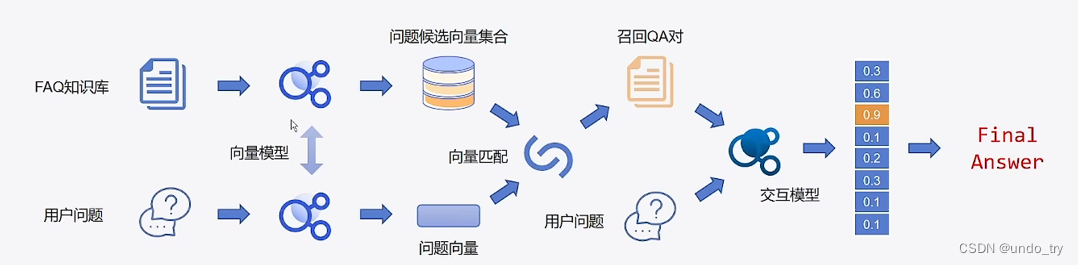
2.2 向量匹配和交互策略结合实现检索对话机器人
法律知道数据集
https://github.com/SophonPlus/ChineseNlpCorpus
预训练模型
1.2章节训练的交互模型
1.3章节训练的匹配模型
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2.2.1 加载自己训练的向量匹配模型
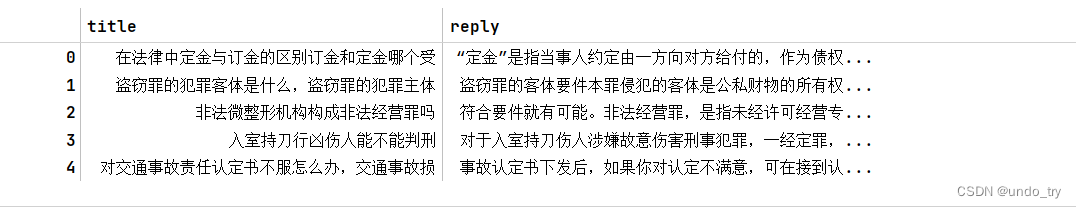
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("./law_faq.csv")
data.head()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
# dual_model.py文件中是自定义的DualModel
from dual_model import DualModel
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
# 加载自己训练好的模型
dual_model = DualModel.from_pretrained("../12-sentence_similarity/dual_model/checkpoint-500/")
dual_model = dual_model.cuda()
dual_model.eval()
print("匹配模型加载成功!")
# 加载tokenzier
model_path = '/root/autodl-fs/models/chinese-macbert-base'
tokenzier = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2.2.2 将知识库中的问题编码为向量
import torch
from tqdm import tqdm
questions = data["title"].to_list()
vectors = []
with torch.inference_mode():
for i in tqdm(range(0, len(questions), 32)):
batch_sens = questions[i: i + 32]
inputs = tokenzier(batch_sens, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, max_length=128, truncation=True)
inputs = {k: v.to(dual_model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
# 这里拿出[CLS]的向量表示
vector = dual_model.bert(**inputs)[1]
vectors.append(vector)
vectors = torch.concat(vectors, dim=0).cpu().numpy()
vectors.shape
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
(18213, 768)
- 1
2.2.3 将知识库中的问题向量存入向量库中
# pip install faiss-cpu
import faiss
index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(768)
faiss.normalize_L2(vectors)
index.add(vectors)
index
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.2.4 将用户问题编码为向量
quesiton = "寻衅滋事"
with torch.inference_mode():
inputs = tokenzier(quesiton, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, max_length=128, truncation=True)
inputs = {k: v.to(dual_model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
vector = dual_model.bert(**inputs)[1]
q_vector = vector.cpu().numpy()
q_vector.shape
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
(1, 768)
- 1
2.2.5 向量匹配
faiss.normalize_L2(q_vector)
# 使用faiss进行搜索
scores, indexes = index.search(q_vector, 10)
# 将匹配到的相似问题及答案召回
topk_result = data.values[indexes[0].tolist()]
# 匹配到的相似问题
topk_result[:, 0]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
array(['涉嫌寻衅滋事', '两个轻微伤够寻衅滋事', '敲诈勒索罪', '聚群斗殴', '飞达暴力催收', '打架斗殴',
'涉嫌犯罪?????', '殴打他人治安处罚', '遵守法律的措施', '十级伤残工伤'], dtype=object)
- 1
- 2
2.2.6 加载自己训练的交互模型
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassification
corss_model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("../12-sentence_similarity/cross_model/checkpoint-500/")
corss_model = corss_model.cuda()
corss_model.eval()
print("模型加载成功!")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.2.7 最终的预测结果
# 候选问题集合
canidate = topk_result[:, 0].tolist()
ques = [quesiton] * len(canidate)
inputs = tokenzier(ques, canidate, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, max_length=128, truncation=True)
inputs = {k: v.to(corss_model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
with torch.inference_mode():
logits = corss_model(**inputs).logits.squeeze()
result = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
result
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
tensor(0, device='cuda:0')
- 1
# 候选答案集合
canidate_answer = topk_result[:, 1].tolist()
match_quesiton = canidate[result.item()]
final_answer = canidate_answer[result.item()]
match_quesiton, final_answer
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
('涉嫌寻衅滋事',
'说明具有寻衅滋事行为,应受到相应的处罚,行为人情形严重或行为恶劣的涉嫌了寻衅滋事罪。寻衅滋事是指行为人结伙斗殴的、追逐、拦截他人的、强拿硬要或者任意损毁、占用公私财物的、其他寻衅滋事的行为。寻衅滋事罪,是指在公共场所无事生非、起哄闹事,造成公共场所秩序严重混乱的,追逐、拦截、辱骂、恐吓他人,强拿硬要或者任意损毁、占用公私财物,破坏社会秩序,情节严重的行为。对于寻衅滋事行为的处罚:1、《中华人*共和国治安管理处罚法》第二十六条规定,有下列行为之一的,处五日以上十日以下拘留,可以并处五百元以下罚款;情节较重的,处十日以上十五日以下拘留,可以并处一千元以下罚款:(一)结伙斗殴的;(二)追逐、拦截他人的;(三)强拿硬要或者任意损毁、占用公私财物的;(四)其他寻衅滋事行为;...)
- 1
- 2


评论记录:
回复评论: