本文基于复旦大学的《大规模语言模型:从理论到实践》中的理论部分总结出我自己的理解,算是初步学习。
定义
大规模语言模型(Large Language Models,LLM),也称大语言模型 或大型语言模型 ,是一种由包含数百亿以上参数的深度神经网络构建的语言模型,通常使用自监督学习方法通过大量无标注文本进行训练。
发展历程
-
基础模型阶段主要集中于 2018 年至 2021 年,集中于语言模型本身,仅编码器、编码器-解码器、仅解码器。
-
能力探索阶段集中于 2019 年至 2022 年,由于大规模语言模型很难针对特定任务进行微调,研究人员们开始探索在不针对单一任务进行微调的情况下如何能够发挥大规模语言模型的能力。在零样本或少量样本的基础上,利用生成式框架对大量任务有监督的微调。
-
突破发展阶段以 2022 年 11 月 ChatGPT 的发布为起点。ChatGPT 通过一个简单的对话框,利用一个大规模语言模型就可以实现问题回答、文稿撰写、代码生成、数学解题等过去自然语言处理系统需要大量小模型订制开发才能分别实现的能力。
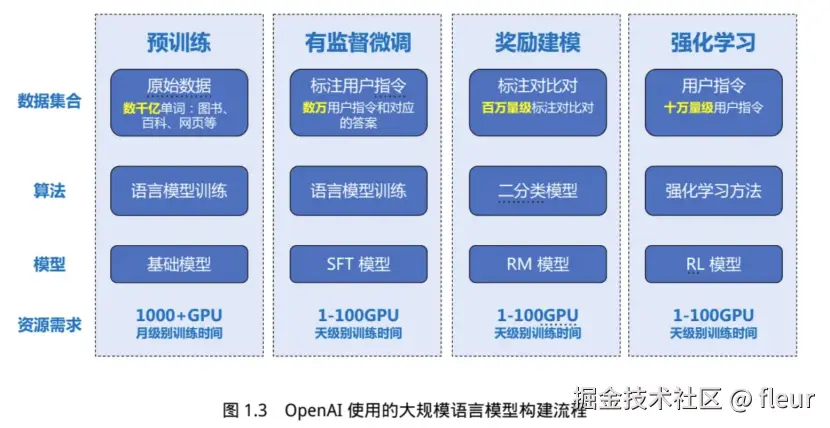
建模流程
Transformer模型
Google发布的论文《Attention is all you need》中提出了Transformer模型,通过词元嵌入、位置编码、多层的多头自注意力和位置感知前馈网络,通过残差连接和归一化实现输出数据和输入数据的连贯,并且给解码层最终的输出数据,以此来生成下一步的数据。
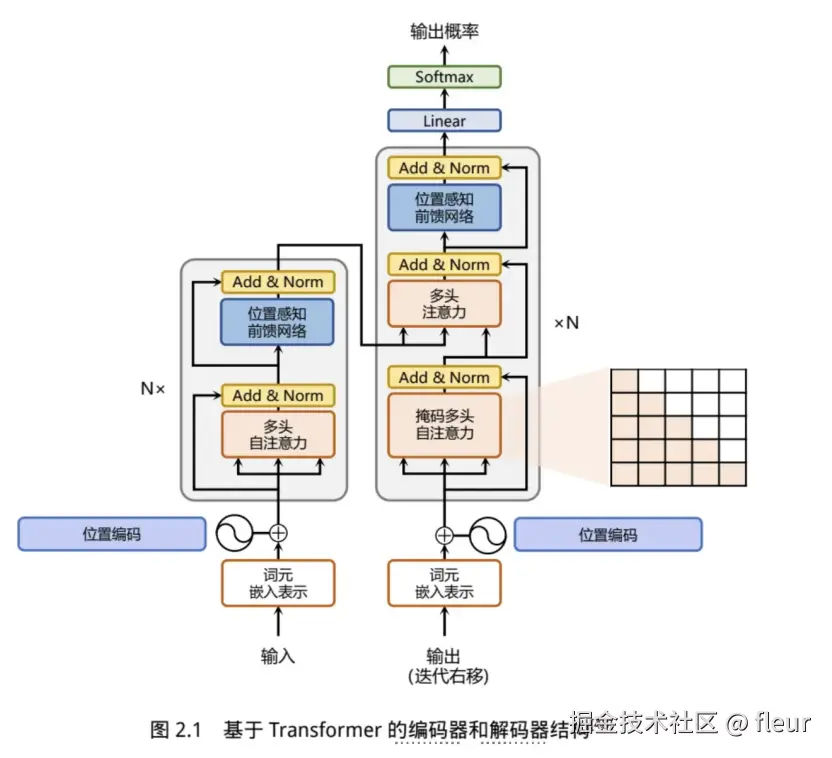
词元嵌入&位置编码
对于输入文本序列,首先通过输入嵌入层(Input Embedding)将每个单词转换为其相对应的向量表示。通常直接对每个单词创建一个向量表示。实际就是添加一个位置编码。
自注意力层
将输入的数据分为查询、键和数值,通过查询和键值运算,并除以缩放因子,计算结果通过softmax归一化后,再与数值向量点积运算,最后实现自注意力的输出。
前馈层
前馈层接受自注意力子层的输出作为输入,并通过一个带有 Relu 激活函数的两层全连接网络对输入进行更加复杂的非线性变换。实验结果表明,增大前馈子层隐状态的维度有利于提升最终翻译结果的质量,因此,前馈子层隐状态的维度一般比自注意力子层要大。
残差连接和层归一化
残差连接主要是指使用一条直连通道直接将对应子层的输入连接到输出上去,从而避免由于网络过深在优化过程中潜在的梯度消失问题。层归一化是利用均值和方差,消解较大的差异化。
解码层
掩码多头注意力:这一额外增加的掩码是用来掩盖后续的文本信息,以防模型在训练阶段直接看到后续的文本序列进而无法得到有效地训练。
基于上述的编码器和解码器结构,待翻译的源语言文本,首先经过编码器端的每个Transformer 块对其上下文语义的层层抽象,最终输出每一个源语言单词上下文相关的表示。解码器端以自回归的方式生成目标语言文本,即在每个时间步 t,根据编码器端输出的源语言文本表示,以及前 t − 1 个时刻生成的目标语言文本,生成当前时刻的目标语言单词。
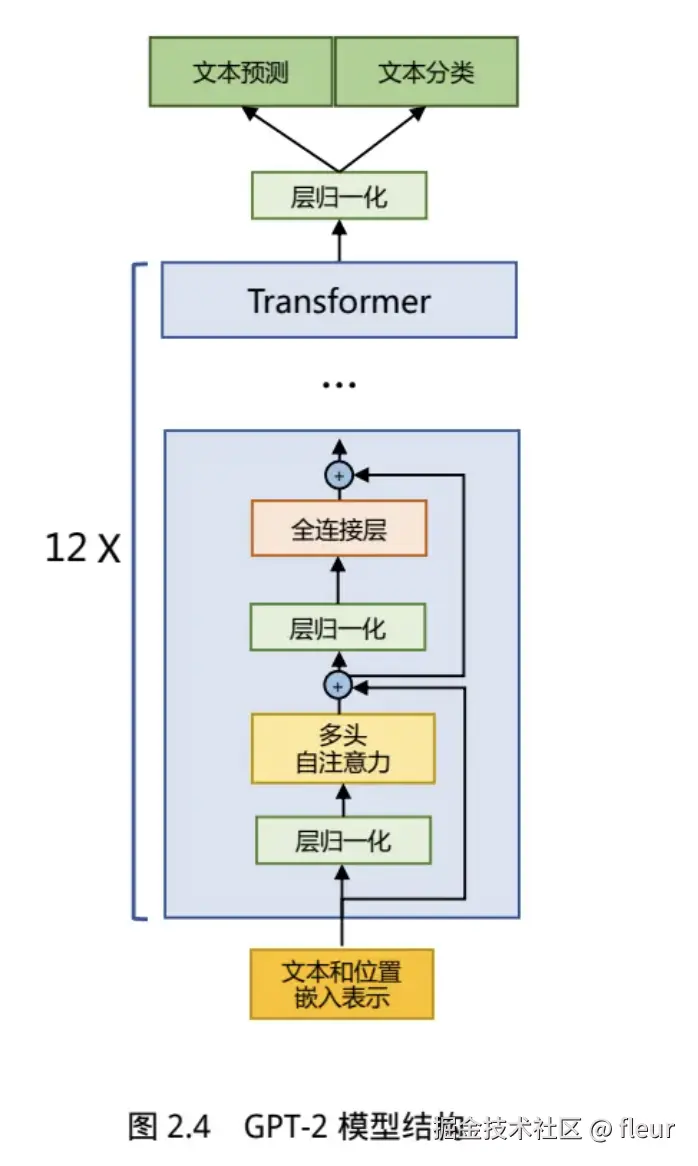
生成式预训练语言模型GPT
无监督预训练
训练数据转换维向量位置数据,输入到多层的transformer层,经过层层的学习,进行数据的输出。
有监督的下游任务微调
带有标签的数据,针对下游的目的,进行有针对性啊的微调,微调过程还要注意灾难性遗忘的问题。
基于huggingface的预训练语言模型实战
开源的自然语言处理软件库,提供全面的工具、库和模型,使得自然语言技术对于开发人员和研究人员更易于使用,基于BERT模型的构建和使用代码参考。
构建步骤
- 数据集下载:dataset库中下载预训练数据集,并按需保留数据集数据,将训练数据进行分割,留出10%的数据用于测试的数据集。
- 训练词元分析器:(tokenizer),可以使用 transformers 库中的BertWordPieceTokenizer 类进行训练。
- 预训练语料集合:将超出最大长度的预料进行分割,将较小的预料进行组合
- 模型训练:训练语料输入和测试语料评估
- 模型使用:文本挖空,模型对挖空文本进行预测
代码
python 代码解读复制代码
import json
from datasets import concatenate_datasets, load_dataset, load_from_disk
from tokenizers import BertWordPieceTokenizer
from transformers import BertTokenizerFast
from transformers import BertConfig, BertForMaskedLM, DataCollatorForLanguageModeling, TrainingArguments, Trainer
# 1. 数据集合准备,此处需要单独准备,可能下载不下来,可以选择阿里的modelspace
# 加载数据集
#bookcorpus = load_dataset("bookcorpus", split="train")
# 下载到本地 save_to_disk, 后面直接 load_from_disk就行
#bookcorpus.save_to_disk("./bookcorpus")
# 从本地加载数据
bookcorpus = load_from_disk("./bookcorpus")
dataset = concatenate_datasets([bookcorpus])
# 90% 用于训练,10%用于测试
d = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
# 将训练和测试数据分别保持在本地文件中
"""print(t, file=f) writes the content of t to the file f.
The print function automatically adds a newline after each item t,
so each item from dataset["text"] will be on a new line in the output file."""
def dataset_to_text(dataset, output_filename):
print(output_filename, "writing")
with open(output_filename, "w") as f:
for t in dataset["text"]:
print(t, file=f)
print(output_filename, "finish")
# save the training set to train.txt and save the testing set to test.txt
# dataset_to_text(d['train'], './train.txt')
# dataset_to_text(d['test'], './test.txt')
# 2. 训练词元分析器(Tokenizer)
"""训练分词器的主要目的是将文本转换成BERT模型能够理解的格式,并生成input_ids和attention_mask。
分词(Tokenization):将原始文本分解成词汇单元(tokens),比如单词、标点符号等。
生成input_ids:将分词后的结果转换为词汇表中对应的索引(ID),因为模型是通过这些索引来理解文本的。
生成attention_mask:因为处理的文本长度不一,我们通常会将所有文本填充(pad)到相同长度。attention_mask用于指示哪些位置是真实文本,哪些位置是填充的,以便模型在处理时能够区分。"""
"""BERT 采用了 WordPiece 分词,根据训练语料中的词频决定是否将一个完整的词切分为多个词元。
需要首先训练词元分析器(Tokenizer)。"""
special_tokens = ["[PAD]", "[UNK]", "[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[MASK]", "", "" ]
# if you want to train the tokenizer on both sets
# training the tokenizer on the trainiing set
files = ['./train.txt']
# 30,522 vocab is BERT's default vocab size, feel free to tweak
vocab_size = 30_522
# maximum sequence length, lowering will result to faster training (when increasing batch size)
max_length = 512
"""truncate_longer_samples 布尔变量来控制用于对数据集进行词元处理的 encode() 回调函数。
如果设置为 True,则会截断超过最大序列长度(max_length)的句子。否则,不会截断。
如果设置为 False,需要将没有截断的样本连接起来,并组合成固定长度的向量。"""
truncate_longer_samples = False
# initialize the WordPiece tokenizer
tokenizer = BertWordPieceTokenizer()
# train the tokenizer
# tokenizer.train(files=files, vocab_size=vocab_size, special_tokens=special_tokens)
# 启用截断功能,最多可截断 512 个标记
tokenizer.enable_truncation(max_length=max_length)
model_path = "'./pretrained-bert"
# if not os.path.isdir(model_path):
# os.mkdir(model_path)
# tokenizer.save_model(model_path)
# 将部分标记符配置转储到配置文件中,包括特殊标记、是否小写以及最大序列长度
with open(os.path.join(model_path, "config.json"), 'w') as f:
tokenizer_cfg = {
"do_lower_case": True,
"unk_token": "[UNK]",
"sep_token": "[SEP]",
"pad_token": "[PAD]",
"cls_token": "[CLS]",
"mask_token": "[MASK]",
"model_max_length": max_length,
"max_len": max_length,
}
json.dump(tokenizer_cfg, f)
# when the tokenizer is trained and configured, load it as BertTokenizerFast
# 初始化分词器
tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_path)
# 3. 预处理语料集合
# 使用预训练的分词器来编码文本
"""在启动整个模型训练之前,还需要将预训练语料根据训练好的 Tokenizer 进行处理。
如果文档长度超过512个词元(token),那么就直接进行截断。"""
def encode_with_truncation(examples):
"""Mapping function to tokenize the sentences pass with truncation"""
return tokenizer(examples["text"], truncation=True, padding="max_length",
max_length=max_length, return_special_tokens_mask=True)
def encode_without_truncation(examples):
"""Mapping function to tokenize the sentences pass without truncation"""
return tokenizer(examples["text"], return_special_tokens_mask=True)
"""在使用 Hugging Face 的 datasets 库处理数据集以准备用于 PyTorch 训练时,您可能需要执行一些额外的步骤来优化数据集格式。
具体来说,如果您想移除非必要列并将 input_ids 和 attention_mask 设置为 PyTorch 张量(tensors),
可以通过使用数据集的 .map() 方法来应用转换函数,然后使用 .set_format() 方法来指定输出格式。"""
# the encode function will depend on the truncate_longer_samples variable
encode = encode_with_truncation if truncate_longer_samples else encode_without_truncation
# tokenizing the train dataset, test dataset。map: 对数据集应用encode函数,批量处理
train_dataset = d["train"].map(encode, batched=True)
test_dataset = d["test"].map(encode, batched=True)
if truncate_longer_samples:
# 移除其他列之后,将input_ids和attention_mask 设置为 PyTorch 张量
train_dataset.set_format(type="torch", columns=["input_ids", "attention_mask"])
test_dataset.set_format(type="torch", columns=["input_ids", "attention_mask"])
else:
# 移除其他列之后,直接将需要的列保留为Python列表
train_dataset.set_format(columns=["input_ids", "attention_mask", "special_tokens_mask"])
test_dataset.set_format(columns=["input_ids", "attention_mask", "special_tokens_mask"])
from itertools import chain
# 主要数据处理函数,用于连接数据集中的所有文本, 并生成长度为 max_seq_length 的数据块。
def group_texts(examples):
# concatentate all texts
concatenated_examples = {k: list(chain(*examples[k])) for k in examples.keys()}
total_length = len(concatenated_examples[list(examples.keys())[0]])
# 如果模型支持,我们可以添加衬垫,而不是填充,您可以根据自己的需要定制这一部分。
if total_length >= max_length:
total_length = (total_length // max_length) * max_length
# Split by chunks of max_len.
result = {
k: [t[i : i + max_length] for i in range(0, total_length, max_length)]
for k, t in concatenated_examples.items() }
return result
# 请注意,在 `batched=True` 的情况下,这个映射会同时处理 1,000 个文本,因此 group_texts 会为每组 1,000 个文本丢弃一个余数。
# 可以在此调整 batch_size,但如果数值越大,预处理速度可能越慢。
if not truncate_longer_samples:
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(group_texts, batched=True,
desc=f"Grouping texts in chunks of {max_length}")
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(group_texts, batched=True,
desc=f"Grouping texts in chunks of {max_length}")
# convert them from lists to torch tensors
train_dataset.set_format("torch")
test_dataset.set_format("torch")
# 4. 模型训练
# 在构建了处理好的预训练语料之后,就可以开始训练模型
# 使用配置初始化模型
model_config = BertConfig(vocab_size=vocab_size, max_position_embeddings=max_length)
# 在MLM任务中,模型的目标是预测输入句子中被随机遮蔽掉的单词。这是 BERT 训练过程的一部分,有助于模型学习语言的深层次理解。
model = BertForMaskedLM(config=model_config)
# 初始化数据整理器,随机屏蔽 20%(默认为 15%)的标记,用于屏蔽语言建模 (MLM) 任务
data_collator = DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(
tokenizer=tokenizer, mlm=True, mlm_probability=0.2
)
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=model_path,
evaluation_strategy="steps", # evaluate each 'logging_steps'
overwrite_output_dir=True,
num_train_epochs=10, # number of training epochs, feel free to tweak
per_device_train_batch_size=10, # the training batch size, put it as high as your GPU memory fits
gradient_accumulation_steps=8, # accumulating the gradients before updating the weights
per_gpu_eval_batch_size=64, # evaluate batch size
logging_steps=1000, # evaluate, log and save model checkpoints every 1000 step
save_steps=1000,
# load_best_model_at_end=True, # whether to load the best model (in terms of loss) at the end of training
# save_total_limit=3, # whether you don't have much space so you let only 3 model weights saved in the disk
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
data_collator=data_collator,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=test_dataset,
)
# train the model
trainer.train()
# 5. 模型使用
from transformers import pipeline
# load the model checkpoint
model = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(os.path.join(model_path, "checkpoint-10000"))
# load the tokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_path)
# 已经完成了 BERT 模型的训练。使用 fill-mask 管道进行预测
fill_mask = pipeline("fill-mask", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
# perform predictions
examples = [
"Today's most trending hashtags on [MASK] is Donald Trump",
"The [MASK] was cloudy yesterday, but today it's rainy.",
]
for example in examples:
predictions = fill_mask(example)
print(f"Input: {example}")
for prediction in predictions:
print(f"{prediction['sequence']}, confidence: {prediction['score']}")
print("="*50)
Transformer模型实际使用下的变更
基于llama模型进行分析作为解码器实际模型中的变更,包括前置层归一化,使用RMSNorm函数,激活函数变更为SwiGLU,并使用了相对位置编码:旋转位置嵌入。
-
RSMnorm归一化函数的位置:将第一个层归一化移动到多头自注意力层之前,第二个层归一化也移动到了全连接层之前,同时残差连接的位置也调整到了多头自注意力层与全连接层之后。
-
SwiGLU:性能更高的激活函数。
-
RoPE的相对位置编码:在位置编码上,使用旋转位置嵌入(Rotary Positional Embeddings,RoPE) 代替原有的绝对位置编码。RoPE 借助了复数的思想,出发点是通过绝对位置编码的方式实现相对位置编码。

评论记录:
回复评论: