1. Spring 概述
1.1 什么是Spring
Spring是由Rod Johnson组织和开发的一个分层的轻量级框架,它以IoC(控制反转),AOP(面向切面编程)为内核,使用JavaBean来完成工作。
Spring 致力于JavaEE应用各层的解决方案,在表现层它提供了Spring MVC以及与Structs框架的整合功能;在业务逻辑层可以管理事务,记录日志等;在持久层可以整合MyBatis,Hibernate,JdbcTemplate等技术。因此可以说Spring是企业应用开发很好“一战式”选择。虽然Spring贯穿于表现层,业务逻辑层和持久层,但它并不想取代那些已有的框架,而是以高度的开放性与他们进行无缝整合。
1.2 Spring 框架的优点
Spring具有简单、可测试和松耦合等特点,从这个角度出发,Spring不仅可以用于服务器端开发,也可以应用于任何Java应用的开发中。关于 Spring 框架优点的忌结,具体如下。
- 非侵入式设计
Spring是一种非侵入式( non-invasive )框架,它可以使应用程序代码对框架的依赖最小化。 - 方便解耦、简化开发
Spring 就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象的创建和依赖关系的维护工作都交给Spring容器管理,大大地降低了组件之间的耦合性。 - 支持 AOP
Spring提供了对 AOP的支持,它允许将一些通用任务,如安全、事务、日志等进行集中式处理,从而提高了程序的复用性。 - 支持声明式事务处理
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无须手动编程。 - 方便程序的测试
Spring提供了对Junit4 的支持,可以通过注解方便地测试Spring程序。 - 方便集成各种优秀框架
Spring 不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种伏委框架(加Struts. Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持。 - 降低Java EE API的使用难度
Spring对 Java EE 开发中非常难用的一些API(如JDBC. lavaMail笑)却提供了封装,使这些 API 应用难度大大降低。
1.3 Spring的体系结构
Spring框架采用的是分层架构,它一系列的功能要素被分成20个模块,主要包括以下部分
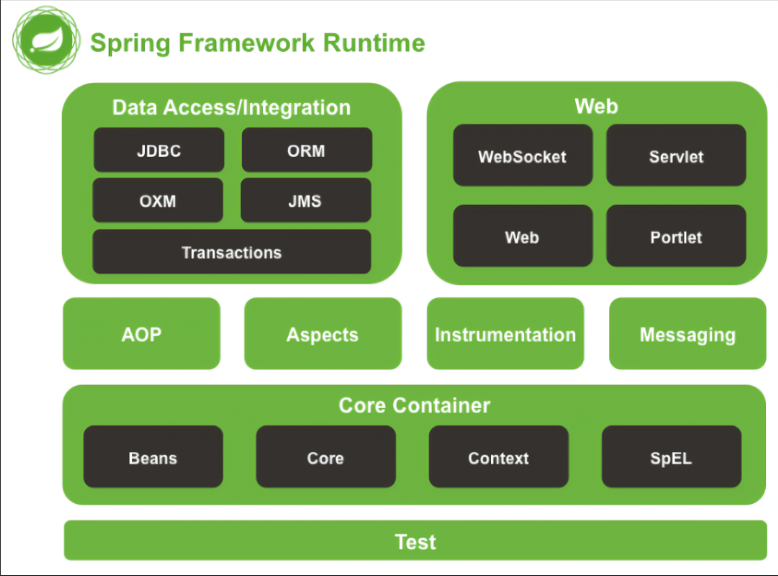
2. Spring的核心容器
2.1 BeanFactory
BeanFactory由org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory接口定义,是基础类型的IoC容器,就作用来说,BeanFactory就是一个管理Bean的工厂,它主要负责初始化Bean,并调用它们的生命周期方法。
2.2 ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,也被称为应用上下文,是另一种常用的Spring容器。
创建ApplicationContext接口实例,通常有两种方法:
-
通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext创建
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext会从指定的类路径(相对路径)中去找XML配置文件,并装载完成ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String config);- 1
-
通过FileSystemXmlApplicationContext创建
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext会从系统文件路径(绝对路径)去找XML配置文件,并装载完成ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String config);- 1
3. Spring的入门程序
3.1 在pom下利用maven导入Spring所需要的jar包
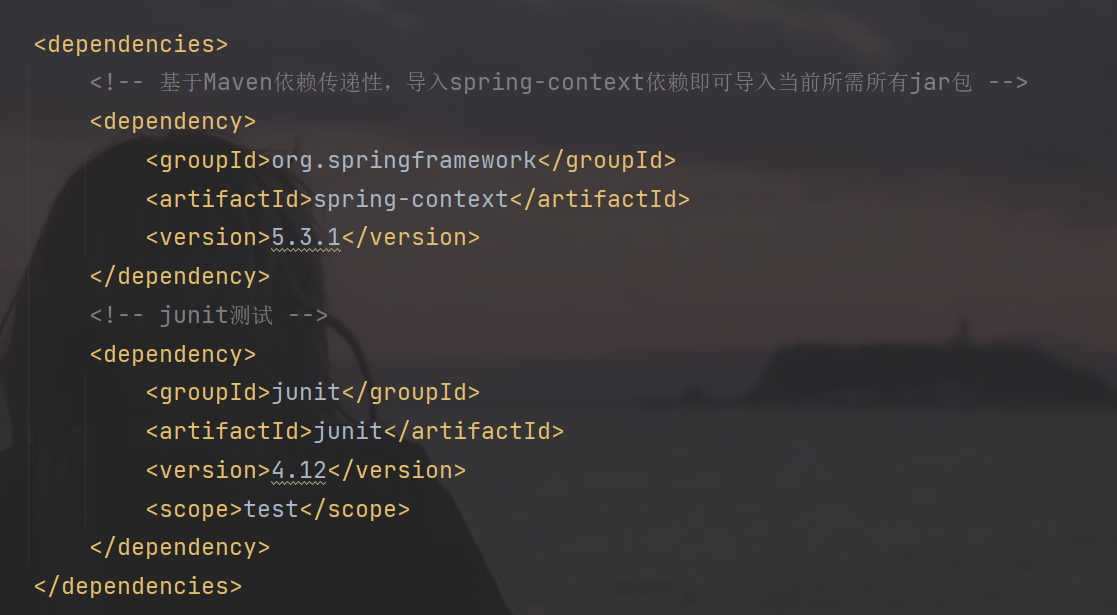
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
3.2 简单搭建起demo结构
注意检查一下Spring的四个jar包是否导入成功
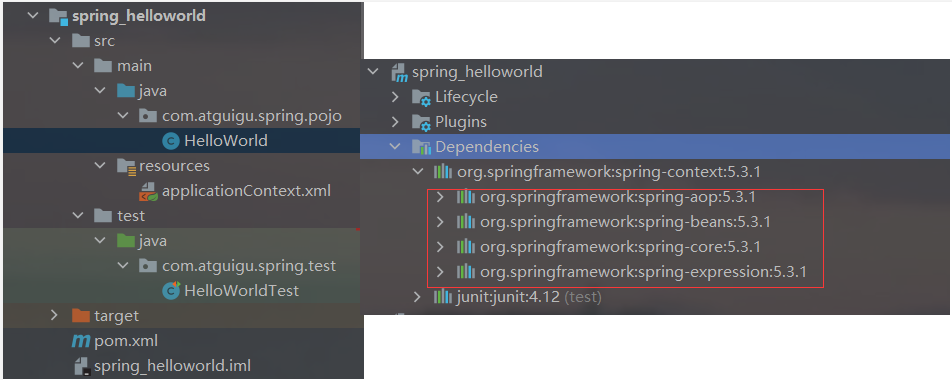
3.3 编写一个简单的JavaBean
package com.atguigu.spring.pojo;
public class HelloWorld {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello,spring");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.4 将JavaBean加入到Ioc容器的管理中
编写applicationContext.xml文件

<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloworld" class="com.atguigu.spring.pojo.HelloWorld">bean>
beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3.5 创建test方法
这里关键在于Ioc容器的获取
package com.atguigu.spring.test;
import com.atguigu.spring.pojo.HelloWorld;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloWorldTest {
@Test
public void test(){
//获取IOC容器
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取IOC容器中的bean
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ioc.getBean("helloworld");
helloworld.sayHello();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
3.6 启动测试
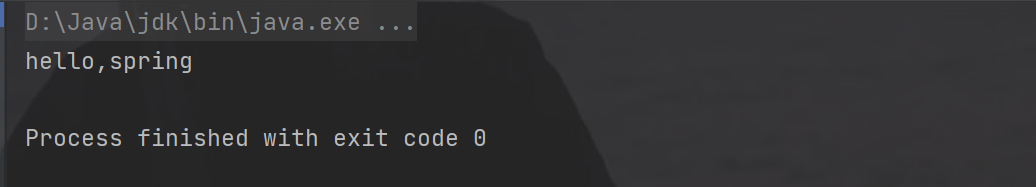


评论记录:
回复评论: