题目——1.两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案,并且你不能使用两次相同的元素。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
ini 代码解读复制代码输入: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出: [0,1]
解释: 因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
ini 代码解读复制代码输入: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出: [1,2]
示例 3:
ini 代码解读复制代码输入: nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出: [0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109- 只会存在一个有效答案
二、小白题解(正是本人)
js 代码解读复制代码/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[]}
*/
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
for(let i=0;ilength ;i++){
for(let j=i+1;jlength ;j++){
if(nums[i]+nums[j]===target){
return [i,j];
}
}
}
};
这个解题思路有很多缺点—— 时间复杂度高、没有异常处理、看上去像作者自己写的......
总之就是一个暴力题解,我们在最坏的情况下是的时间复杂度,会将nums中的所有元素组合遍历知道找到符合条件的两个元素的下标,那么有没有更好的解法呢?
三、有的兄弟,肯定有的(时间复杂度上的最优解)
js 代码解读复制代码/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[]}
*/
function twoSum(nums, target) {
const numMap = {};
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const complement = target - nums[i];
if (complement in numMap) {
return [numMap[complement], i];
}
numMap[nums[i]] = i;
}
return [];
}
这个解法用到了哈希表,这里我们并不需要去详细研究哈希表是个什么东西,我们这里可以把哈希表理解为一个容器,里面的数据可以拿出来和我们想要的目标数据对比,每次对比是的复杂度。
我们来看题解的主体
js 代码解读复制代码 for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const complement = target - nums[i];
if (complement in numMap) {
return [numMap[complement], i];
}
numMap[nums[i]] = i;
}
1.每个元素遍历了几次?
我们只有一个for循环,这意味着每个数组里面的元素只会遍历一遍
2.每个元素遍历经历了什么
存入哈希表之前
1.被用作计算和自己组合起来符合题意的元素的值
js 代码解读复制代码const complement = target - nums[i];
2.被存储在哈希表中作为键值存储在哈希表中,同时下表作为对应键值的值
js代码解读复制代码numMap[nums[i]] = i;
存入哈希表之后
3.作为可被寻找的、其他元素的“另一半”,如果确定是,则输出两元素在原数组的下标
js 代码解读复制代码 if (complement in numMap) {
return [numMap[complement], i];
}
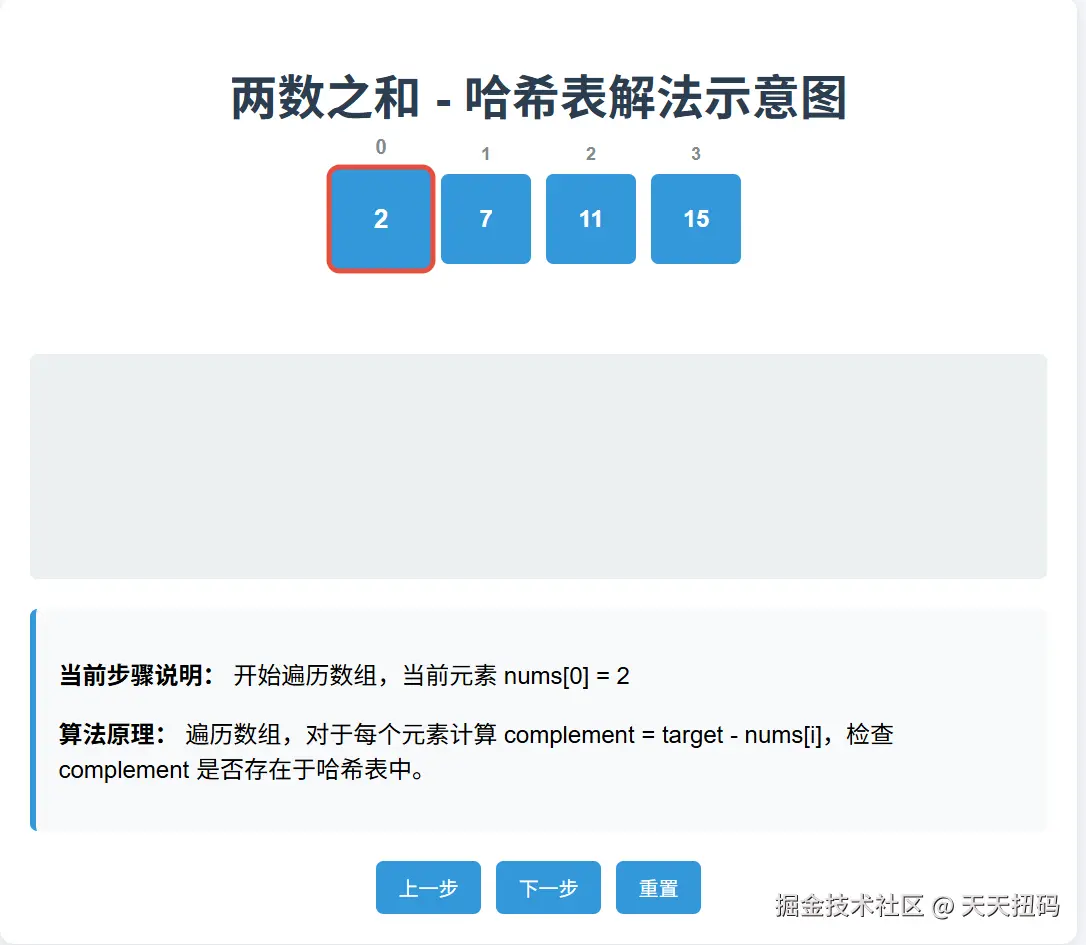
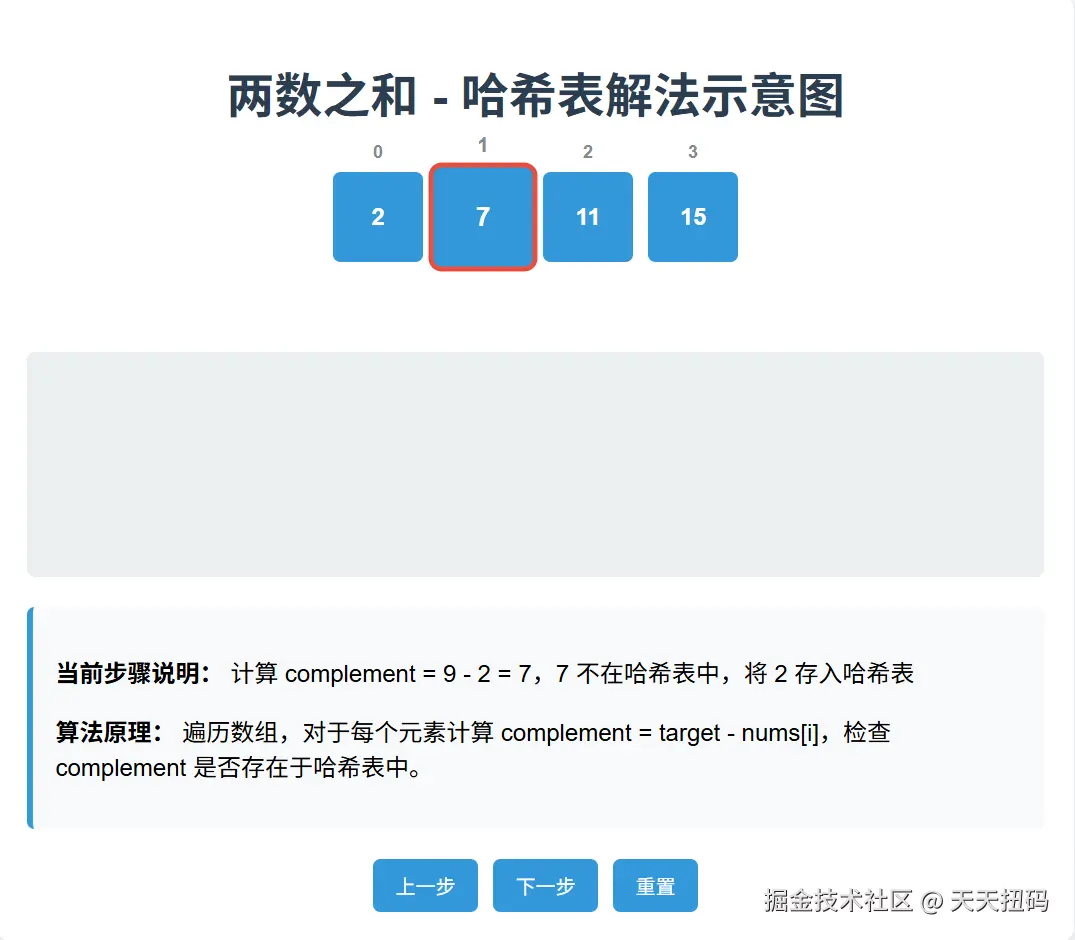
四、下面我们用一个例子来分析最优解的执行过程
js 代码解读复制代码nums = [2,7,11,15];
target = 9
具体过程如下(图解)


五、可执行流程(将代码复杂到编译器运行即可得到动态图解)
html 代码解读复制代码html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>两数之和 - 哈希表解法示意图title>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f5f7fa;
}
.container {
background: white;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
h1 {
color: #2c3e50;
text-align: center;
}
.visualization {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 20px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
.array-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
position: relative;
height: 100px;
}
.array-element {
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
background: #3498db;
color: white;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
border-radius: 5px;
margin: 0 5px;
position: relative;
transition: all 0.3s;
font-weight: bold;
}
.array-index {
position: absolute;
top: -20px;
color: #7f8c8d;
font-size: 12px;
}
.hash-table {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 10px;
justify-content: center;
min-height: 120px;
background: #ecf0f1;
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.hash-entry {
background: #2ecc71;
color: white;
padding: 8px 12px;
border-radius: 5px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
opacity: 0;
transform: scale(0.8);
transition: all 0.5s;
}
.hash-entry.visible {
opacity: 1;
transform: scale(1);
}
.hash-key {
font-weight: bold;
border-bottom: 1px solid white;
margin-bottom: 3px;
padding-bottom: 3px;
}
.current {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px #e74c3c;
transform: scale(1.1);
}
.complement {
background: #e74c3c;
}
.found {
background: #f39c12;
animation: pulse 0.5s 2;
}
@keyframes pulse {
0% { transform: scale(1); }
50% { transform: scale(1.1); }
100% { transform: scale(1); }
}
.explanation {
background: #f8f9fa;
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 5px;
margin-top: 20px;
border-left: 4px solid #3498db;
}
.controls {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
gap: 10px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
button {
padding: 8px 15px;
background: #3498db;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: background 0.3s;
}
button:hover {
background: #2980b9;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>两数之和 - 哈希表解法示意图h1>
<div class="visualization">
<div class="array-container">
div>
<div class="hash-table">
div>
div>
<div class="explanation">
<p><strong>当前步骤说明:strong> <span id="step-explanation">初始化数组和哈希表span>p>
<p><strong>算法原理:strong> 遍历数组,对于每个元素计算 complement = target - nums[i],检查 complement 是否存在于哈希表中。p>
div>
<div class="controls">
<button id="prev-btn">上一步button>
<button id="next-btn">下一步button>
<button id="reset-btn">重置button>
div>
div>
<script>
// 示例数据
const nums = [2, 7, 11, 15];
const target = 9;
let currentStep = 0;
let hashMap = {};
// 初始化可视化
function initVisualization() {
const arrayContainer = document.querySelector('.array-container');
arrayContainer.innerHTML = '';
// 创建数组元素
nums.forEach((num, index) => {
const element = document.createElement('div');
element.className = 'array-element';
element.textContent = num;
element.id = `num-${index}`;
const indexLabel = document.createElement('div');
indexLabel.className = 'array-index';
indexLabel.textContent = index;
element.appendChild(indexLabel);
arrayContainer.appendChild(element);
});
updateHashTable();
updateExplanation();
}
// 更新哈希表显示
function updateHashTable() {
const hashTable = document.querySelector('.hash-table');
hashTable.innerHTML = '';
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(hashMap)) {
const entry = document.createElement('div');
entry.className = 'hash-entry visible';
entry.innerHTML = `
${key}
→ ${value}
`;
hashTable.appendChild(entry);
}
}
// 更新步骤说明
function updateExplanation() {
const explanation = document.getElementById('step-explanation');
const currentElement = document.getElementById(`num-${currentStep}`);
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('.array-element');
// 重置所有元素样式
elements.forEach(el => {
el.classList.remove('current', 'complement', 'found');
});
switch(currentStep) {
case 0:
explanation.textContent = "开始遍历数组,当前元素 nums[0] = 2";
currentElement.classList.add('current');
break;
case 1:
explanation.textContent = "计算 complement = 9 - 2 = 7,7 不在哈希表中,将 2 存入哈希表";
currentElement.classList.add('current');
break;
case 2:
explanation.textContent = "移动到 nums[1] = 7,计算 complement = 9 - 7 = 2";
currentElement.classList.add('current');
document.getElementById('num-0').classList.add('complement');
break;
case 3:
explanation.textContent = "发现 2 在哈希表中(索引 0),找到解 [0, 1]!";
currentElement.classList.add('current');
document.getElementById('num-0').classList.add('found');
currentElement.classList.add('found');
break;
default:
explanation.textContent = "遍历完成";
}
}
// 下一步
function nextStep() {
if (currentStep >= 4) return;
switch(currentStep) {
case 0:
// 准备处理第一个元素
break;
case 1:
// 处理 nums[0] = 2
hashMap[nums[0]] = 0;
break;
case 2:
// 处理 nums[1] = 7
const complement = target - nums[1];
if (complement in hashMap) {
// 找到解的情况
}
break;
case 3:
// 完成
break;
}
currentStep++;
updateHashTable();
updateExplanation();
}
// 上一步
function prevStep() {
if (currentStep <= 0) return;
currentStep--;
// 回退哈希表状态
if (currentStep < 1) {
hashMap = {};
} else if (currentStep < 2) {
hashMap = { [nums[0]]: 0 };
}
updateHashTable();
updateExplanation();
}
// 重置
function reset() {
currentStep = 0;
hashMap = {};
initVisualization();
}
// 事件监听
document.getElementById('next-btn').addEventListener('click', nextStep);
document.getElementById('prev-btn').addEventListener('click', prevStep);
document.getElementById('reset-btn').addEventListener('click', reset);
// 初始化
initVisualization();
script>
body>
html>
六、结语
再见!

评论记录:
回复评论: