戳蓝字“CSDN云计算”关注我们哦!

一份来自富莱睿(Flexera)的《RightScale 2019年云计算现状报告》划出了当下企业云战略的关注重点:企业在云计算方面的支出增加,基于此,各企业重视对云支出进行优化。
根据全球知名软件资产管理提供商富莱睿(Flexera)发布的《RightScale 2019年云计算现状报告》,企业将逐步采用多云方案,而当中有一半的企业在公有云上的花费超过100万美元。与此同时,微软Azure的工作量继续增加,云方案的采用及云支出的优化仍然是2019年重要的主题。
这份来自RightScale的报告(以下简称为报告)采访了786位相关人士,其中有58%的受访者被归类为企业客户。在这之前,大数据分析公司Kentik和云资源管理公司Densify也相应做过类似的调查并同样强调“多云应用中的成本优化是关键议题”的观点。
2019年是把优化云支出作为当务之急的第三年,持有这一观点的比例也从2018年的58%增至64%。虽然64%的受访者将优化云支出列为首要举措,但这一比例在中高级云用户中更高,分别为70%和76%。
根据报告,平台即服务(PaaS)、无服务器(serverless)、机器学习和容器的使用等正在激增。
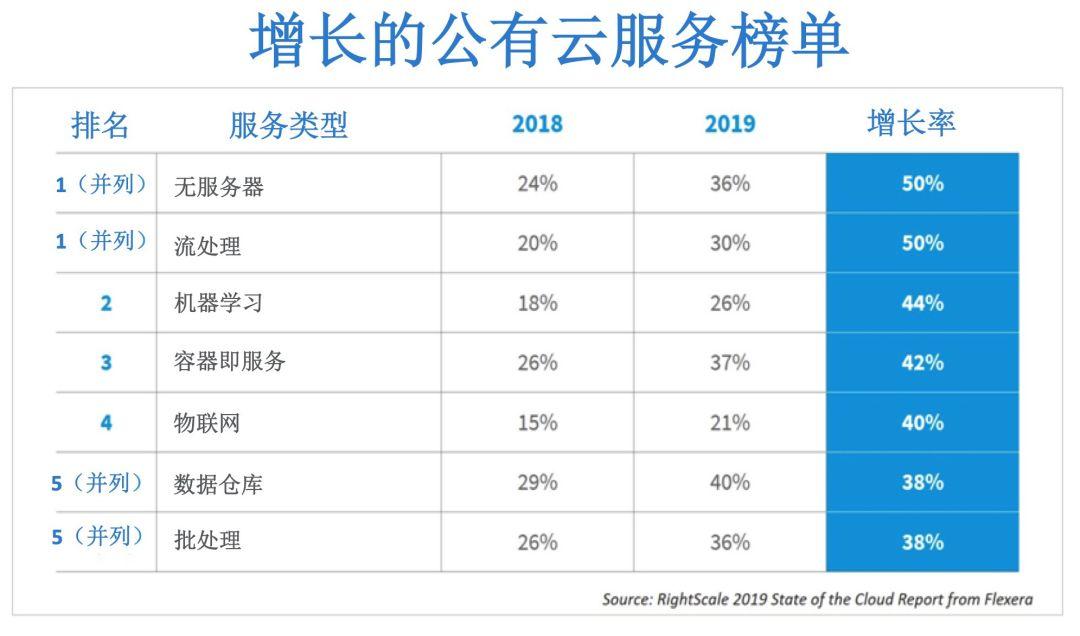 消息来源:富莱睿《RightScale 2019年云计算现状报告》
消息来源:富莱睿《RightScale 2019年云计算现状报告》
RightScale发现,84%的企业已在实施多云战略,其中有61%为中小企业。总的来说,RightScale报告的受访者平均使用4.9个公有云和私有云。
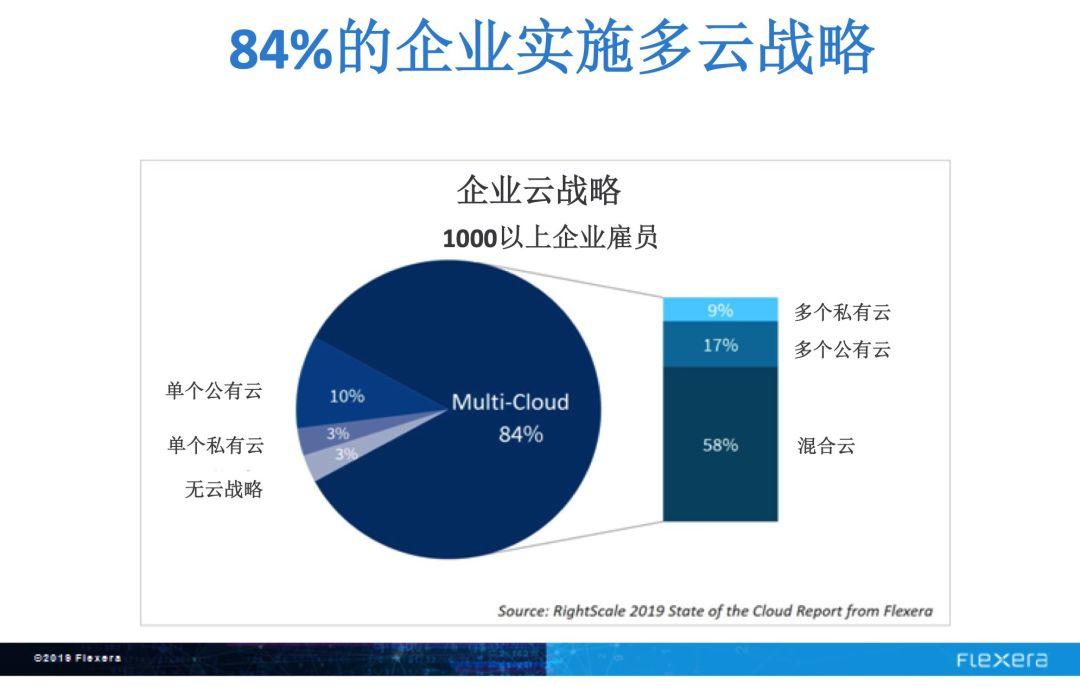
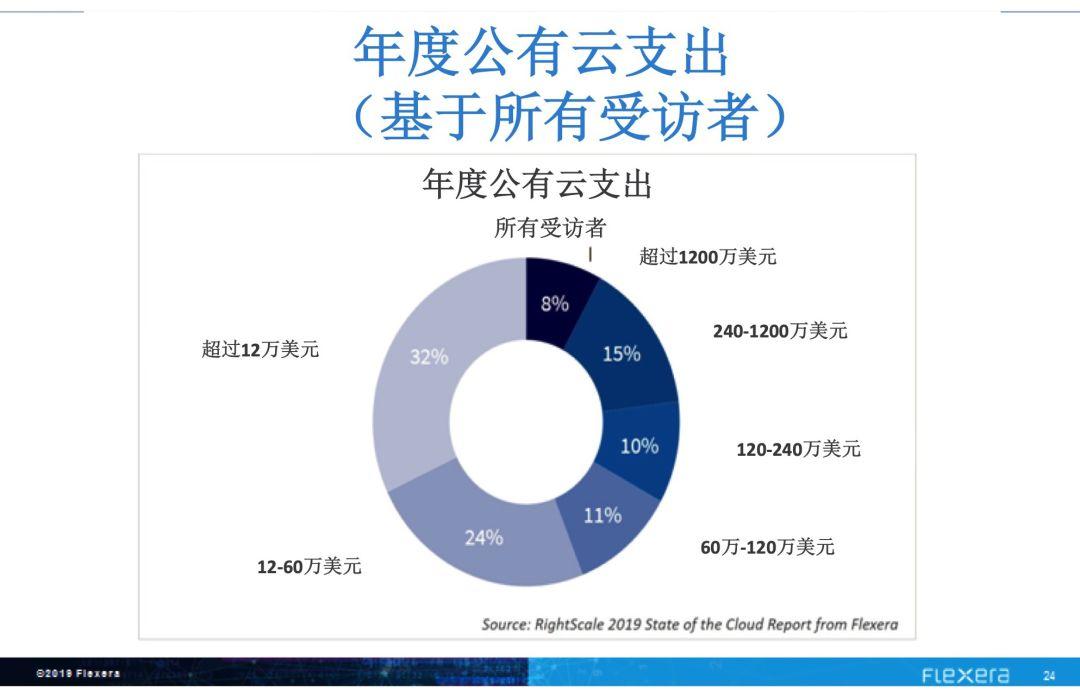
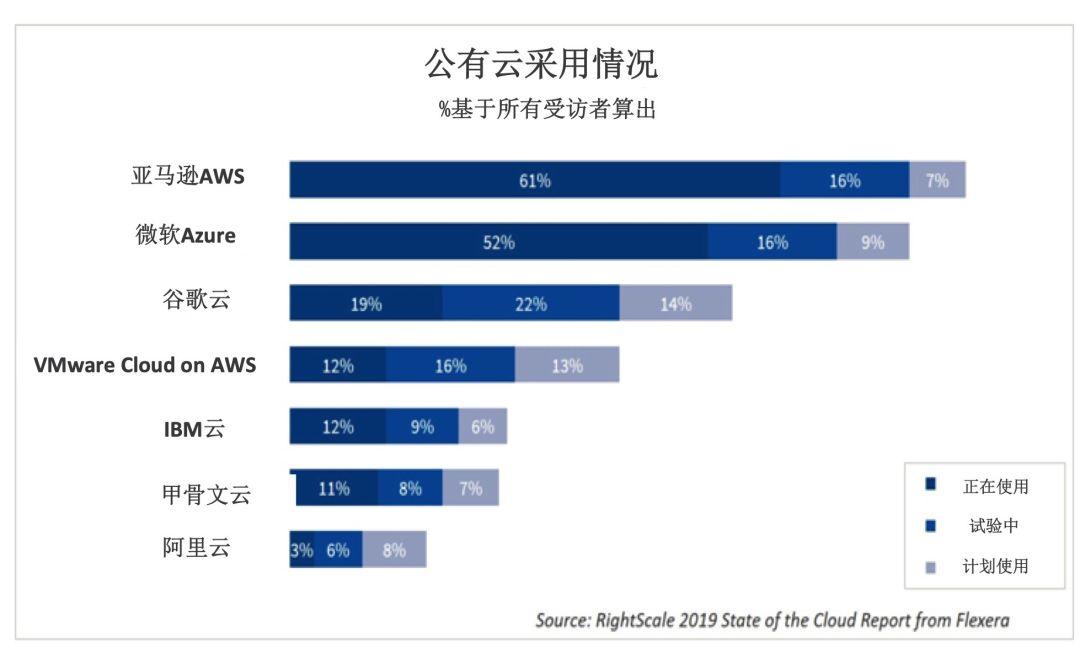
企业在云支出增长主要原因是使用微软Azure。以下为RightScale关于这个结论的分析:
从总体来看,微软Azure采用率从之前的45%增长到52%,与亚马逊AWS之间的差距进一步缩小,目前Azure采用率已达到AWS采用率的85%,高于去年的70%。Azure在企业方面追赶AWS的增速最快,其中,Azure的采用率从58%略微增至60%,而AWS相应的采用率则相对平稳,为67%。谷歌则保持处于第三的排名,其采用率从18%略微增长至19%。自2018上市以来,AWS上的VMware Cloud采用率从上市第一年的8%上升到了今年的第四位,增长率达50%。报告在2018年对其他公有云提供商的调查中发现,今年这些提供商采用率均有所提高,甲骨文从10%增长到16%(增长率为60%),IBM云从15%增长到18%(增长率为20%),阿里云则从2%增长到4%(增长率为100%)。
随着对云计算支出的激增,其中一半的企业每年公有云支出超过120万美元,关于云支出的担忧也随之产生。根据报告,66%的企业已经创建了一个云中心团队来管理云服务。
根据RightScale调查发现,公司正在寻求在移动工作负载之上优化现有的云方案,由此可见,企业对云中心团队的部署主要出于成本管理的原因。
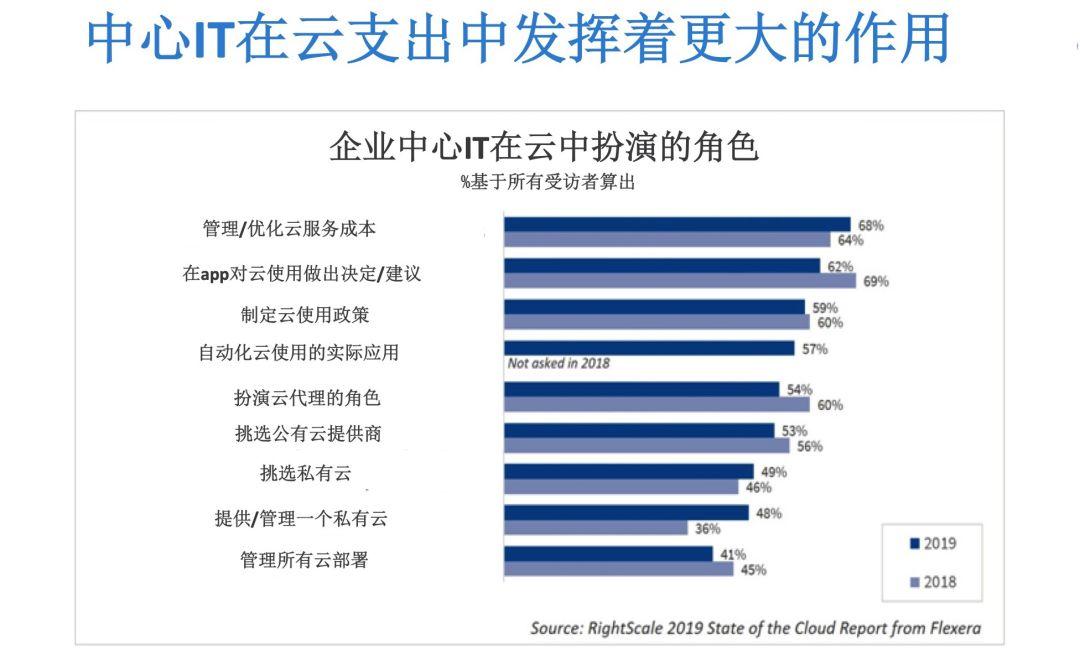
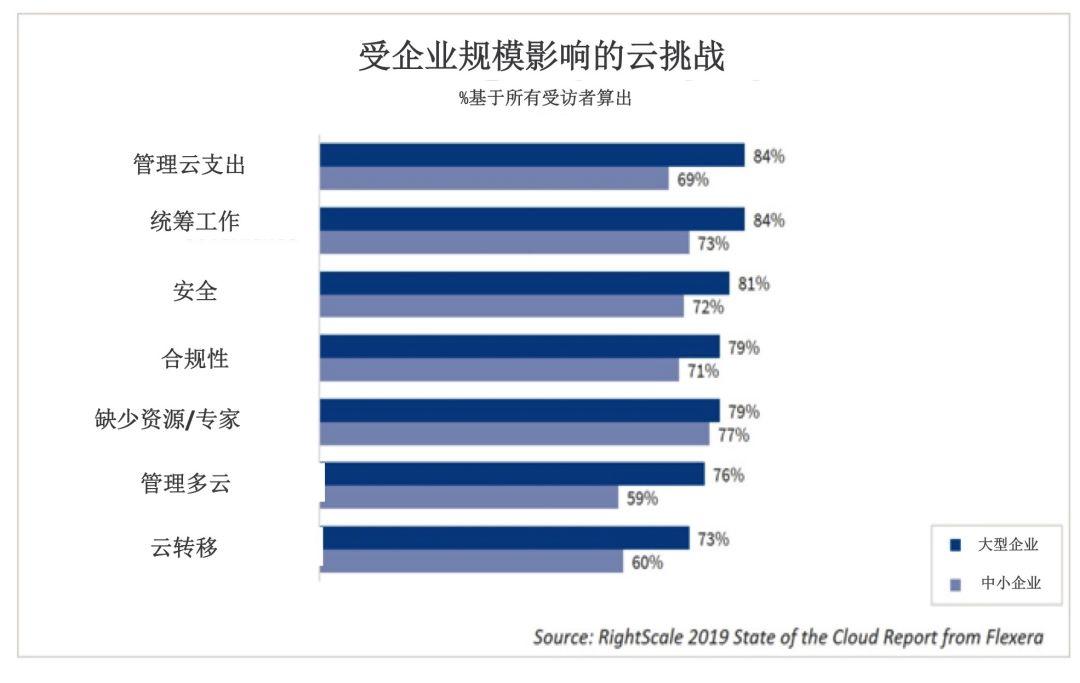
总的来说,企业没有对云使用政策进行自动化,也低估了他们在这方面的开支,企业甚至没有大范围地使用折扣来降低成本。
与此同时,容器也被迅速采用。
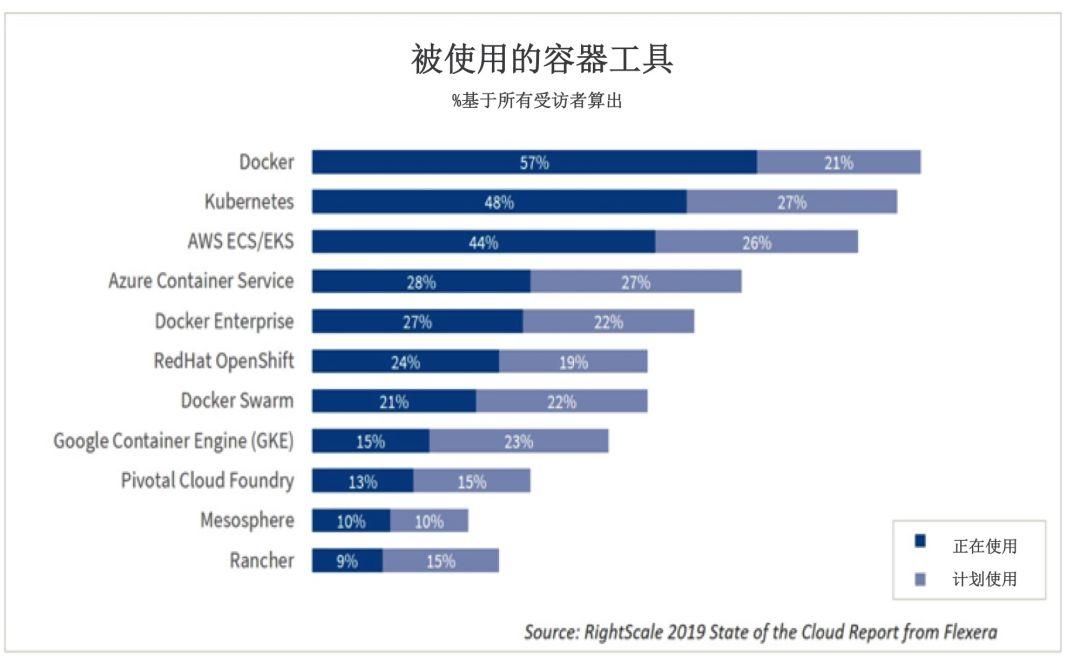
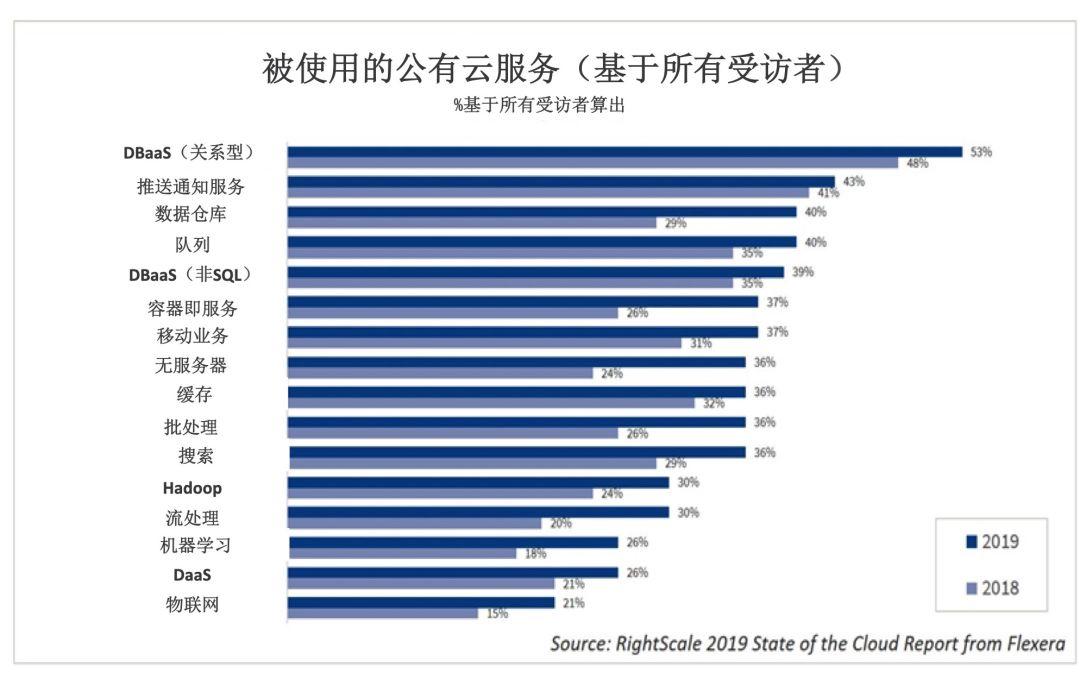
增长最快的公有云服务是无服务器类型,但数据库作为服务工具已被广泛采用。

福利
扫描添加小编微信,备注“姓名+公司职位”,加入【云计算学习交流群】,和志同道合的朋友们共同打卡学习!
推荐阅读:
都道业务提升坑大事儿多,但英特尔云方案却说“简单”
云有约 | 蚂蚁金服bPaaS究竟是什么?
再不编程就老了!05 后比特币专家准备赚个 134,000,000 元!
Pig变飞机?AI为什么这么蠢 | Adversarial Attack
互联网没有春天
麦克阿瑟奖得主Dawn Song:区块链能保密和保护隐私?图样图森破!
2019年最值得关注的五大微服务发展趋势
 喜欢就点击“在看”吧
喜欢就点击“在看”吧
本文涉及知识点
P5960 【模板】差分约束
题目描述
给出一组包含 m m m 个不等式,有 n n n 个未知数的形如:
{
x
c
1
−
x
c
1
′
≤
y
1
x
c
2
−
x
c
2
′
≤
y
2
⋯
x
c
m
−
x
c
m
′
≤
y
m
{xc1−xc′1≤y1xc2−xc′2≤y2⋯xcm−xc′m≤ym
的不等式组,求任意一组满足这个不等式组的解。
输入格式
第一行为两个正整数 n , m n,m n,m,代表未知数的数量和不等式的数量。
接下来 m m m 行,每行包含三个整数 c , c ′ , y c,c',y c,c′,y,代表一个不等式 x c − x c ′ ≤ y x_c-x_{c'}\leq y xc−xc′≤y。
输出格式
一行,
n
n
n 个数,表示
x
1
,
x
2
⋯
x
n
x_1 , x_2 \cdots x_n
x1,x2⋯xn 的一组可行解,如果有多组解,请输出任意一组,无解请输出 NO。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
3 3
1 2 3
2 3 -2
1 3 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
输出 #1
5 3 5
- 1
说明/提示
样例解释
{
x
1
−
x
2
≤
3
x
2
−
x
3
≤
−
2
x
1
−
x
3
≤
1
{x1−x2≤3x2−x3≤−2x1−x3≤1
一种可行的方法是 x 1 = 5 , x 2 = 3 , x 3 = 5 x_1 = 5, x_2 = 3, x_3 = 5 x1=5,x2=3,x3=5。
{
5
−
3
=
2
≤
3
3
−
5
=
−
2
≤
−
2
5
−
5
=
0
≤
1
{5−3=2≤33−5=−2≤−25−5=0≤1
数据范围
对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据, 1 ≤ n , m ≤ 5 × 1 0 3 1\leq n,m \leq 5\times 10^3 1≤n,m≤5×103, − 1 0 4 ≤ y ≤ 1 0 4 -10^4\leq y\leq 10^4 −104≤y≤104, 1 ≤ c , c ′ ≤ n 1\leq c,c'\leq n 1≤c,c′≤n, c ≠ c ′ c \neq c' c=c′。
评分策略
你的答案符合该不等式组即可得分,请确保你的答案中的数据在 int 范围内。
如果并没有答案,而你的程序给出了答案,SPJ 会给出 There is no answer, but you gave it,结果为 WA;
如果并没有答案,而你的程序输出了 NO,SPJ 会给出 No answer,结果为 AC;
如果存在答案,而你的答案错误,SPJ 会给出 Wrong answer,结果为 WA;
如果存在答案,且你的答案正确,SPJ 会给出 The answer is correct,结果为 AC。
图论 差分约束
每个变量看成一个点,不等式看成边。增加一个超级源点src(0),到各点的距离为0。src到节点1的距离为x1,src到节点2的距离为x2,x1 - x2<=3
⟺
\iff
⟺ x有权位3的边到x1。如果没有负环,最短距离就是一组解,则解各未知数增加任意数d,也是解。如果有负环,则无解。
贝尔曼-福特(Bellman-Ford)算法松弛N次,看和松弛N-1是否有区别,如果有区别则返回NO。否则各点最短距离。
代码
核心代码
#include
#include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
单元测试
void Check(const vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edge,const vector<int>& res) {
for (const auto& [x1, x2, y] : edge) {
Assert::IsTrue(res[x1 - 1] - res[x2 - 1] <= y);
}
}
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edge = { {1,2,3},{2,3,-2},{1,3,1} };
auto res = Solution().Ans(3,edge);
Check(edge, res);
}
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod12)
{
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edge = { {1,2,1} };
auto res = Solution().Ans(2, edge);
AssertEx({ 0,0 }, res);
}
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod13)
{
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edge = { {1,2,-1} };
auto res = Solution().Ans(2, edge);
AssertEx({ -1,0 }, res);
}
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod14)
{
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edge = { {1,2,-1},{2,3,-2},{3,1,-2} };
auto res = Solution().Ans(4, edge);
Assert::IsTrue(0 == res.size());
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
扩展阅读
| 我想对大家说的话 |
|---|
| 工作中遇到的问题,可以按类别查阅鄙人的算法文章,请点击《算法与数据汇总》。 |
| 学习算法:按章节学习《喜缺全书算法册》,大量的题目和测试用例,打包下载。重视操作 |
| 有效学习:明确的目标 及时的反馈 拉伸区(难度合适) 专注 |
| 闻缺陷则喜(喜缺)是一个美好的愿望,早发现问题,早修改问题,给老板节约钱。 |
| 子墨子言之:事无终始,无务多业。也就是我们常说的专业的人做专业的事。 |
| 如果程序是一条龙,那算法就是他的是睛 |
| 失败+反思=成功 成功+反思=成功 |
视频课程
先学简单的课程,请移步CSDN学院,听白银讲师(也就是鄙人)的讲解。
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/38771
如何你想快速形成战斗了,为老板分忧,请学习C#入职培训、C++入职培训等课程
https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/6176
测试环境
操作系统:win7 开发环境: VS2019 C++17
或者 操作系统:win10 开发环境: VS2022 C++17
如无特殊说明,本算法用**C++**实现。
 QQ群名片
QQ群名片



评论记录:
回复评论: