- Swift Combine 学习(一):Combine 初印象
- Swift Combine 学习(二):发布者 Publisher
- Swift Combine 学习(三):Subscription和 Subscriber
- Swift Combine 学习(四):操作符 Operator
- Swift Combine 学习(五):Backpressure和 Scheduler
- Swift Combine 学习(六):自定义 Publisher 和 Subscriber
- Swift Combine 学习(七):实践应用场景举例
引言
在前两篇文章中,我们了解了 Combine 的基本概念和发布者(Publisher)的工作机制。本文将深入探讨 Combine 中的订阅机制和订阅者(Subscriber)。通过理解订阅的生命周期、订阅者的类型和使用方式,我们可以更好地掌握 Combine 框架中的数据流动,为后续的实际应用打下基础。
Subscription
A protocol representing the connection of a subscriber to a publisher.
一个表示订阅者与发布者连接的协议。
swift 代码解读复制代码public protocol Subscription : Cancellable, CustomCombineIdentifierConvertible {
/// Tells a publisher that it may send more values to the subscriber.
func request(_ demand: Subscribers.Demand)
}
Publisher 和 Subscriber 之间是通过 Subscription 连接起来的。每当 Subscriber 订阅 Publisher 时,都会创建一个 Subscription 对象。
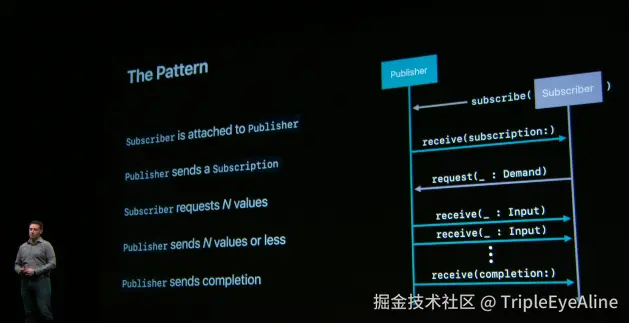
根据这张 WWDC2019 年 Introducing Combine 的视频截图,大概简单写下 Combine 的订阅过程:
- 发起订阅:
Subscriber告诉Publisher它需要一个订阅。 - 返回订阅实体:
Publisher返给Subscriber一个Subscription对象。 - 请求数据:
Subscriber通过Subscription请求一定数量的数据。 - 发送事件:
Publisher根据Demand发送数据或错误事件。如果Subscriber继续请求,Publisher会继续发布。(Demand是用以控制发送速率的) - 完成订阅:当所有请求的事件都已发送,
Publisher会发送一个Completion。
Subscription 的生命周期
swift 代码解读复制代码import Combine
import Foundation
class SimpleSubscriber: Subscriber {
typealias Input = Int
typealias Failure = Never
// 2. 接收订阅
func receive(subscription: Subscription) {
print("🔵 第二步:收到订阅")
subscription.request(.max(1))
}
// 3. 接收值
func receive(_ input: Int) -> Subscribers.Demand {
print("🟢 第三步:收到值: \(input)")
// 继续请求一个值
return .max(1)
}
// 4. 接收完成
func receive(completion: Subscribers.Completion<Never>) {
print("🔴 第四步:订阅完成")
}
}
// 展示订阅生命周期
func showSubscriptionLifecycle() {
let publisher = [1, 2, 3].publisher
let subscriber = SimpleSubscriber()
// 1. 建立订阅关系
print("⚪️ 第一步:开始订阅")
publisher.subscribe(subscriber)
}
showSubscriptionLifecycle()
/* 输出:
⚪️ 第一步:开始订阅
🔵 第二步:收到订阅
🟢 第三步:收到值: 1
🟢 第三步:收到值: 2
🟢 第三步:收到值: 3
🔴 第四步:订阅完成
*/
订阅者 (Subscriber)
A protocol that declares a type that can receive input from a publisher.
一种定义了能够接收来自发布者输入类型的协议。
相当于观察者模式中的 Observer 。在 Combine 框架中,Subscriber 定义了如何接收 Publisher 发出的值。
swift 代码解读复制代码public protocol Subscriber<Input, Failure> : CustomCombineIdentifierConvertible {
/// The kind of values this subscriber receives.
associatedtype Input
/// The kind of errors this subscriber might receive.
///
/// Use `Never` if this `Subscriber` cannot receive errors.
associatedtype Failure : Error
/// Tells the subscriber that it has successfully subscribed to the publisher and may request items.
/// 通知订阅者它已成功订阅到发布者并且可以请求项目。
/// Use the received ``Subscription`` to request items from the publisher.
/// - Parameter subscription: A subscription that represents the connection between publisher and subscriber.
func receive(subscription: any Subscription)
/// Tells the subscriber that the publisher has produced an element.
/// 告诉订阅者发布者已经发布了一个元素
/// - Parameter input: The published element.
/// - Returns: A `Subscribers.Demand` instance indicating how many more elements the subscriber expects to receive.
func receive(_ input: Self.Input) -> Subscribers.Demand
/// Tells the subscriber that the publisher has completed publishing, either normally or with an error. 告诉订阅者发布者已经结束了发布,可能是正常结束,也可能是因为发生了错误。
///
/// - Parameter completion: A ``Subscribers/Completion`` case indicating whether publishing completed normally or with an error.
func receive(completion: Subscribers.Completion<Self.Failure>)
}
-
它接受两个泛型参数:
Input类型,代表它能够接收的值的类型Failure类型,代表它能够接收的错误类型。
-
Publisher协议有两个泛型参数:Output代表它发出的值的类型,Failure代表它可能发出的错误类型。Publisher和Subscriber类型参数需要一一对应匹配。 -
在 Combine 中,连接
Publisher和Subscriber的桥梁是Subscription。使用sink方法和assign(to:)方法时,Combine 框架会自动创建一个Subscription来连接两者。 -
Subscriber通过遵循Cancellable协议支持取消操作swift代码解读复制代码import Combine import Dispatch import Foundation // 定时发布者每秒发送一个数字 let publisher = Timer.publish(every: 1.0, on: .main, in: .common) .autoconnect() // 存订阅 var cancellable: AnyCancellable? // 创建订阅 cancellable = publisher .sink { value in print("收到 value:\(value)") } // 3秒后取消订阅 DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 3) { print("取消订阅") cancellable?.cancel() // 取消订阅 } /* 收到 value:2024-12-17 07:43:23 +0000 收到 value:2024-12-17 07:43:24 +0000 收到 value:2024-12-17 07:43:25 +0000 取消订阅 */
Combine 框架内置了两种 Subscriber:
-
sink:是一个很灵活的Subscriber,通过闭包处理接收到的值和完成事件。有两种方法:-
swift代码解读复制代码
/// This method creates the subscriber and immediately requests an unlimited number of values, prior to returning the subscriber.此方法创建订阅者并立即请求无限数量的值,然后返回订阅者。 /// The return value should be held, otherwise the stream will be canceled.返回值必须被持有,否则数据流会被取消。 /// /// - parameter receiveComplete: The closure to execute on completion. /// - parameter receiveValue: The closure to execute on receipt of a value. /// - Returns: A cancellable instance, which you use when you end assignment of the received value. Deallocation of the result will tear down the subscription stream.一个可取消的实例,用于结束接收值的订阅。当此结果被释放时,订阅流会被清理。 public func sink(receiveCompletion: @escaping ((Subscribers.Completion<Self.Failure>) -> Void), receiveValue: @escaping ((Self.Output) -> Void)) -> AnyCancellableswift代码解读复制代码import Combine let publisher = [1, 2, 3].publisher let cancellable = publisher.sink { completion in switch(completion) { case .finished: print("发布完成") case .failure(let error): print("出错: \(error)") } } receiveValue: { value in print("接收到值: \(value)") } /* 接收到值: 1 接收到值: 2 接收到值: 3 发布完成 */ -
swift代码解读复制代码
/// This method creates the subscriber and immediately requests an unlimited number of values, prior to returning the subscriber.此方法创建订阅者并立即请求无限数量的值,然后返回订阅者。 /// The return value should be held, otherwise the stream will be canceled.返回值必须被持有,否则数据流会被取消。 /// /// - parameter receiveValue: The closure to execute on receipt of a value. /// - Returns: A cancellable instance, which you use when you end assignment of the received value. Deallocation of the result will tear down the subscription stream.Returns: 一个可取消的实例,用于结束接收值的订阅。当此结果被释放时,订阅流会被清理。 public func sink(receiveValue: @escaping ((Self.Output) -> Void)) -> AnyCancellableswift代码解读复制代码.sink { value in print("received value: \(String(describing: value))") }
-
-
assign:是一个特殊的Subscriber。它将接收到的值赋值给一个属性,通常用于将Publisher的输出绑定到 UI 元素或其他属性上。assign支持通过KeyPath直接进行赋值。-
assign(to:on:)swift代码解读复制代码/// Assigns each element from a publisher to a property on an object. public func assign<Root>(to keyPath: ReferenceWritableKeyPath<Root, Self.Output>, on object: Root) -> AnyCancellable小例子:
swift代码解读复制代码import Combine import Foundation class User { var name: String = "" { didSet { print("User's name is: \(name)") } } } let user = User() // 发布者发布一个字符串 terence let publisher = Just("terence") // 使用 assign 订阅发布者,将发布的值赋值给 user 的 name 属性 let cancellable = publisher .assign(to: \.name, on: user) //"User's name is: terence" -
assign(to:),此方法是assign(to:on:)的一个变体。语法somePublisher.assign(to: &object.$property)。使用&是因为此方法需要一个inout参数。这个方法专门用于 @Published 属性,且会自动管理订阅的生命周期,在发布者发送完成或失败信号时会自动取消订阅。swift代码解读复制代码/// Republishes elements received from a publisher, by assigning them to a property marked as a publisher. /// /// Use this operator when you want to receive elements from a publisher and republish them through a property marked with the `@Published` attribute. The `assign(to:)` operator manages the life cycle of the subscription, canceling the subscription automatically when the ``Published`` instance deinitializes. Because of this, the `assign(to:)` operator doesn't return an ``AnyCancellable`` that you're responsible for like ``assign(to:on:)`` does. public func assign(to published: inout Published<Self.Output>.Publisher)小例子:
swift代码解读复制代码import Combine import Foundation class User { @Published var name: String = "" { didSet { print("From didSet user's name is: \(name)") } } } let user = User() var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>() let publisher = Just("terence") publisher.assign(to: &user.$name) // 这里不会触发 didSet print("User's name value after assign(to:): \(user.name)") Just("maple") .sink { value in user.name = value // 这里会触发 didSet } .store(in: &cancellables) /* User's name value after assign(to:): terence From didSet user's name is: maple */
@Published属性包装器:- 当属性被
@Published修饰时,属性除了可作常规属性访问使用外,Combine 会自动为该属性创建一个publisher。可以通过在属性名前加$符号来访问这个publisher。
AnyCancellable:- 订阅操作返回一个
AnyCancellable对象本质上是一个“取消订阅”的句柄。通过持有这个句柄,可以随时手动取消订阅,以停止接收后续的事件。 - 遵循
Cancellable协议 - 在
deinit时自动调用cancel() - 可以手动调用
cancel()取消订阅 - 每一个订阅都需要持有这个
AnyCancellable对象,不然在当前作用域结束时,就会被释放。
避免循环引用:
-
使用
assign(to:)而不是assign(to:on:)可以避免潜在的引用循环。-
比如
assign(to:on:)生成的AnyCancellable如果被类实例持有,而AnyCancellable也对类实例引用,循环引用。swift代码解读复制代码// 可能导致循环引用的示例 class MyModel { var cancellable: AnyCancellable? var value: Int = 0 init() { Timer.publish(every: 1, on: .main, in: .common) .autoconnect() .assign(to: \.value, on: self) // self 被强引用 .store(in: &cancellable) // cancellable 又被 self 持有 } }
-
-
assign(to:)不返回AnyCancellable,订阅会随对象释放自动取消。 -
当
@Published修饰的属性所在的对象被释放时,订阅会自动取消。
-
结语
订阅者(Subscriber)是 Combine 框架中核心部分,它负责接收和处理发布者发送的数据。通过学习订阅者的工作原理和使用方法,能够更高效地管理数据流动。在下一篇文章中会开始继续介绍操作符(operator),并基本都配上可运行的代码示例帮助理解。

评论记录:
回复评论: