之前的博客有限状态机与UCOS任务调度器介绍了状态机实现、多任务并行机制、任务调度原理、线程管理等,本文主要从RT-Thread与UCOS的对比与差异看RT-Thread线程调度器与线程对象管理的实现。
一、线程对象管理
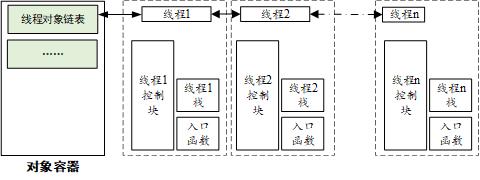
RT-Thread 线程管理的主要功能是对线程进行管理和调度,系统中总共存在两类线程,分别是系统线程和用户线程,系统线程是由 RT-Thread 内核创建的线程,用户线程是由应用程序创建的线程,这两类线程都会从内核对象容器中分配线程对象,当线程被删除时,也会被从对象容器中删除,每个线程都有重要的属性,如线程控制块、线程栈、入口函数等,RT-Thread线程对象管理链表如下图所示:
RT-Thread 的线程调度器是抢占式的,主要的工作就是从就绪线程列表中查找最高优先级线程,保证最高优先级的线程能够被运行,最高优先级的任务一旦就绪,总能得到 CPU 的使用权。
当一个运行着的线程使一个比它优先级高的线程满足运行条件,当前线程的 CPU 使用权就被剥夺了,或者说被让出了,高优先级的线程立刻得到了 CPU 的使用权。
如果是中断服务程序使一个高优先级的线程满足运行条件,中断完成时,被中断的线程挂起,优先级高的线程开始运行。
当调度器调度线程切换时,先将当前线程上下文保存起来,当再切回到这个线程时,线程调度器将该线程的上下文信息恢复。
1.1 线程状态切换
线程运行的过程中,同一时间内只允许一个线程在处理器中运行,从运行的过程上划分,线程有多种不同的运行状态,如初始状态、挂起状态、就绪状态等。在 RT-Thread 中,线程包含五种状态,操作系统会自动根据它运行的情况来动态调整它的状态。 RT-Thread 提供一系列的操作系统调用接口,使得线程的状态在这五个状态之间来回切换。几种状态间的转换关系如下图所示:
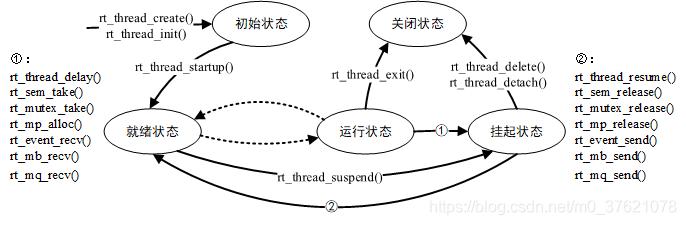
线程通过调用函数 rt_thread_create/init() 进入到初始状态(RT_THREAD_INIT);初始状态的线程通过调用函数 rt_thread_startup() 进入到就绪状态(RT_THREAD_READY);就绪状态的线程被调度器调度后进入运行状态(RT_THREAD_RUNNING);当处于运行状态的线程调用 rt_thread_delay(),rt_sem_take(),rt_mutex_take(),rt_mb_recv() 等函数或者获取不到资源时,将进入到挂起状态(RT_THREAD_SUSPEND);处于挂起状态的线程,如果等待超时依然未能获得资源或由于其他线程释放了资源,那么它将返回到就绪状态。挂起状态的线程,如果调用 rt_thread_delete/detach() 函数,将更改为关闭状态(RT_THREAD_CLOSE);而运行状态的线程,如果运行结束,就会在线程的最后部分执行 rt_thread_exit() 函数,将状态更改为关闭状态。五种状态的宏定义如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\include\rtdef.h
/*
* thread state definitions
*/
#define RT_THREAD_INIT 0x00 /**< Initialized status */
#define RT_THREAD_READY 0x01 /**< Ready status */
#define RT_THREAD_SUSPEND 0x02 /**< Suspend status */
#define RT_THREAD_RUNNING 0x03 /**< Running status */
#define RT_THREAD_BLOCK RT_THREAD_SUSPEND /**< Blocked status */
#define RT_THREAD_CLOSE 0x04 /**< Closed status */
#define RT_THREAD_STAT_MASK 0x0f
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
1.2 线程控制块
在 RT-Thread 中,线程控制块由结构体 struct rt_thread 表示,线程控制块是操作系统用于管理线程的一个数据结构,它会存放线程的一些信息,例如优先级、线程名称、线程状态等,也包含线程与线程之间连接用的链表结构,线程等待事件集合等,详细定义如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\include\rtdef.h
/**
* Thread structure
*/
struct rt_thread
{
/* rt object */
char name[RT_NAME_MAX]; /**< the name of thread */
rt_uint8_t type; /**< type of object */
rt_uint8_t flags; /**< thread's flags */
#ifdef RT_USING_MODULE
void *module_id; /**< id of application module */
#endif
rt_list_t list; /**< the object list */
rt_list_t tlist; /**< the thread list */
/* stack point and entry */
void *sp; /**< stack point */
void *entry; /**< entry */
void *parameter; /**< parameter */
void *stack_addr; /**< stack address */
rt_uint32_t stack_size; /**< stack size */
/* error code */
rt_err_t error; /**< error code */
rt_uint8_t stat; /**< thread status */
#ifdef RT_USING_SMP
rt_uint8_t bind_cpu; /**< thread is bind to cpu */
rt_uint8_t oncpu; /**< process on cpu` */
rt_uint16_t scheduler_lock_nest; /**< scheduler lock count */
rt_uint16_t cpus_lock_nest; /**< cpus lock count */
#endif /*RT_USING_SMP*/
/* priority */
rt_uint8_t current_priority; /**< current priority */
rt_uint8_t init_priority; /**< initialized priority */
#if RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX > 32
rt_uint8_t number;
rt_uint8_t high_mask;
#endif
rt_uint32_t number_mask;
#if defined(RT_USING_EVENT)
/* thread event */
rt_uint32_t event_set;
rt_uint8_t event_info;
#endif
#if defined(RT_USING_SIGNALS)
rt_sigset_t sig_pending; /**< the pending signals */
rt_sigset_t sig_mask; /**< the mask bits of signal */
#ifndef RT_USING_SMP
void *sig_ret; /**< the return stack pointer from signal */
#endif
rt_sighandler_t *sig_vectors; /**< vectors of signal handler */
void *si_list; /**< the signal infor list */
#endif
rt_ubase_t init_tick; /**< thread's initialized tick */
rt_ubase_t remaining_tick; /**< remaining tick */
struct rt_timer thread_timer; /**< built-in thread timer */
void (*cleanup)(struct rt_thread *tid); /**< cleanup function when thread exit */
/* light weight process if present */
#ifdef RT_USING_LWP
void *lwp;
#endif
rt_uint32_t user_data; /**< private user data beyond this thread */
};
typedef struct rt_thread *rt_thread_t;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
线程对象rt_thread前四个成员相当于继承自基对象rt_object:rt_thread.name保存线程名,rt_thread.type值为RT_Object_Class_Thread,rt_thread.flags未使用,rt_thread.list为已初始化/创建线程对象的链表节点(所有线程对象通过该节点组织成一个双向链表),此时的线程处于RT_THREAD_INIT初始状态。
线程列表rt_thread.tlist为处于就绪状态、参与调度线程的链表节点,所有已启动且处于RT_THREAD_READY就绪状态(参与线程调度)的线程通过该节点组织成一个双向链表。该链表保存在线程优先级链表数组rt_thread_priority_table[]内,像定时器链表以超时时间排序一样,就绪线程优先级链表则以线程的优先级排序,相关代码如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\scheduler.c
rt_list_t rt_thread_priority_table[RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX];
rt_uint32_t rt_thread_ready_priority_group;
#if RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX > 32
/* Maximum priority level, 256 */
rt_uint8_t rt_thread_ready_table[32];
#endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
栈指针rt_thread.sp,在前篇RT-Thread系统CPU架构移植时介绍过移植接口函数:堆栈初始化函数rt_hw_stack_init,堆栈初始化后返回的栈指针(即rt_hw_stack_init的返回值)便赋值给了rt_thread.sp。入口函数指针rt_thread.entry是用户要实现的线程主体函数指针,rt_thread.parameter便是入口函数的参数指针。线程栈地址指针rt_thread.stack_addr是用于保存线程上下文的线程栈首地址,rt_thread.stack_size是用户分配的线程栈大小。这些成员变量值都是在线程初始化/创建时用户要为线程定义的属性(即为线程构造函数传入的参数)。
线程状态rt_thread.stat在前面已经介绍过了,记录线程当前的状态,在线程状态变化时修改该状态值。线程错误代码rt_thread.error记录线程的错误类型,线程错误代码的宏定义如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\include\rtdef.h
/* RT-Thread error code definitions */
#define RT_EOK 0 /**< There is no error */
#define RT_ERROR 1 /**< A generic error happens */
#define RT_ETIMEOUT 2 /**< Timed out */
#define RT_EFULL 3 /**< The resource is full */
#define RT_EEMPTY 4 /**< The resource is empty */
#define RT_ENOMEM 5 /**< No memory */
#define RT_ENOSYS 6 /**< No system */
#define RT_EBUSY 7 /**< Busy */
#define RT_EIO 8 /**< IO error */
#define RT_EINTR 9 /**< Interrupted system call */
#define RT_EINVAL 10 /**< Invalid argument */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
被条件宏定义RT_USING_SMP(Symmetric multiprocessing)包含的成员是为多核心处理器准备的,对于我们的STM32L475单核处理器用不到这部分成员。单核处理器的线程调度比较简单,一次只有一个线程处于运行状态,只需要处理好线程间的同步与互斥即可;对称多核处理器除了线程间的互斥同步,还要考虑核心与核心间的互斥同步,目前处理多核心间互斥访问的主要方式是自旋锁(比如上面的cpus_lock_nest与scheduler_lock_nest),为了提高CPU高速缓存cache的命中率也支持线程与核心的绑定(比如上面的bind_cpu与oncpu)。
上面只展示了线程控制块,有一部分成员服务于SMP多核心线程调度,对于SMP多核心处理器,在CUP端也有相应的数据结构配合完成线程调度管理,比如下面的rt_cpu数据结构(每个线程控制块表示一个线程,每个CPU控制块则表示一个核心):
// rt-thread-4.0.1\include\rtdef.h
/**
* CPUs definitions
*/
struct rt_cpu
{
struct rt_thread *current_thread;
rt_uint16_t irq_nest;
rt_uint8_t irq_switch_flag;
rt_uint8_t current_priority;
rt_list_t priority_table[RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX];
#if RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX > 32
rt_uint32_t priority_group;
rt_uint8_t ready_table[32];
#else
rt_uint32_t priority_group;
#endif
rt_tick_t tick;
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
前面介绍线程链表节点rt_thread.tlist时,提到了保存就绪线程链表的优先级数组rt_thread_priority_table[]是全局变量,但对于多核心处理器,每个核心上都有一个线程优先级链表数组和线程就绪表,用于完成多线程在多核心处理器SMP上的调度管理。RT-Thread是从V4.0.0版本开始支持SMP线程调度的,虽然对底层处理器的调度逻辑跟单核心有区别,但提供给用户的线程管理接口函数完全一致。
线程优先级相关的成员:current_priority、init_priority、number_mask,分别表示线程的当前优先级、初始优先级、优先级掩码,线程优先级是可以动态修改的,所以提供了当前优先级和初始优先级两个成员,优先级掩码则是为了提高处理线程就绪表和优先级数组的速度为增加的成员(UCOS为此也增加了一些辅助成员,比如 OSTCBX / OSTCBY / OSTCBBitX / OSTCBBitY)。
线程条件宏RT_USING_EVENT包含的是与线程同步中的事件相关的成员,线程条件宏RT_USING_SIGNALS包含的是与线程通信中的信号相关的成员,这两部分放到后面介绍线程间同步与通信时再介绍。
线程时间片相关的成员:init_tick、remaining_tick,分别表示线程初始时间片与剩余时间片,系统对优先级相同的就绪态线程采用时间片轮转的调度方式进行调度时,时间片起到约束线程单次运行时长的作用,其单位是一个系统节拍(OS Tick)。每个系统节拍超时处理(函数SysTick_Handler)都会调用rt_tick_increase,在rt_tick_increase函数中会减少当前线程的remaining_tick值(详见博客RT-Thread时钟管理),当线程剩余时间片减至0时则会调用rt_thread_yield让出CPU使用权,重新调度。
线程延时、睡眠相关的成员:thread_timer,是一个定时器对象,当线程需要延时或睡眠时,启动单次触发定时器,定时器超时后调用超时处理函数将该线程重新插入就绪线程链表参与调度。
线程清理函数指针cleanup,线程退出后在空闲线程中被调用,以清理线程资源。轻量级线程指针lwp,轻量级线程LWP与普通线程相比只有一个最小的执行上下文和调度程序所需的统计信息,多个LWP之间可以共享它们的大部分资源。最后线程的私有数据user_data可根据用户需要来使用。
1.3 线程调度器接口函数
线程切换过程在前篇CPU架构移植时简单介绍过了,线程调度主要就是管理就绪态线程的优先级链表。每当有事件(有更高优先级线程就绪或当前线程时间片耗尽)或中断发生都会执行线程切换,线程切换过程便是从线程就绪表rt_thread_ready_table中找到就绪态线程的最高优先级highest_ready_priority,再根据最高优先级查询线程优先级链表数组rt_thread_priority_table[]找到最高优先级线程指针highest_priority_thread作为切换的目的线程。线程调度器的常用接口函数原型如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\scheduler.c
/**
* @ingroup SystemInit
* This function will initialize the system scheduler
*/
void rt_system_scheduler_init(void);
/**
* @ingroup SystemInit
* This function will startup scheduler. It will select one thread
* with the highest priority level, then switch to it.
*/
void rt_system_scheduler_start(void);
/**
* This function will perform one schedule. It will select one thread
* with the highest priority level, then switch to it.
*/
void rt_schedule(void);
/*
* This function will insert a thread to system ready queue. The state of
* thread will be set as READY and remove from suspend queue.
* @param thread the thread to be inserted
* @note Please do not invoke this function in user application.
*/
void rt_schedule_insert_thread(struct rt_thread *thread);
/*
* This function will remove a thread from system ready queue.
* @param thread the thread to be removed
* @note Please do not invoke this function in user application.
*/
void rt_schedule_remove_thread(struct rt_thread *thread);
/**
* This function will lock the thread scheduler.
*/
void rt_enter_critical(void);
/**
* This function will unlock the thread scheduler.
*/
void rt_exit_critical(void);
/**
* Get the scheduler lock level
* @return the level of the scheduler lock. 0 means unlocked.
*/
rt_uint16_t rt_critical_level(void);
/**
* This function will set a hook function, which will be invoked when thread
* switch happens.
*
* @param hook the hook function
*/
void rt_scheduler_sethook(void (*hook)(struct rt_thread *from, struct rt_thread *to));
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
前两个函数rt_system_scheduler_init与rt_system_scheduler_start在系统启动函数rtthread_startup中被调用;rt_schedule则在需要线程调度的地方都会被调用,一般由系统内核函数调用;接下来的两个函数rt_schedule_insert_thread与rt_schedule_remove_thread主要是将当前线程rt_thread.tlist插入就绪态线程链表(以优先级高低顺序插入)或从就绪态线程链表中移除;最后三个函数rt_enter_critical、rt_exit_critical、rt_critical_level用于临界区管理,主要管理调度嵌套锁全局变量rt_scheduler_lock_nest,类似于介绍中断时,通过rt_interrupt_enter、rt_interrupt_leave、rt_interrupt_get_nest管理中断嵌套全局变量rt_interrupt_nest。
在线程调度时也可以通过函数rt_scheduler_sethook设置钩子函数,可以在线程切换时做一些额外的动作或者观察某一时刻调度的源线程与目的线程,但在这个钩子函数中,基本上不允许调用系统 API,更不应该导致当前运行的上下文挂起。
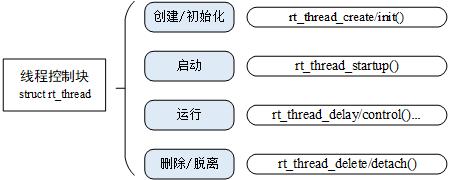
1.4 线程对象接口函数
下图描述了线程的相关操作,包含:创建 / 初始化线程、启动线程、运行线程、删除 / 脱离线程。可以使用 rt_thread_create() 创建一个动态线程,使用 rt_thread_init() 初始化一个静态线程,动态线程与静态线程的区别是:动态线程是系统自动从动态内存堆上分配栈空间与线程句柄(初始化 heap 之后才能使用 create 创建动态线程),静态线程是由用户分配栈空间与线程句柄。
线程的构造/析构函数也分为两部分:一部分是继承基对象rt_object的构造/析构;另一部分是线程私有成员的构造/析构。这个过程在定时器对象管理中介绍过,下面给出线程构造/析构函数原型:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will create a thread object and allocate thread object memory
* and stack.
*
* @param name the name of thread, which shall be unique
* @param entry the entry function of thread
* @param parameter the parameter of thread enter function
* @param stack_size the size of thread stack
* @param priority the priority of thread
* @param tick the time slice if there are same priority thread
*
* @return the created thread object
*/
rt_thread_t rt_thread_create(const char *name,
void (*entry)(void *parameter),
void *parameter,
rt_uint32_t stack_size,
rt_uint8_t priority,
rt_uint32_t tick);
/**
* This function will delete a thread. The thread object will be removed from
* thread queue and deleted from system object management in the idle thread.
*
* @param thread the thread to be deleted
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_delete(rt_thread_t thread);
/**
* This function will initialize a thread, normally it's used to initialize a
* static thread object.
*
* @param thread the static thread object
* @param name the name of thread, which shall be unique
* @param entry the entry function of thread
* @param parameter the parameter of thread enter function
* @param stack_start the start address of thread stack
* @param stack_size the size of thread stack
* @param priority the priority of thread
* @param tick the time slice if there are same priority thread
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_init(struct rt_thread *thread,
const char *name,
void (*entry)(void *parameter),
void *parameter,
void *stack_start,
rt_uint32_t stack_size,
rt_uint8_t priority,
rt_uint32_t tick);
/**
* This function will detach a thread. The thread object will be removed from
* thread queue and detached/deleted from system object management.
*
* @param thread the thread to be deleted
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_detach(rt_thread_t thread);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
线程的静态创建与动态创建的区别与基对象rt_object类似,两种创建方式对接口函数传入的参数也有些许区别,且构造/析构函数需要成对使用,这是需要用户注意的地方。
创建(初始化)的线程状态处于初始状态,并未进入就绪线程的调度队列,我们可以在线程初始化 / 创建成功后调用下面的函数接口让该线程进入就绪态:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will start a thread and put it to system ready queue
*
* @param thread the thread to be started
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_startup(rt_thread_t thread);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
在实际应用中,我们有时需要让运行的当前线程延迟一段时间,在指定的时间到达后重新运行(通过调用超时回调函数rt_thread_timeout),这就叫做 “线程睡眠”。线程睡眠可使用以下三个函数接口(最后一个是线程睡眠超时唤醒函数):
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will let current thread sleep for some ticks.
*
* @param tick the sleep ticks
*
* @return RT_EOK
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_sleep(rt_tick_t tick);
/**
* This function will let current thread delay for some ticks.
*
* @param tick the delay ticks
*
* @return RT_EOK
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_delay(rt_tick_t tick);
/**
* This function will let current thread delay for some milliseconds.
*
* @param tick the delay time
*
* @return RT_EOK
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_mdelay(rt_int32_t ms);
/**
* This function is the timeout function for thread, normally which is invoked
* when thread is timeout to wait some resource.
*
* @param parameter the parameter of thread timeout function
*/
void rt_thread_timeout(void *parameter);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
当线程调用 rt_thread_delay() 时,线程将主动挂起;当调用 rt_sem_take(),rt_mb_recv() 等函数时,资源不可使用也将导致线程挂起。处于挂起状态的线程,如果其等待的资源超时(超过其设定的等待时间),那么该线程将不再等待这些资源,并返回到就绪状态;或者,当其他线程释放掉该线程所等待的资源时,该线程也会返回到就绪状态。线程的挂起和恢复接口函数原型如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will suspend the specified thread.
*
* @param thread the thread to be suspended
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*
* @note if suspend self thread, after this function call, the
* rt_schedule() must be invoked.
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_suspend(rt_thread_t thread);
/**
* This function will resume a thread and put it to system ready queue.
*
* @param thread the thread to be resumed
*
* @return the operation status, RT_EOK on OK, -RT_ERROR on error
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_resume(rt_thread_t thread);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
当需要对线程进行一些其他控制时,例如动态更改线程的优先级,可以调用如下函数接口:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will control thread behaviors according to control command.
*
* @param thread the specified thread to be controlled
* @param cmd the control command, which includes
* RT_THREAD_CTRL_CHANGE_PRIORITY for changing priority level of thread;
* RT_THREAD_CTRL_STARTUP for starting a thread;
* RT_THREAD_CTRL_CLOSE for delete a thread;
* RT_THREAD_CTRL_BIND_CPU for bind the thread to a CPU.
* @param arg the argument of control command
*
* @return RT_EOK
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_control(rt_thread_t thread, int cmd, void *arg);
// rt-thread-4.0.1\include\rtdef.h
/**
* thread control command definitions
*/
#define RT_THREAD_CTRL_STARTUP 0x00 /**< Startup thread. */
#define RT_THREAD_CTRL_CLOSE 0x01 /**< Close thread. */
#define RT_THREAD_CTRL_CHANGE_PRIORITY 0x02 /**< Change thread priority. */
#define RT_THREAD_CTRL_INFO 0x03 /**< Get thread information. */
#define RT_THREAD_CTRL_BIND_CPU 0x04 /**< Set thread bind cpu. */
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
在程序的运行过程中,相同的一段代码可能会被多个线程执行,在执行的时候可以通过rt_thread_self获得当前执行的线程句柄,也可以通过rt_thread_find获得指定线程名对应的线程句柄,两个函数的原型如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will return self thread object
*
* @return the self thread object
*/
rt_thread_t rt_thread_self(void);
/**
* This function will find the specified thread.
*
* @param name the name of thread finding
*
* @return the found thread
*
* @note please don't invoke this function in interrupt status.
*/
rt_thread_t rt_thread_find(char *name);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
当前线程的时间片用完或者该线程主动要求让出处理器资源时,它将不再占有处理器,调度器会选择相同优先级的下一个线程执行。线程调用这个接口后,这个线程仍然在就绪队列中。如果想直接结束当前线程,可以调用函数rt_thread_exit,将当前线程状态切换为RT_THREAD_CLOSE,并释放该线程资源,rt_thread_exit跟线程析构函数功能类似,但可以不区分当前线程是动态对象还是静态对象。这两个函数的原型如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* This function will let current thread yield processor, and scheduler will
* choose a highest thread to run. After yield processor, the current thread
* is still in READY state.
*
* @return RT_EOK
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_yield(void);
void rt_thread_exit(void);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
线程也支持钩子函数,下面先介绍设置初始化、挂起、恢复线程钩子函数的原型如下(空闲线程钩子函数等会儿在介绍空闲线程时再给出):
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\thread.c
/**
* @ingroup Hook
* This function sets a hook function when a thread is initialized.
*
* @param hook the specified hook function
*/
void rt_thread_inited_sethook(void (*hook)(rt_thread_t thread));
/**
* @ingroup Hook
* This function sets a hook function when the system suspend a thread.
*
* @param hook the specified hook function
*
* @note the hook function must be simple and never be blocked or suspend.
*/
void rt_thread_suspend_sethook(void (*hook)(rt_thread_t thread));
/**
* @ingroup Hook
* This function sets a hook function when the system resume a thread.
* * @param hook the specified hook function
* * @note the hook function must be simple and never be blocked or suspend.
*/
void rt_thread_resume_sethook(void (*hook)(rt_thread_t thread));
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
1.5 常用系统线程
系统线程是指由系统创建的线程,用户线程是由用户程序调用线程管理接口创建的线程,在 RT-Thread 内核中的系统线程有空闲线程和主线程。
- 主线程
在系统启动时,系统会创建 main 线程,它的入口函数为 main_thread_entry(),用户的应用入口函数 main() 就是从这里真正开始的,系统调度器启动后,main 线程就开始运行,用户可以在 main() 函数里添加自己的应用程序初始化代码,过程如下图(在博客RT-Thread系统启动与初始化中介绍过):

- 空闲线程
空闲线程是系统创建的最低优先级的线程,线程状态永远为就绪态。当系统中无其他就绪线程存在时,调度器将调度到空闲线程,它通常是一个死循环,且永远不能被挂起。另外,空闲线程在 RT-Thread 也有着它的特殊用途:
若某线程运行完毕,系统将自动删除线程:自动执行 rt_thread_exit() 函数,先将该线程从系统就绪队列中删除,再将该线程的状态更改为关闭状态,不再参与系统调度,然后挂入 rt_thread_defunct 僵尸队列(资源未回收、处于关闭状态的线程队列)中,最后空闲线程会回收被删除线程的资源。
空闲线程也提供了接口来运行用户设置的钩子函数,在空闲线程运行时会调用该钩子函数,适合钩入功耗管理、看门狗喂狗等工作。设置、删除空闲线程钩子函数的原型如下:
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\idle.c
/**
* @ingroup Hook
* This function sets a hook function to idle thread loop. When the system performs
* idle loop, this hook function should be invoked.
*
* @param hook the specified hook function
*
* @return RT_EOK: set OK
* -RT_EFULL: hook list is full
*
* @note the hook function must be simple and never be blocked or suspend.
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_idle_sethook(void (*hook)(void));
/**
* delete the idle hook on hook list
*
* @param hook the specified hook function
*
* @return RT_EOK: delete OK
* -RT_ENOSYS: hook was not found
*/
rt_err_t rt_thread_idle_delhook(void (*hook)(void));
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
空闲线程的初始化由系统同样由系统启动函数rtthread_startup调用,空闲线程初始化代码如下(空闲线程初始化后直接启动):
// rt-thread-4.0.1\src\idle.c
static void (*idle_hook_list[RT_IDEL_HOOK_LIST_SIZE])();
/**
* @ingroup SystemInit
*
* This function will initialize idle thread, then start it.
*
* @note this function must be invoked when system init.
*/
void rt_thread_idle_init(void)
{
rt_ubase_t i;
char tidle_name[RT_NAME_MAX];
for (i = 0; i < _CPUS_NR; i++)
{
rt_sprintf(tidle_name, "tidle%d", i);
rt_thread_init(&idle[i],
tidle_name,
rt_thread_idle_entry,
RT_NULL,
&rt_thread_stack[i][0],
sizeof(rt_thread_stack[i]),
RT_THREAD_PRIORITY_MAX - 1,
32);
#ifdef RT_USING_SMP
rt_thread_control(&idle[i], RT_THREAD_CTRL_BIND_CPU, (void*)i);
#endif
/* startup */
rt_thread_startup(&idle[i]);
}
}
static void rt_thread_idle_entry(void *parameter)
{
......
while (1)
{
#ifdef RT_USING_IDLE_HOOK
rt_size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < RT_IDEL_HOOK_LIST_SIZE; i++)
{
if (idle_hook_list[i] != RT_NULL)
{
idle_hook_list[i]();
}
}
#endif
rt_thread_idle_excute();
#ifdef RT_USING_PM
rt_system_power_manager();
#endif
}
}
/**
* @ingroup Thread
* This function will perform system background job when system idle.
*/
void rt_thread_idle_excute(void)
{
......
/* invoke thread cleanup */
if (thread->cleanup != RT_NULL)
thread->cleanup(thread);
........
}
/**
* @ingroup Thread
* This function will get the handler of the idle thread.
*/
rt_thread_t rt_thread_idle_gethandler(void);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
二、线程对象管理示例
下面创建一个动态线程,初始化一个静态线程,两个线程共用入口函数但传入不同的参数,使用相同的优先级但使用不同的时间片,达到特定的条件后挂起指定的线程并延时另外的线程,最后线程运行完毕被系统自动删除。
调用打印函数时,由于涉及到uart串口通讯,速度相对慢些,会出现两个线程打印的字符串相互错位的情况,为了解决字符串错位问题,使用了调度锁机制,通过rt_enter_critical与rt_exit_critical保证在执行临界区内代码时,线程不会被调度切换。
在目录projects\stm32l475_kernel_sample\applications下新建文件thread_sample.c,并在thread_sample.c文件中编辑该示例的实现代码如下:
// projects\stm32l475_kernel_sample\applications\thread_sample.c
#include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
在ENV中运行scons --target=mdk5命令编译生成Keil MDK V5工程代码,并用MDK打开工程文件,编译无错误,烧录到我们的STM32L475潘多拉开发板内,运行结果如下:
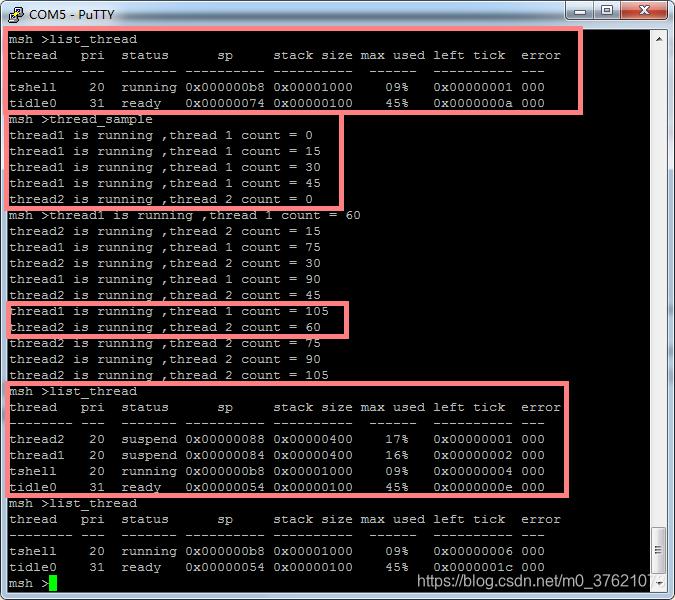
由于thread1的时间片比thread2的时间片更长,两个线程在优先级相同的情况下按时间片轮转调度算法进行线程调度,所以thread1的计数增长速度比thread2更快,也更先执行完相同的任务(计数增加到105的任务)。
通过finsh提高的系统命令list_thread查看运行自定义导出命令thread_sample前后的线程情况,系统正常运行只有tshell和tidle0两个系统线程,运行thread_sample后新增了两个线程thread1和thread2。而且两个线程的最大堆栈利用率仅17%,说明我们为这两个线程分配的堆栈空间过多了,如果内存空间不是很充裕,可以减少为其分配的空间大小,这也为我们提供了一个为创建线程合理分配堆栈空间的方法。
我们在线程入口函数thread_entry中设置了延时结束后返回的代码,延时结束后再通过list_thread命令查看线程,发现我们创建的两个线程thread1和thread2已经被删除了,RT-Thread系统会在线程运行完毕后自动删除该线程,在 rt_thread_exit() 里完成删除动作。
如果想看看我们创建的两个线程thread1和thread2被系统自动删除并切换到空闲线程的过程,可以设置一个调度器钩子,在文件thread_sample.c中新增如下代码:
// projects\stm32l475_kernel_sample\applications\thread_sample.c
static void hook_of_scheduler(struct rt_thread* from, struct rt_thread* to)
{
if(from == tid1 || from == &thread2)
rt_kprintf("scheduler from: %s --> to: %s. \n", from->name , to->name);
}
static int thread_sample(void)
{
/* 设置调度器钩子 */
rt_scheduler_sethook(hook_of_scheduler);
......
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
上面的代码在调度器中设置了一个钩子,在调度器发生任务切换时会打印出源线程from和目的线程to,重新编译烧录程序到开发板中,运行结果如下:
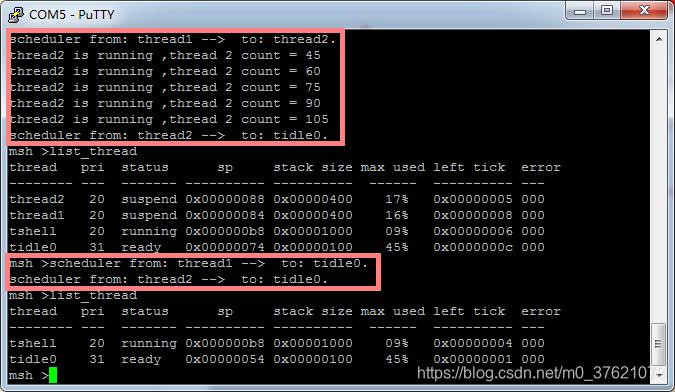
从上图执行结果可以看出,thread1时间片用完后切换到thread2,后面thread1挂起待thread2时间片用完后切换到空闲线程tidle0,两个函数延时后均返回,返回后两个线程都切换到空闲线程tidle0,而后两个线程均被系统自动删除,list_thread已看不到两线程资源。
该工程的实现代码下载地址:https://github.com/StreamAI/RT-Thread_Projects/tree/master/projects/stm32l475_kernel_sample


评论记录:
回复评论: