【华为OD-E卷 - 计算网络信号 100分(python、java、c++、js、c)】
题目
网络信号经过传递会逐层衰减,且遇到阻隔物无法直接穿透,在此情况下需要计算某个位置的网络信号值。注意:网络信号可以绕过阻隔物。
array[m][n] 的二维数组代表网格地图, array[i][j] = 0代表i行j列是空旷位置; array[i][j] = x(x为正整数)代表i行j列是信号源,信号强度是x; array[i][j] = -1代表i行j列是阻隔物。 信号源只有1个,阻隔物可能有0个或多个 网络信号衰减是上下左右相邻的网格衰减1 现要求输出对应位置的网络信号值。
输入描述
- 输入为三行,
第一行为 m 、n ,代表输入是一个 m × n 的数组。 第二行是一串 m × n 个用空格分隔的整数。每连续 n 个数代表一行,再往后 n 个代表下一行,以此类推。对应的值代表对应的网格是空旷位置,还是信号源,还是阻隔物。 第三行是 i 、 j,代表需要计算array[i][j]的网络信号值。 注意:此处 i 和 j 均从 0 开始,即第一行 i 为 0。
例如
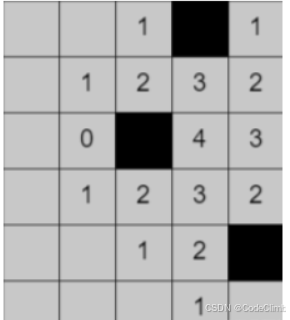
6 5 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 1 4 代表如下地图

需要输出第1行第4列的网络信号值,如下图,值为2。
输出描述
- 输出对应位置的网络信号值,如果网络信号未覆盖到,也输出0。
一个网格如果可以途径不同的传播衰减路径传达,取较大的值作为其信号值
用例
用例一:
输入:
6 5
0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0
1 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
输出:
2
- 1
用例二:
输入:
6 5
0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
输出:
0
- 1
python解法
- 解题思路:
更新中
- 1
java解法
- 解题思路
- 问题描述
给定一个二维网格,每个位置可能为以下几种情况:
0 表示无信号覆盖区域。
正整数表示信号源,数值越大,信号越强。
信号可以向上下左右传播,且每传播一步信号减弱 1。传播到信号值为 0 时停止。需要确定目标位置的信号强度。
算法设计
使用 广度优先搜索(BFS) 算法模拟信号传播的过程:
遍历网格,找到所有信号源,将其加入 BFS 队列。
从队列中取出信号源,向其上下左右的方向传播信号,直到信号减弱为 0。
最终得到目标位置的信号强度。
输入输出格式
输入:网格大小 m x n,信号源及其强度,以及目标位置的坐标。
输出:目标位置的信号强度。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 读取网格的行数和列数
int m = input.nextInt();
int n = input.nextInt();
// 初始化网格
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
// BFS 队列,用于处理信号传播
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 定义信号源的初始坐标
int signalX = -1, signalY = -1;
// 读取网格数据,找到所有信号源并将其加入队列
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = input.nextInt();
if (grid[i][j] > 0) { // 发现信号源
signalX = i;
signalY = j;
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j, grid[i][j]}); // 将信号源加入队列
}
}
}
// 读取目标位置
int targetX = input.nextInt();
int targetY = input.nextInt();
// 调用 BFS 方法,计算目标位置的信号强度
System.out.println(bfs(grid, m, n, queue, targetX, targetY));
}
/**
* 广度优先搜索 (BFS) 计算目标位置的信号强度
*
* @param grid 网格表示信号传播区域
* @param m 网格的行数
* @param n 网格的列数
* @param queue 信号源队列
* @param targetX 目标位置的行坐标
* @param targetY 目标位置的列坐标
* @return 目标位置的信号强度
*/
public static int bfs(int[][] grid, int m, int n, Queue<int[]> queue, int targetX, int targetY) {
// 定义四个方向的移动向量(上、下、左、右)
int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
// 开始 BFS 遍历
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 从队列中取出当前信号源
int[] current = queue.poll();
int x = current[0], y = current[1], signal = current[2];
// 遍历四个方向
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int newX = x + dir[0]; // 新的行坐标
int newY = y + dir[1]; // 新的列坐标
// 检查新位置是否在网格范围内且未被覆盖
if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < n && grid[newX][newY] == 0) {
// 更新新位置的信号强度
grid[newX][newY] = signal - 1;
// 如果信号强度仍大于 0,则将其加入队列继续传播
if (signal - 1 > 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY, signal - 1});
}
}
}
}
// 返回目标位置的信号强度
return grid[targetX][targetY];
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
C++解法
- 解题思路
使用 广度优先搜索(BFS) 模拟信号传播:
找到所有信号源,初始化 BFS 队列。
从信号源开始,依次向上下左右传播信号,更新网格中各位置的信号强度。
如果信号传播到目标位置 (tx, ty),记录其信号值。
由于 BFS 会按照距离由近及远的顺序进行遍历,保证每个位置的信号强度为其最强值。
#include - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
C解法
-
解题思路
-
采用 广度优先搜索(BFS) 模拟信号的传播过程:
初始化信号源队列 sources,将所有信号源的位置加入队列。
遍历队列中的每个信号源,向其上下左右的方向传播信号:
若某位置信号值尚未覆盖(为 0),则更新该位置信号值为 当前信号 - 1;
若更新后的信号值仍大于 0,将该位置加入队列以继续传播。
循环直至所有信号源的传播结束。
- 1
JS解法
给定一个二维网格,包含以下类型的值:
0 表示无信号区域;
正整数表示信号源,其值越大,信号强度越高。
信号可以向上下左右传播,每传播一步信号值减 1,直至信号值为 0 时停止传播。
输入目标位置 (tx, ty),输出该位置的信号强度。
算法设计
采用 广度优先搜索(BFS) 模拟信号的传播过程:
初始化信号源队列 sources,将所有信号源的位置加入队列。
遍历队列中的每个信号源,向其上下左右的方向传播信号:
若某位置信号值尚未覆盖(为 0),则更新该位置信号值为 当前信号 - 1;
若更新后的信号值仍大于 0,将该位置加入队列以继续传播。
循环直至所有信号源的传播结束。
输入输出格式
输入:
第一行:网格的行数 m 和列数 n;
第二行:一维数组表示网格中的信号值;
第三行:目标位置 (tx, ty)。
输出:目标位置的信号强度。
流程
将一维数组转为二维网格;
将所有信号源记录为队列的初始状态;
使用 BFS 模拟信号传播过程;
输出目标位置的信号值
const readline = require('readline');
// 创建读写接口
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout,
});
// 存储输入数据
const input = [];
// 按行读取输入
rl.on('line', (line) => {
input.push(line);
// 当读取到三行输入时开始处理
if (input.length === 3) {
const [m, n] = input[0].split(' ').map(Number); // 读取网格的行数和列数
const nums = input[1].split(' ').map(Number); // 读取一维信号值数组
const [tx, ty] = input[2].split(' ').map(Number); // 读取目标位置坐标
const grid = []; // 初始化二维网格
let sources = []; // 初始化信号源队列
// 将一维数组转为二维网格并记录信号源
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
grid.push(nums.slice(i * n, (i + 1) * n)); // 从一维数组切片生成二维网格
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) sources.push([i, j]); // 如果是信号源,记录其位置
}
}
// 定义四个方向的移动向量(上下左右)
const directions = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]];
// BFS 模拟信号传播
while (sources.length) {
const [x, y] = sources.shift(); // 取出队列头部的信号源
// 遍历信号传播的四个方向
for (const [dx, dy] of directions) {
const nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy; // 计算新位置坐标
// 检查新位置是否在网格范围内且未被信号覆盖
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && grid[nx][ny] === 0) {
grid[nx][ny] = grid[x][y] - 1; // 更新新位置的信号值
if (grid[nx][ny] > 0) sources.push([nx, ny]); // 若信号值仍大于 0,加入队列
}
}
}
// 输出目标位置的信号强度
console.log(grid[tx][ty]);
rl.close(); // 关闭读写接口
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
注意:
如果发现代码有用例覆盖不到的情况,欢迎反馈!会在第一时间修正,更新。
解题不易,如对您有帮助,欢迎点赞/收藏

评论记录:
回复评论: