(一)TSP问题
TSP问题:旅行商问题,即TSP问题(Traveling Salesman Problem),给定一组城市和每对城市之间的距离,商家从其中一个城市出发,要求每个城市都要经过且每个城市经过一次,最后回到起点城市,求解商家访问这些城市的最短路径。
(二)蚁群算法
(1)蚁群算法简单介绍
蚁群算法简介:蚁群算法是对自然界蚂蚁的寻径方式进行模似而得出的一种仿生算法:蚂蚁在运动过程中,能够在它所经过的路径上留下信息素(pheromone)的物质进行信息传递,而且蚂蚁在运动过程中能够感知这种物质,并以此指导自己的运动方向。
当有很多蚂蚁觅食时,刚开始每个蚂蚁会随机选择一条路径,并在该路径中释放信息素,路径短的蚂蚁要比路径长的更先到达目的地,往返的频率也更快,所有该路径上的信息素更浓。信息素也会随着时间会有部分挥发。当下一代蚂蚁觅食时,下一代蚂蚁会选择信息素浓度高的路径走,而选择该路径的蚂蚁最多,又会释放更多的信息素,因此由大量蚂蚁组成的蚁群集体行为便表现出一种信息正反馈现象:某一路径上走过的蚂蚁越多,则后来者选择该路径的概率就越大。蚁群算法具有分布计算、信息正反馈和启发式搜索的特征,本质上是进化算法中的一种启发式全局优化算法。
(2)蚁群算法解决TSP问题基本原理
在蚁群算法中,蚂蚁的行走路径表示待优化问题的可行解,整个蚂蚁群体的所有路径构成待优化问题的解空间。算法基本原理如下:
(1)根据具体问题设置蚂蚁种群数量AntCount,分头并行搜索。
(2)每只蚂蚁完成一次周游后,在行进的路上释放信息素,信息素量与解的质量成正比。
(3)蚂蚁路径的选择(当前城市i到下一城市j)根据信息素浓度Tij,同时考虑两点之间的距离 η \eta ηij( η \eta ηij为城市i和城市j之间距离的倒数),采用随机的局部搜索策略。这使得距离较短的边,其上的信息素量较大,后来的蚂蚁选择该边的概率也较大。
(4)每只蚂蚁只能走合法路线(经过每个城市1次且仅1次),为此设置禁忌表(即以前走过的城市列表)来控制。
(5)所有蚂蚁都搜索完一次就是迭代一次,每迭代一次就对所有的边做一次信息素更新,原来的蚂蚁死掉,新的蚂蚁进行新一轮搜索。注意,同一代的蚂蚁互相之间不会受到之前蚂蚁留下的信息素浓度的影响,计算到下一城市j的概率时所用到T是上一代蚂蚁留下的信息素。第一代蚂蚁用的信息素是初始值为1,所有城市之间信息素浓度一样。
(6)更新信息素包括原有信息素的蒸发和经过的路径上信息素的增加。
(7)达到预定的迭代步数,或出现停滞现象(所有蚂蚁都选择同样的路径,解不再变化),则算法结束,以当前最优解作为问题的最优解。
(3)蚁群算法的核心步骤
3.1 路径构建
路径构建包括初始城市的选择和下一个到达城市的选择。每个蚂蚁都随机选择一个城市作为其出发城市,并维护一个路径记忆表(候选集列表candidate,是一个Antcount-citycount二维矩阵),用来存放蚂蚁依次经过的城市。
蚂蚁在当前所在城市选择下一个城市时,转移概率 p i j pij pij是有两部分组成,一个是信息素浓度Tij,另一个是当前城市到下一城市的距离 η \eta ηij。 α \alpha α是信息素重要程度因子, β \beta β是启发函数重要程度因子。其中t时刻,蚂蚁k从i城市到j城市的转移概率是按照下列公式来进行计算的:
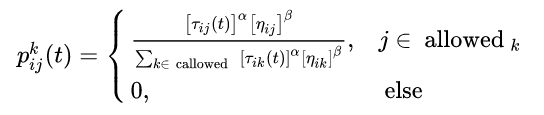

3.2 信息素更新
迭代过程中,问题空间中的所有路径上的信息素都会发生改变。其中第一部分是信息素的蒸发, ρ \rho ρ(rho)是挥发因子,代表信息素的挥发速度。然后,所有的蚂蚁根据自己构建的路径长度在它们本轮经过的边上释放信息素,公式如下:
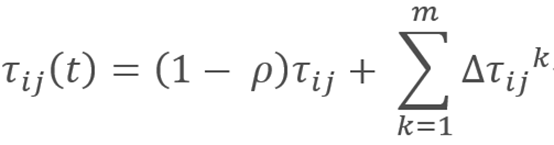
等式右边第一部分代表了信息素自身挥发后剩余的信息素,第二部分是每只蚂蚁经过城市i到城市j留下的信息素。在一次迭代中,每只蚂蚁经过城市i到城市j都会留下信息素,在该次迭代结束后,所有蚂蚁留下的信息素总和即为该路径信息素的增量。注意,同一代的蚂蚁互相之间不会受到之前蚂蚁留下的信息素浓度的影响,计算到下一城市j的概率时所用到T是上一代所有蚂蚁留下的信息素。
(三)代码分析
(1)设置参数
#蚂蚁数量
AntCount = 100
#城市数量
city_count = len(city_name)
alpha = 1 # 信息素重要程度因子
beta = 2 # 启发函数重要程度因子
rho = 0.1 #挥发速度
iter = 0 # 迭代初始值
MAX_iter = 200 # 最大迭代值
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
(2)距离矩阵
建立一个citycount-citycount二维数组,存放每对城市之间的距离。注意,因为要根据距离矩阵求启发函数 η \eta ηij( η \eta ηij为城市i和城市j之间距离的倒数),所有距离矩阵的对角线不能为0,我把对角线设置为10000,其实只要不为零就可以。
#Distance距离矩阵
city_count = len(city_name)
Distance = np.zeros((city_count, city_count))
for i in range(city_count):
for j in range(city_count):
if i != j:
Distance[i][j] = math.sqrt((city_condition[i][0] - city_condition[j][0]) ** 2 + (city_condition[i][1] - city_condition[j][1]) ** 2)
else:
Distance[i][j] = 100000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
(3)设置信息素矩阵和蚂蚁路径矩阵
建立一个citycount-citycount二维的信息素矩阵pheromonetable,存放每对城市之间的信息素。初始信息素矩阵,全是为1组成的矩阵。在每次迭代之后,更新该信息素矩阵。
建立一个AntCount-city_count二维矩阵candidate,在每次迭代中,存放所有蚂蚁的路径(一只蚂蚁一个路径)。
建立一个MAX_iter-city_count二维矩阵path_best,存放的是相应的,每次迭代后的最优路径,每次迭代只有一个值。
建立一个一维数组distance_best,存放每次迭代的最优距离。
# 初始信息素矩阵,全是为1组成的矩阵
pheromonetable = np.ones((city_count, city_count))
# 候选集列表,存放100只蚂蚁的路径(一只蚂蚁一个路径),一共就Antcount个路径,一共是蚂蚁数量*31个城市数量
candidate = np.zeros((AntCount, city_count)).astype(int)
# path_best存放的是相应的,每次迭代后的最优路径,每次迭代只有一个值
path_best = np.zeros((MAX_iter, city_count))
# 存放每次迭代的最优距离
distance_best = np.zeros( MAX_iter)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
(4)当前城市选择下一城市
蚂蚁由当前城市i选择到下一个城市j。首先建立一个列表 unvisit存放还未访问过的城市,每次访问一个城市之后,把该城市从unvisit里面移除。由当前城市选择下一个城市时,使用概率函数分别计算当前城市到还未访问的所有城市之间概率。 累计概率,轮盘赌选择下一次个城市。
# second:选择下一个城市选择
for i in range(AntCount):
# 移除已经访问的第一个元素
unvisit = list(range(city_count)) # 列表形式存储没有访问的城市编号
visit = candidate[i, 0] # 当前所在点,第i个蚂蚁在第一个城市
unvisit.remove(visit) # 在未访问的城市中移除当前开始的点
for j in range(1, city_count):#访问剩下的city_count个城市,city_count次访问
protrans = np.zeros(len(unvisit))#每次循环都更改当前没有访问的城市的转移概率矩阵1*30,1*29,1*28...
# 下一城市的概率函数
for k in range(len(unvisit)):
# 计算当前城市到剩余城市的(信息素浓度^alpha)*(城市适应度的倒数)^beta
# etable[visit][unvisit[k]],(alpha+1)是倒数分之一,pheromonetable[visit][unvisit[k]]是从本城市到k城市的信息素
protrans[k] = np.power(pheromonetable[visit][unvisit[k]], alpha) * np.power(
etable[visit][unvisit[k]], (alpha + 1))
# 累计概率,轮盘赌选择
cumsumprobtrans = (protrans / sum(protrans)).cumsum()
cumsumprobtrans -= np.random.rand()
# 求出离随机数产生最近的索引值
k = unvisit[list(cumsumprobtrans > 0).index(True)]
# 下一个访问城市的索引值
candidate[i, j] = k
unvisit.remove(k)
length[i] += Distance[visit][k]
visit = k # 更改出发点,继续选择下一个到达点
length[i] += Distance[visit][candidate[i, 0]]#最后一个城市和第一个城市的距离值也要加进去
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
(5)更新信息素
每迭代一次之后,更新所有城市之间的信息素。首先建一个信息素的增加量矩阵,存放该次迭代后每条路径的信息素增量。每条路径上的信息素等于信息素自身挥发后剩余的信息素加上每只蚂蚁经过城市i到城市j留下的信息素。
注意,更新信息素其实有三种方式。我选择的是第一种:△τ=Q/L,Q为常数,描述蚂蚁释放信息素的浓度,L为每只蚂蚁周游中所走路径的总长度。即每只蚂蚁从城市i到城市j之间信息素的增量等于Q除以周游中所走路径的长度。对于同一只蚂蚁,所有的路径上(任意两个城市之间)△τ是一样的。
#信息素的增加量矩阵
changepheromonetable = np.zeros((city_count, city_count))
for i in range(AntCount):
for j in range(city_count - 1):
# 当前路径比如城市23之间的信息素的增量:1/当前蚂蚁行走的总距离的信息素
changepheromonetable[candidate[i, j]][candidate[i][j + 1]] += Q / length[i]
#Distance[candidate[i, j]][candidate[i, j + 1]]
#最后一个城市和第一个城市的信息素增加量
changepheromonetable[candidate[i, j + 1]][candidate[i, 0]] += Q / length[i]
#信息素更新的公式:
pheromonetable = (1 - rho) * pheromonetable + changepheromonetable
iter += 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
(6)30城市的坐标.txt
下面是30城市的坐标,大家建一个‘30城市的坐标.txt’文件然后放到和代码同目录下就可以啦。
1,41,94
2,37,84
3,53,67
4,25,62
5,7,64
6,2,99
7,68,58
8,71, 44
9,54,62
10,83,69
11,64,60
12,18,54
13,22,60
14,83,46
15,91,38
16,25,38
17,24,42
18,58,69
19,71,71
20,74,78
21,87,76
22,18,40
23,13,40
24,82,7
25,62,32
26,58,35
27,45,21
28,41,26
29,44,35
30,4,50
(7) 完整代码
#蚁群算法解决TSP
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import math
import random
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'STSong'
city_name = []
city_condition = []
with open('30城市的坐标.txt','r',encoding='UTF-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
#调用readlines()一次读取所有内容并按行返回list给lines
#for循环每次读取一行
for line in lines:
line = line.split('\n')[0]
line = line.split(',')
city_name.append(line[0])
city_condition.append([float(line[1]), float(line[2])])
city_condition = np.array(city_condition)#获取30城市坐标
#Distance距离矩阵
city_count = len(city_name)
Distance = np.zeros((city_count, city_count))
for i in range(city_count):
for j in range(city_count):
if i != j:
Distance[i][j] = math.sqrt((city_condition[i][0] - city_condition[j][0]) ** 2 + (city_condition[i][1] - city_condition[j][1]) ** 2)
else:
Distance[i][j] = 100000
# 蚂蚁数量
AntCount = 100
# 城市数量
city_count = len(city_name)
# 信息素
alpha = 1 # 信息素重要程度因子
beta = 2 # 启发函数重要程度因子
rho = 0.1 #挥发速度
iter = 0 # 迭代初始值
MAX_iter = 200 # 最大迭代值
Q = 1
# 初始信息素矩阵,全是为1组成的矩阵
pheromonetable = np.ones((city_count, city_count))
# 候选集列表,存放100只蚂蚁的路径(一只蚂蚁一个路径),一共就Antcount个路径,一共是蚂蚁数量*31个城市数量
candidate = np.zeros((AntCount, city_count)).astype(int)
# path_best存放的是相应的,每次迭代后的最优路径,每次迭代只有一个值
path_best = np.zeros((MAX_iter, city_count))
# 存放每次迭代的最优距离
distance_best = np.zeros( MAX_iter)
# 倒数矩阵
etable = 1.0 / Distance
while iter < MAX_iter:
# first:蚂蚁初始点选择
if AntCount <= city_count:
#np.random.permutation随机排列一个数组的
candidate[:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(city_count))[:AntCount]
else:
m =AntCount -city_count
n =2
candidate[:city_count, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(city_count))[:]
while m >city_count:
candidate[city_count*(n -1):city_count*n, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(city_count))[:]
m = m -city_count
n = n + 1
candidate[city_count*(n-1):AntCount,0] = np.random.permutation(range(city_count))[:m]
length = np.zeros(AntCount)#每次迭代的N个蚂蚁的距离值
# second:选择下一个城市选择
for i in range(AntCount):
# 移除已经访问的第一个元素
unvisit = list(range(city_count)) # 列表形式存储没有访问的城市编号
visit = candidate[i, 0] # 当前所在点,第i个蚂蚁在第一个城市
unvisit.remove(visit) # 在未访问的城市中移除当前开始的点
for j in range(1, city_count):#访问剩下的city_count个城市,city_count次访问
protrans = np.zeros(len(unvisit))#每次循环都更改当前没有访问的城市的转移概率矩阵1*30,1*29,1*28...
# 下一城市的概率函数
for k in range(len(unvisit)):
# 计算当前城市到剩余城市的(信息素浓度^alpha)*(城市适应度的倒数)^beta
# etable[visit][unvisit[k]],(alpha+1)是倒数分之一,pheromonetable[visit][unvisit[k]]是从本城市到k城市的信息素
protrans[k] = np.power(pheromonetable[visit][unvisit[k]], alpha) * np.power(
etable[visit][unvisit[k]], (alpha + 1))
# 累计概率,轮盘赌选择
cumsumprobtrans = (protrans / sum(protrans)).cumsum()
cumsumprobtrans -= np.random.rand()
# 求出离随机数产生最近的索引值
k = unvisit[list(cumsumprobtrans > 0).index(True)]
# 下一个访问城市的索引值
candidate[i, j] = k
unvisit.remove(k)
length[i] += Distance[visit][k]
visit = k # 更改出发点,继续选择下一个到达点
length[i] += Distance[visit][candidate[i, 0]]#最后一个城市和第一个城市的距离值也要加进去
"""
更新路径等参数
"""
# 如果迭代次数为一次,那么无条件让初始值代替path_best,distance_best.
if iter == 0:
distance_best[iter] = length.min()
path_best[iter] = candidate[length.argmin()].copy()
else:
# 如果当前的解没有之前的解好,那么当前最优还是为之前的那个值;并且用前一个路径替换为当前的最优路径
if length.min() > distance_best[iter - 1]:
distance_best[iter] = distance_best[iter - 1]
path_best[iter] = path_best[iter - 1].copy()
else: # 当前解比之前的要好,替换当前解和路径
distance_best[iter] = length.min()
path_best[iter] = candidate[length.argmin()].copy()
"""
信息素的更新
"""
#信息素的增加量矩阵
changepheromonetable = np.zeros((city_count, city_count))
for i in range(AntCount):
for j in range(city_count - 1):
# 当前路径比如城市23之间的信息素的增量:1/当前蚂蚁行走的总距离的信息素
changepheromonetable[candidate[i, j]][candidate[i][j + 1]] += Q / length[i]
#Distance[candidate[i, j]][candidate[i, j + 1]]
#最后一个城市和第一个城市的信息素增加量
changepheromonetable[candidate[i, j + 1]][candidate[i, 0]] += Q / length[i]
#信息素更新的公式:
pheromonetable = (1 - rho) * pheromonetable + changepheromonetable
iter += 1
print("蚁群算法的最优路径",path_best[-1]+1)
print("迭代", MAX_iter,"次后","蚁群算法求得最优解",distance_best[-1])
# 路线图绘制
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title("Best roadmap")
x = []
y = []
path = []
for i in range(len(path_best[-1])):
x.append(city_condition[int(path_best[-1][i])][0])
y.append(city_condition[int(path_best[-1][i])][1])
path.append(int(path_best[-1][i])+1)
x.append(x[0])
y.append(y[0])
path.append(path[0])
for i in range(len(x)):
plt.annotate(path[i], xy=(x[i], y[i]), xytext=(x[i] + 0.3, y[i] + 0.3))
plt.plot(x, y,'-o')
# 距离迭代图
fig = plt.figure()
#plt.figure语()---在plt中绘制一张图片
plt.title("Distance iteration graph")#距离迭代图
plt.plot(range(1, len(distance_best) + 1), distance_best)
plt.xlabel("Number of iterations")#迭代次数
plt.ylabel("Distance value")#距离值
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160


评论记录:
回复评论: