
| C++语法 | 相关知识点 | 可以通过点击 | 以下链接进行学习 | 一起加油! |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 命名空间 | 缺省参数与函数重载 | C++相关特性 | 类和对象-上篇 | 类和对象-中篇 |
| 类和对象-下篇 | 日期类 | C/C++内存管理 | 模板初阶 | String使用 |
| String模拟实现 | Vector使用及其模拟实现 | List使用及其模拟实现 | 容器适配器Stack与Queue |
这篇文章将深入探讨优先队列的工作原理,并详细讲解仿函数在其优化过程中的应用。


?个人主页:是店小二呀
?C语言专栏:C语言
?C++专栏: C++
?初阶数据结构专栏: 初阶数据结构
?高阶数据结构专栏: 高阶数据结构
?Linux专栏: Linux
?喜欢的诗句:无人扶我青云志 我自踏雪至山巅 
文章目录
一、优先级队列
1.1 优先级队列介绍
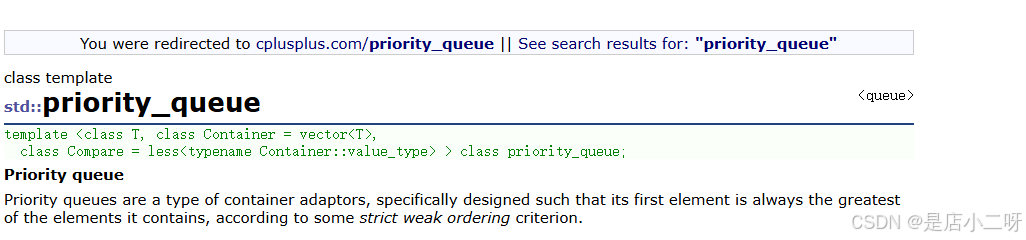
[优先级队列文档介绍](priority_queue - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com))
- 优先队列是一个容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所含的元素中最大的
- 此上下文类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先队列中位于顶部的元素)
- 优先级队列已经不能称为队列,不符合FIFO特性拉
- 优先队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器即将特定的容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素,元素从特定容器的"尾部"弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部
- 底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是特定设计的容器类,容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作
- empty():检测容器是否为空
- size():返回容器中有效元素个数
- front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
- push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
- pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
标准容器类vector和deque满足这些需求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector
需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用算法函数make_head,push_heap和pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
1.2 优先级队列使用
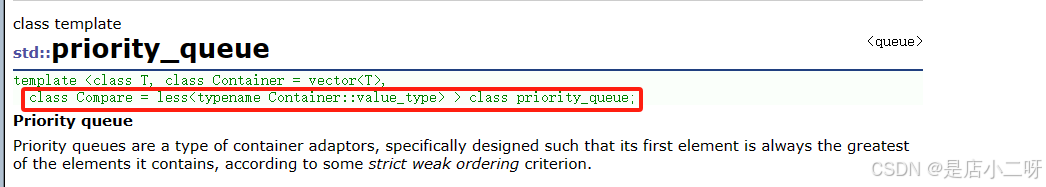
优先级队列属于容器适配器,并跟堆具有是否相似的结构与功能,这里可以看成堆。由于堆是通过完全二叉树进行搭建,优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,调用库中priority_queue类使用头文件
默认情况下priority_queue是大堆
#pragma once
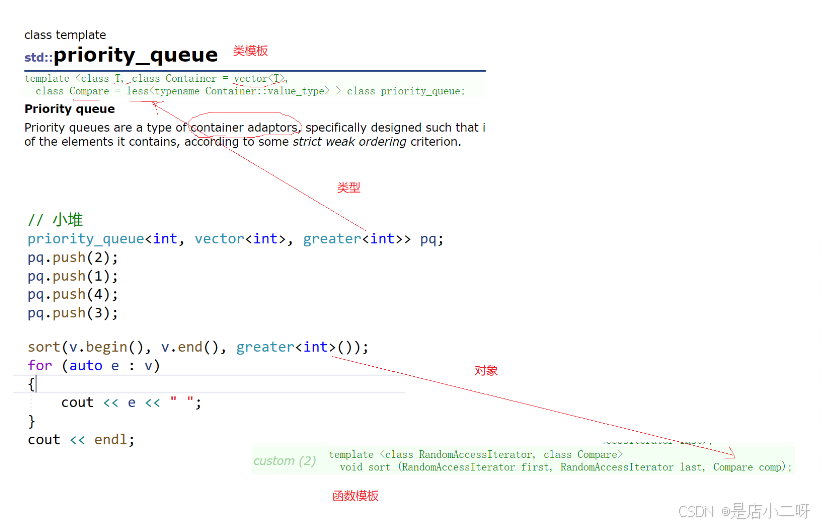
#include 以上就是建堆的逻辑,但是如果需要建小堆,需要去内部修改大于小于号,显得有些繁琐。对此引用了一个类模板适应不同类型,对operator()函数进行运算符重载,作为控制比较逻辑,其中在外部进行开关的控制。
问题:
- 如果需要比较的逻辑,C语言中的sqort函数不行吗?
答:
- C++不喜欢使用qsort函数,参数部分的函数指针显得很麻烦,C++喜欢使用类模板中的仿函数。
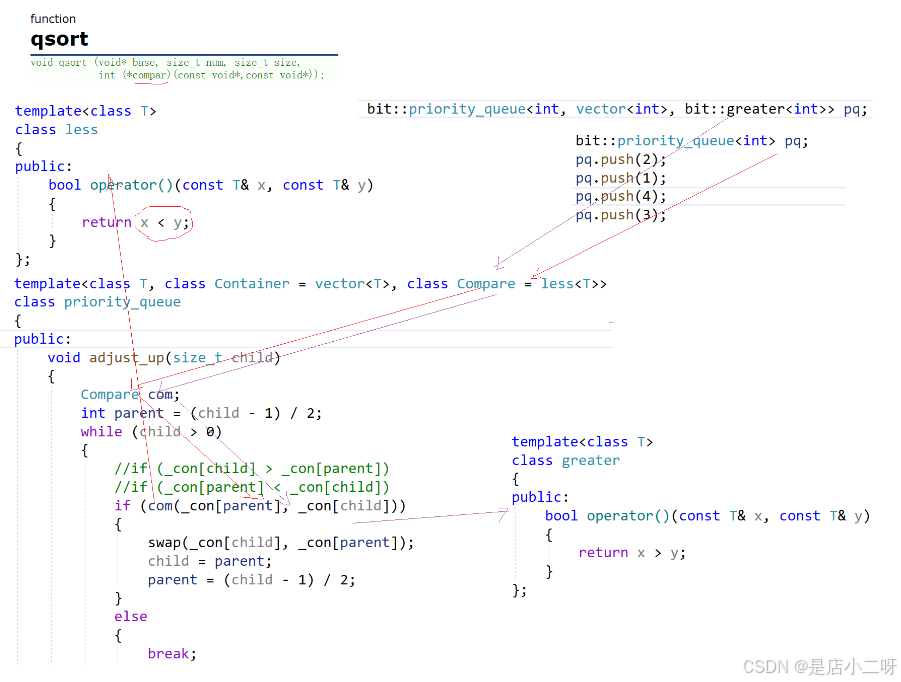
1.3 小补充:priority_queue类提供的仿函数
关于仿函数,库中已经实现好了greater和less仿函数可以直接使用,priority_queue默认使用的是less建大堆
二、仿函数
2.1 仿函数概念
仿函数是通过类中运算符重载()实现特定的功能,通过使用匿名对象使用,它的对象可以想函数一样去使用,使得很难区分是调用函数还是调用匿名对象
Less lessfunc;
cout << lessfunc(1, 2) << endl;
cout << lessfunc.operator()(1, 2) << endl;
cout << Less()(1, 2) << endl;
这里推荐使用第二种和第三种,为了提高代码的可读性,第一种写法可能会引起歧义。
2.2 仿函数访问限定符
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
仿函数中数据是需要公开使用,对于可以通过strcut或将class访问权限设置为public。仿函数/函数对象可以像函数一样去使用,**但是本质是类调用运算符重载。**那么为什么这么麻烦呢?直接写个函数不就行吗?还仿函数,听起来很牛逼哄哄呀!
2.3 仿函数相较于普通函数优势
虽然普通函数在大多数情况下足够,但仿函数提供了更强大的功能和灵活性。
仿函数的优势
- 仿函数是模板编程的重要组成部分,可以与模板一起使用,实现泛型编程的目的。
- 将逻辑和数据封装在一个类中,并且可以轻松调整或扩展仿函数的行为,而不需要改变其调用接口
- 仿函数可以将复杂逻辑和数据封装在类对象中,使得代码更加模块化和可维护,重点体现在封装。
- 仿函数可以有成员变量,在不同的调用之间保持状态。
- 每个仿函数都有不同的类去封装,也可以更好适应泛型编程,灵活地去调整
通过一个类来控制这里的比较逻辑,并且内置类型与自定义类型都支持这种做法。
2.4 当T为指针类型
class Date
{
public:
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
int main()
{
priority_queue <Date*, vector<Date*>, greater<Date*>> pqptr;
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 14));
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 11));
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 15));
while (!pqptr.empty())
{
cout << *(pqptr.top()) << " ";
pqptr.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

结果说明:正如图中问题,多次运行出现的结果是不同的,导致这种情况的原因是因为地址的大小new出来是随机的,这里如果是单纯的比较大小,只是比较地址编号的大小,而不是比较日期的大小。这里没有对*进行重载,对此需要单独写。
解决措施:
class GteaterDate
{
public:
bool operator()(const Date* p1, const Date* p2)
{
return *p1 > *p2;
}
};
在类名实现比较指针的可调用函数对象(仿函数控制比较逻辑,控制任何比较)在优先级队列参数部分传递。

2.5 仿函数解决实际问题
场景如下:
假如我这里有一堆商品,我需要某个商品的排序,但是这里对于实际中需要排序的类型不止一种,那么如果需要看不同类型的排序,就需要修改,如何破局只有大于或者小于,但是总不能说"请稍等,程序员正在改代码"吧!对此需要使用仿函数的配合,模板帮我们控制的是类型不同的类型。
struct Goods
{
string _name; // 名字
double _price; // 价格
int _evaluate; // 评价
Goods(const char* str, double price, int evaluate)
:_name(str)
, _price(price)
, _evaluate(evaluate)
{}
};
struct ComparePriceLess
{
bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr)
{
return gl._price < gr._price;
}
};
struct ComparePriceGreater
{
bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr)
{
return gl._price > gr._price;
}
};
struct CompareEvaluateLess
{
bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr)
{
return gl._evaluate < gr._evaluate;
}
};
struct CompareEvaluateGreater
{
bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr)
{
return gl._evaluate > gr._evaluate;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<Goods> v = { { "苹果", 2.1, 5 }, { "香蕉", 3, 4 }, { "橙子", 2.2,
3 }, { "菠萝", 1.5, 4 } };
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceLess());
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceGreater());
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), CompareEvaluateLess());
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), CompareEvaluateGreater());
}
注意:有些容器是没有迭代器的,这样子话就会破坏某种特性,一般不提供
三、反向迭代器
反向迭代器本质是写一个反向迭代器的类模板,给编译器传不同的容器的正向迭代器实例化,编译器帮助我们实例化出各种容器的对应反向迭代器。
3.1 反向与正向迭代器不同点
从功能上是类似的,但是运算符重载++与–运算符行为相反的。
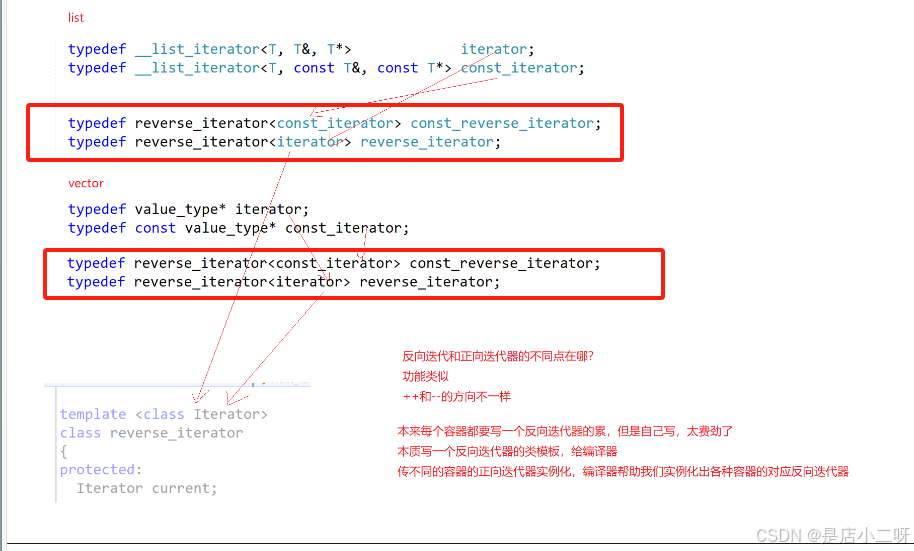
同时反向与迭代器起始位置和结束位置是相反的,库里面也是形成对称,但是不是绝对的,如果满足反向迭代器逻辑就行。

思考:
这里it.rbegin()指向的位置(it.end)是哨兵位的位置,我们不希望访问到哨兵位的位置
解决办法:
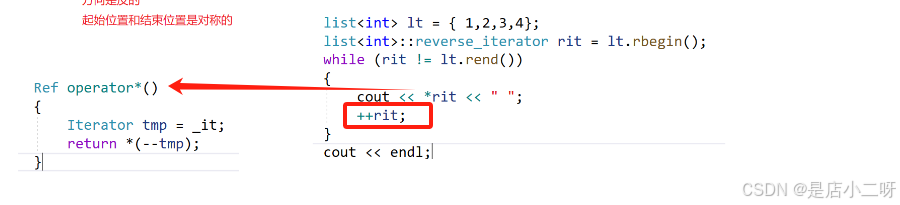
需要注意:
这里++不是正向迭代器++运算符重载的逻辑,而是–的逻辑,因为是反向迭代器。这里是不支持tmp-1的,tmp是自定义类型,而没有-的运算符重载。
四、priority_queue.h
#pragma once
#include > pqptr;
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 14));
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 11));
pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 15));
while (!pqptr.empty())
{
cout << *(pqptr.top()) << " ";
pqptr.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
以上就是本篇文章的所有内容,在此感谢大家的观看!这里是店小二呀C++笔记,希望对你在学习C++语言旅途中有所帮助!

评论记录:
回复评论: