第三十~三十一章:字符串转换成整数,带通配符的字符串匹配
前言
之前本一直想写写神经网络算法和EM算法,但写这两个算法实在需要大段大段的时间,而平时上班,周末则跑去北大教室自习看书(顺便以时间为序,说下过去半年看过的自觉还不错的数学史方面的书:《数理统计学简史》《微积分概念发展史》《微积分的历程:从牛顿到勒贝格》《数学恩仇录》《数学与知识的探求》《古今数学思想》《素数之恋》),故一直未曾有时间写。
然最近在负责一款在线编程挑战平台:http://hero.pongo.cn/(简称hero,通俗理解是中国的topcoder,当然,一直在不断完善中,与一般OJ不同点在于,OJ侧重为参与ACM竞赛者提供刷题练习的场所,而hero则着重为企业招聘面试服务),在上面出了几道编程面试题,有些题目看似简单,但一coding,很多问题便立马都在hero上给暴露出来了,故就从hero上的编程挑战题切入,继续更新本程序员编程艺术系列吧。
况且,前几天与一朋友聊天,他说他认识的今年360招进来的三四十人应届生包括他自己找工作时基本都看过我的博客,则更增加了更新此编程艺术系列的动力。
OK,本文讲两个问题:
- 第三十章、字符串转换成整数,从确定思路,到写出有瑕疵的代码,继而到microsoft & linux的atoi实现,再到第一份比较完整的代码,最后以Net/OS中的实现结尾,看似很简单的一个问题,其实非常不简单;
- 第三十一章、字符串匹配问题
第三十章、字符串转换成整数
先看题目:
输入一个表示整数的字符串,把该字符串转换成整数并输出,例如输入字符串"345",则输出整数345。
给定函数原型int StrToInt(const char *str) ,完成函数StrToInt,实现字符串转换成整数的功能,不得用库函数atoi(即便准许使用,其对于溢出情况的处理也达不到题目的要求,详情请参看下文第7节末)。
我们来一步一步分析(共9小节,重点在下文第8小节及后续内容),直至写出第一份准确的代码:
1、本题考查的实际上就是字符串转换成整数的问题,或者说是要你自行实现atoi函数。那如何实现把表示整数的字符串正确地转换成整数呢?以"345"作为例子:
- 当我们扫描到字符串的第一个字符'3'时,由于我们知道这是第一位,所以得到数字3。
- 当扫描到第二个数字'4'时,而之前我们知道前面有一个3,所以便在后面加上一个数字4,那前面的3相当于30,因此得到数字:3*10+4=34。
- 继续扫描到字符'5','5'的前面已经有了34,由于前面的34相当于340,加上后面扫描到的5,最终得到的数是:34*10+5=345。
因此,此题的思路便是:每扫描到一个字符,我们便把在之前得到的数字乘以10,然后再加上当前字符表示的数字。
2、思路有了,有一些细节需要注意,如zhedahht所说:
- “由于整数可能不仅仅之含有数字,还有可能以'+'或者'-'开头,表示整数的正负。因此我们需要把这个字符串的第一个字符做特殊处理。如果第一个字符是'+'号,则不需要做任何操作;如果第一个字符是'-'号,则表明这个整数是个负数,在最后的时候我们要把得到的数值变成负数。
- 接着我们试着处理非法输入。由于输入的是指针,在使用指针之前,我们要做的第一件是判断这个指针是不是为空。如果试着去访问空指针,将不可避免地导致程序崩溃。
- 另外,输入的字符串中可能含有不是数字的字符。每当碰到这些非法的字符,我们就没有必要再继续转换。
- 最后一个需要考虑的问题是溢出问题。由于输入的数字是以字符串的形式输入,因此有可能输入一个很大的数字转换之后会超过能够表示的最大的整数而溢出。”
- //copyright@zhedahht 2007
- enum Status {kValid = 0, kInvalid};
- int g_nStatus = kValid;
-
- // Convert a string into an integer
- int StrToInt(const char* str)
- {
- g_nStatus = kInvalid;
- long long num = 0;
-
- if(str != NULL)
- {
- const char* digit = str;
-
- // the first char in the string maybe '+' or '-'
- bool minus = false;
- if(*digit == '+')
- digit ++;
- else if(*digit == '-')
- {
- digit ++;
- minus = true;
- }
-
- // the remaining chars in the string
- while(*digit != '\0')
- {
- if(*digit >= '0' && *digit <= '9')
- {
- num = num * 10 + (*digit - '0');
-
- // overflow
- if(num > std::numeric_limits<int>::max())
- {
- num = 0;
- break;
- }
-
- digit ++;
- }
- // if the char is not a digit, invalid input
- else
- {
- num = 0;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- if(*digit == '\0')
- {
- g_nStatus = kValid;
- if(minus)
- num = 0 - num;
- }
- }
- return static_cast<int>(num);
- }
两个问题:
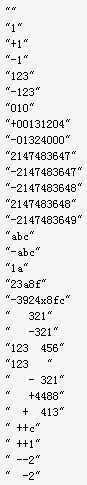
- 当输入的字符串不是数字,而是字符的时候,比如“1a”,上述程序直接返回了0(而正确的结果应该是得到1):
- // if the char is not a digit, invalid input
- else
- {
- num = 0;
- break;
- }
- 处理溢出时,有问题。因为它遇到溢出情况时,直接返回了0:
- // overflow
- if(num > std::numeric_limits<int>::max())
- {
- num = 0;
- break;
- }
- //copyright@SP_daiyq 2013/5/29
- int StrToInt(const char* str)
- {
- int res = 0; // result
- int i = 0; // index of str
- int signal = '+'; // signal '+' or '-'
- int cur; // current digit
-
- if (!str)
- return 0;
-
- // skip backspace
- while (isspace(str[i]))
- i++;
-
- // skip signal
- if (str[i] == '+' || str[i] == '-')
- {
- signal = str[i];
- i++;
- }
-
- // get result
- while (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
- {
- cur = str[i] - '0';
-
- // judge overlap or not
- if ( (signal == '+') && (cur > INT_MAX - res*10) )
- {
- res = INT_MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if ( (signal == '-') && (cur -1 > INT_MAX - res*10) )
- {
- res = INT_MIN;
- break;
- }
-
- res = res * 10 + cur;
- i++;
- }
-
- return (signal == '-') ? -res : res;
- }
- // judge overlap or not
- if ( (signal == '+') && (cur > INT_MAX - res*10) )
- {
- res = INT_MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if ( (signal == '-') && (cur -1 > INT_MAX - res*10) )
- {
- res = INT_MIN;
- break;
- }
cur > INT_MAX - res*101052254545*10 + 4,
然实际上当程序计算到1052254545*10时,
1052254545*10 >
2147483647
此时已经溢出了,若再执意计算,则程序逻辑将出错,故此后也就不能再判断字串的最后一位4是否大于2147483647%10了(耐不得烦想尽快看到最终正确代码的读者可以直接跳到下文第8节)。
- //copyright@fuwutu 2013/5/29
- int StrToInt(const char* str)
- {
- bool negative = false;
- long long result = 0;
- while (*str == ' ' || *str == '\t')
- {
- ++str;
- }
- if (*str == '-')
- {
- negative = true;
- ++str;
- }
- else if (*str == '+')
- {
- ++str;
- }
-
- while (*str != '\0')
- {
- int n = *str - '0';
- if (n < 0 || n > 9)
- {
- break;
- }
-
- if (negative)
- {
- result = result * 10 - n;
- if (result < -2147483648LL)
- {
- result = -2147483648LL;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- result = result * 10 + n;
- if (result > 2147483647LL)
- {
- result = 2147483647LL;
- }
- }
- ++str;
- }
-
- return result;
- }
long long result = 0;- //atol函数
- //Copyright (c) 1989-1997, Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
- long __cdecl atol(
- const char *nptr
- )
- {
- int c; /* current char */
- long total; /* current total */
- int sign; /* if ''-'', then negative, otherwise positive */
-
- /* skip whitespace */
- while ( isspace((int)(unsigned char)*nptr) )
- ++nptr;
-
- c = (int)(unsigned char)*nptr++;
- sign = c; /* save sign indication */
- if (c == ''-'' || c == ''+'')
- c = (int)(unsigned char)*nptr++; /* skip sign */
- total = 0;
- while (isdigit(c)) {
- total = 10 * total + (c - ''0''); /* accumulate digit */
- c = (int)(unsigned char)*nptr++; /* get next char */
- }
- if (sign == ''-'')
- return -total;
- else
- return total; /* return result, negated if necessary */
- }
- isspace(int x)
- {
- if(x==' '||x=='/t'||x=='/n'||x=='/f'||x=='/b'||x=='/r')
- return 1;
- else
- return 0;
- }
-
- isdigit(int x)
- {
- if(x<='9'&&x>='0')
- return 1;
- else
- return 0;
- }
- //atoi调用上述的atol
- int __cdecl atoi(
- const char *nptr
- )
- {
- //Overflow is not detected. Because of this, we can just use
- return (int)atol(nptr);
- }
但很遗憾的是,上述atoi标准代码依然返回的是long:
- long total; /* current total */
- if (sign == ''-'')
- return -total;
- else
- return total; /* return result, negated if necessary */
再者,下面这里定义成long的total与10相乘,即total*10很容易溢出:
- long total; /* current total */
- total = 10 * total + (c - ''0''); /* accumulate digit */
- simple_strtol,把一个字符串转换为一个有符号长整数;
- simple_strtoll,把一个字符串转换为一个有符号长长整数;
- simple_strtoul,把一个字符串转换为一个无符号长整数;
- simple_strtoull,把一个字符串转换为一个无符号长长整数
- //linux/lib/vsprintf.c
- //Copyright (C) 1991, 1992 Linus Torvalds
- //simple_strtol - convert a string to a signed long
- long simple_strtol(const char *cp, char **endp, unsigned int base)
- {
- if (*cp == '-')
- return -simple_strtoul(cp + 1, endp, base);
-
- return simple_strtoul(cp, endp, base);
- }
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(simple_strtol);
- //simple_strtoul - convert a string to an unsigned long
- unsigned long simple_strtoul(const char *cp, char **endp, unsigned int base)
- {
- return simple_strtoull(cp, endp, base);
- }
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(simple_strtoul);
- //simple_strtoll - convert a string to a signed long long
- long long simple_strtoll(const char *cp, char **endp, unsigned int base)
- {
- if (*cp == '-')
- return -simple_strtoull(cp + 1, endp, base);
-
- return simple_strtoull(cp, endp, base);
- }
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(simple_strtoll);
- //simple_strtoull - convert a string to an unsigned long long
- unsigned long long simple_strtoull(const char *cp, char **endp, unsigned int base)
- {
- unsigned long long result;
- unsigned int rv;
-
- cp = _parse_integer_fixup_radix(cp, &base);
- rv = _parse_integer(cp, base, &result);
- /* FIXME */
- cp += (rv & ~KSTRTOX_OVERFLOW);
-
- if (endp)
- *endp = (char *)cp;
-
- return result;
- }
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(simple_strtoull);
- “真正的处理逻辑主要是在_parse_integer里面,关于溢出的处理,_parse_integer处理的很优美,
- 而_parse_integer_fixup_radix是用来自动根据字符串判断进制的”。
- //lib/kstrtox.c, line 39
- //Convert non-negative integer string representation in explicitly given radix to an integer.
- //Return number of characters consumed maybe or-ed with overflow bit.
- //If overflow occurs, result integer (incorrect) is still returned.
- unsigned int _parse_integer(const char *s, unsigned int base, unsigned long long *p)
- {
- unsigned long long res;
- unsigned int rv;
- int overflow;
-
- res = 0;
- rv = 0;
- overflow = 0;
- while (*s) {
- unsigned int val;
-
- if ('0' <= *s && *s <= '9')
- val = *s - '0';
- else if ('a' <= _tolower(*s) && _tolower(*s) <= 'f')
- val = _tolower(*s) - 'a' + 10;
- else
- break;
-
- if (val >= base)
- break;
- /*
- * Check for overflow only if we are within range of
- * it in the max base we support (16)
- */
- if (unlikely(res & (~0ull << 60))) {
- if (res > div_u64(ULLONG_MAX - val, base))
- overflow = 1;
- }
- res = res * base + val;
- rv++;
- s++;
- }
- *p = res;
- if (overflow)
- rv |= KSTRTOX_OVERFLOW;
- return rv;
- }
- 上头出现了个unlikely,其实unlikely和likely经常出现在linux相关内核源码中
- if(likely(value)){
- //等价于if(likely(value)) == if(value)
- }
- else{
- }
- //include/linux/compiler.h
- # ifndef likely
- # define likely(x) (__builtin_constant_p(x) ? !!(x) : __branch_check__(x, 1))
- # endif
- # ifndef unlikely
- # define unlikely(x) (__builtin_constant_p(x) ? !!(x) : __branch_check__(x, 0))
- # endif
- 呈现下div_u64的代码:
- //include/linux/math64.h
- //div_u64
- static inline u64 div_u64(u64 dividend, u32 divisor)
- {
- u32 remainder;
- return div_u64_rem(dividend, divisor, &remainder);
- }
- //div_u64_rem
- static inline u64 div_u64_rem(u64 dividend, u32 divisor, u32 *remainder)
- {
- *remainder = dividend % divisor;
- return dividend / divisor;
- }
- //lib/kstrtox.c, line 23
- const char *_parse_integer_fixup_radix(const char *s, unsigned int *base)
- {
- if (*base == 0) {
- if (s[0] == '0') {
- if (_tolower(s[1]) == 'x' && isxdigit(s[2]))
- *base = 16;
- else
- *base = 8;
- } else
- *base = 10;
- }
- if (*base == 16 && s[0] == '0' && _tolower(s[1]) == 'x')
- s += 2;
- return s;
- }
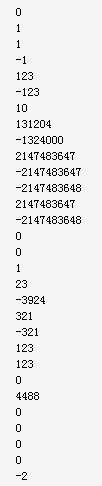
2147483647 : 2147483647 2147483648 : -2147483648 10522545459 : 1932610867 -2147483648 : -2147483648 -2147483649 : -2147483647 -10522545459 : 1932610867
8、根据我们第1小节达成一致的字符串转换成整数的思路:“每扫描到一个字符,我们便把在之前得到的数字乘以10,然后再加上当前字符表示的数字”,相信读者已经觉察到,在扫描到最后一个字符的时候,如果之前得到的数比较大,此时若再让其扩大10倍,相对来说是比较容易溢出的。
- 与其将n扩大10倍,,冒着溢出的风险, 再与MAX_INT进行比较(如果已经溢出, 则比较的结果没有意义),
- 不如未雨绸缪先用n与MAX_INT/10进行比较: 若n>MAX_INT/10(当然同时还要考虑n=MAX_INT/10的情况), 说明最终得到的整数一定会溢出, 故此时可以当即进行溢出处理,直接返回最大值MAX_INT,从而也就免去了计算n*10这一步骤。
他的代码如下,如有问题请指出:
- //copyright@njnu_mjn 2013
- int StrToDecInt(const char* str)
- {
- static const int MAX = (int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1);
- static const int MIN = -(int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1) - 1;
- unsigned int n = 0;
- int sign = 1;
- int c;
-
- while (isspace(*str))
- ++str;
- if (*str == '+' || *str == '-')
- {
- if (*str == '-')
- sign = -1;
- ++str;
- }
- while (isdigit(*str))
- {
- c = *str - '0';
- if (sign > 0 && (n > MAX/10 || (n == MAX/10 && c > MAX%10)))
- {
- n = MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if (sign < 0 && (n > (unsigned)MIN/10
- || (n == (unsigned)MIN/10 && c > (unsigned)MIN%10)))
- {
- n = MIN;
- break;
- }
- n = n * 10 + c;
- ++str;
- }
- return sign > 0 ? n : -n;
- }
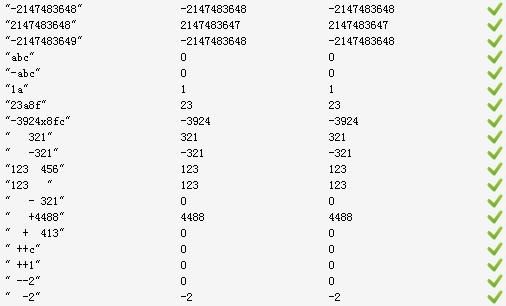
输入 输出
10522545459 : 2147483647
-10522545459 : -2147483648
咱们再来总结下上述代码是如何处理溢出情况的。对于正数来说,它溢出的可能性有两种:
- 一种是诸如2147483650,即n > MAX/10 的;
- 一种是诸如2147483649,即n == MAX/10 && c > MAX%10。
故咱们上面处理溢出情况的代码便是:
- c = *str - '0';
- if (sign > 0 && (n > MAX/10 || (n == MAX/10 && c > MAX%10)))
- {
- n = MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if (sign < 0 && (n > (unsigned)MIN/10
- || (n == (unsigned)MIN/10 && c > (unsigned)MIN%10)))
- {
- n = MIN;
- break;
- }
不过,即便如此,有些细节是改进的,如他自己所说:
- n的声明及定义应该为
int n = 0; - 将MAX/10,MAX%10,(unsigned)MIN/10及(unsigned)MIN%10保存到变量中, 防止重复计算
- //copyright@njnu_mjn 2013
- int StrToDecInt(const char* str)
- {
- static const int MAX = (int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1);
- static const int MIN = -(int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1) - 1;
- static const int MAX_DIV = (int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1) / 10;
- static const int MIN_DIV = (int)((((unsigned)~0 >> 1) + 1) / 10);
- static const int MAX_R = (int)((unsigned)~0 >> 1) % 10;
- static const int MIN_R = (int)((((unsigned)~0 >> 1) + 1) % 10);
- int n = 0;
- int sign = 1;
- int c;
-
- while (isspace(*str))
- ++str;
- if (*str == '+' || *str == '-')
- {
- if (*str == '-')
- sign = -1;
- ++str;
- }
- while (isdigit(*str))
- {
- c = *str - '0';
- if (sign > 0 && (n > MAX_DIV || (n == MAX_DIV && c >= MAX_R)))
- {
- n = MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if (sign < 0 && (n > MIN_DIV
- || (n == MIN_DIV && c >= MIN_R)))
- {
- n = MIN;
- break;
- }
- n = n * 10 + c;
- ++str;
- }
- return sign > 0 ? n : -n;
- }
输入 输出 10522545459 : 2147483647 -10522545459 : -2147483648 2147483648 : 2147483647 -2147483648 : -2147483648是否已是完美?如MJN君本人所说“ 我的实现与linux内核的atoi函数的实现, 都有一个共同的问题: 即使出错, 函数也返回了一个值, 导致调用者误认为自己传入的参数是正确的, 但是可能会导致程序的其他部分产生莫名的错误且很难调试”。
9、最后看下Nut/OS中atoi的实现,同时,本小节内容主要来自参考文献条目9,即MJN的博客:
- 00077 #include
- 00078 #include
- 00079
- 00084
- 00092 int atoi(CONST char *str)
- 00093 {
- 00094 return ((int) strtol(str, (char **) NULL, 10));
- 00095 }
上述代码中strtol实现的思想跟上文第7节所述的MJN君的思路类似,也是除法代替乘法。加上测试函数后的具体代码如下:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
-
- #define CONST const
-
- long mstrtol(CONST char *nptr, char **endptr, int base)
- {
- register CONST char *s;
- register long acc, cutoff;
- register int c;
- register int neg, any, cutlim;
-
- /*
- * Skip white space and pick up leading +/- sign if any.
- * If base is 0, allow 0x for hex and 0 for octal, else
- * assume decimal; if base is already 16, allow 0x.
- */
- s = nptr;
- do {
- c = (unsigned char) *s++;
- } while (isspace(c));
- if (c == '-') {
- neg = 1;
- c = *s++;
- } else {
- neg = 0;
- if (c == '+')
- c = *s++;
- }
- if ((base == 0 || base == 16) && c == '0' && (*s == 'x' || *s == 'X')) {
- c = s[1];
- s += 2;
- base = 16;
- }
- if (base == 0)
- base = c == '0' ? 8 : 10;
-
- /*
- * Compute the cutoff value between legal numbers and illegal
- * numbers. That is the largest legal value, divided by the
- * base. An input number that is greater than this value, if
- * followed by a legal input character, is too big. One that
- * is equal to this value may be valid or not; the limit
- * between valid and invalid numbers is then based on the last
- * digit. For instance, if the range for longs is
- * [-2147483648..2147483647] and the input base is 10,
- * cutoff will be set to 214748364 and cutlim to either
- * 7 (neg==0) or 8 (neg==1), meaning that if we have accumulated
- * a value > 214748364, or equal but the next digit is > 7 (or 8),
- * the number is too big, and we will return a range error.
- *
- * Set any if any `digits' consumed; make it negative to indicate
- * overflow.
- */
- cutoff = neg ? LONG_MIN : LONG_MAX;
- cutlim = cutoff % base;
- cutoff /= base;
- if (neg) {
- if (cutlim > 0) {
- cutlim -= base;
- cutoff += 1;
- }
- cutlim = -cutlim;
- }
- for (acc = 0, any = 0;; c = (unsigned char) *s++) {
- if (isdigit(c))
- c -= '0';
- else if (isalpha(c))
- c -= isupper(c) ? 'A' - 10 : 'a' - 10;
- else
- break;
- if (c >= base)
- break;
- if (any < 0)
- continue;
- if (neg) {
- if ((acc < cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) {
- any = -1;
- acc = LONG_MIN;
- errno = ERANGE;
- } else {
- any = 1;
- acc *= base;
- acc -= c;
- }
- } else {
- if ((acc > cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) {
- any = -1;
- acc = LONG_MAX;
- errno = ERANGE;
- } else {
- any = 1;
- acc *= base;
- acc += c;
- }
- }
- }
- if (endptr != 0)
- *endptr = (char *) (any ? s - 1 : nptr);
- return (acc);
- }
-
- int matoi2(CONST char *str)
- {
- return ((int) mstrtol(str, (char **) NULL, 10));
- }
-
- int mgetline(char* buf, size_t n) {
- size_t idx = 0;
- int c;
-
- while (--n > 0 && (c = getchar()) != EOF && c != '\n') {
- buf[idx++] = c;
- }
- buf[idx] = '\0';
- return idx;
- }
-
- #define MAX_LINE 200
-
- int main() {
- char buf[MAX_LINE];
- while (mgetline(buf, MAX_LINE) >= 0) {
- if (strcmp(buf, "quit") == 0) break;
- printf("matoi2=%d\n", matoi2(buf));
- }
- return 0;
- }
同样,MJN对上述实现测试了下,结果如下:
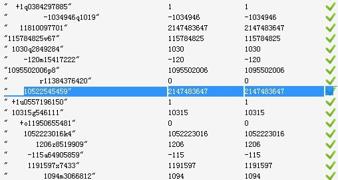
10522545459 matoi2=2147483647 -10522545459 matoi2=-2147483648
程序貌似对溢出的处理是正确的, 真的吗? 再把测试数据换成"10522545454"(与"10522545459"的区别在于最后一个字符)
10522545454 matoi2=1932610862 -10522545454 matoi2=-1932610862
症结就在于下面这段代码:
- if (neg) {
- if ((acc < cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) {
- any = -1;
- acc = LONG_MIN;
- errno = ERANGE;
- } else {
- any = 1;
- acc *= base;
- acc -= c;
- }
- } else {
- if ((acc > cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) {
- any = -1;
- acc = LONG_MAX;
- errno = ERANGE;
要想得到正确的输出结果,需要改动两个地方:
①其中这行:
if ((acc > cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim)应该改为:
if ( acc > cutoff || (acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) )②与此同时,这行:
if ((acc < cutoff || acc == cutoff) && c > cutlim) {改为:
if (acc < cutoff || (acc == cutoff && c > cutlim)) {为何要这样修改呢?细心的读者相信还是会记得上文第8节中关于正数的两种溢出情况的可能性:“对于正数来说,它溢出的可能性有两种:
- 一种是诸如2147483650,即n > MAX/10 的;
- 一种是诸如2147483649,即n == MAX/10 && c > MAX%10。”
也就是说无论是"10522545459",还是"10522545454",都是属于第1种情况,即“诸如2147483650,即n > MAX/10的”,此时直接返回MAX_INT即可,所以不需要也不能再去判断n == MAX/10的情况。
这个处理思路类似于上文第8节处理溢出情况的代码:
- if (sign > 0 && (n > MAX/10 || (n == MAX/10 && c > MAX%10)))
- {
- n = MAX;
- break;
- }
- else if (sign < 0 && (n > (unsigned)MIN/10
- || (n == (unsigned)MIN/10 && c > (unsigned)MIN%10)))
- {
- n = MIN;
- break;
- }
So,修改过后的代码测试正常:
10522545459 matoi2=2147483647 -10522545459\ matoi2=-2147483648 10522545454 matoi2=2147483647 -10522545454 matoi2=-2147483648 quit
第三十一章、带通配符的字符串匹配问题
字符串匹配问题,给定一串字符串,按照指定规则对其进行匹配,并将匹配的结果保存至output数组中,多个匹配项用空格间隔,最后一个不需要空格。
要求:
- 匹配规则中包含通配符?和*,其中?表示匹配任意一个字符,*表示匹配任意多个(>=0)字符。
- 匹配规则要求匹配最大的字符子串,例如a*d,匹配abbdd而非abbd,即最大匹配子串。
- 匹配后的输入串不再进行匹配,从当前匹配后的字符串重新匹配其他字符串。
请实现函数:char* my_find(char input[], char rule[])
举例说明
input:abcadefg
rule:a?c
output:abc
input :newsadfanewfdadsf
rule: new
output: new new
input :breakfastfood
rule: f*d
output:fastfood
注意事项:
- 自行实现函数my_find,勿在my_find函数里夹杂输出,且不准用C、C++库,和Java的String对象;
- 请注意代码的时间,空间复杂度,及可读性,简洁性;
- input=aaa,rule=aa时,返回一个结果aa,即可。
1、本题与上述第三十章的题不同,上题字符串转换成整数更多考察对思维的全面性和对细节的处理,本题则更多的是编程技巧。闲不多说,直接上代码:
- //copyright@cao_peng 2013/4/23
- int str_len(char *a) { //字符串长度
- if (a == 0) {
- return 0;
- }
- char *t = a;
- for (;*t;++t)
- ;
- return (int) (t - a);
- }
-
- void str_copy(char *a,const char *b,int len) { //拷贝字符串 a = b
- for (;len > 0; --len, ++b,++a) {
- *a = *b;
- }
- *a = 0;
- }
-
- char *str_join(char *a,const char *b,int lenb) { //连接字符串 第一个字符串被回收
- char *t;
- if (a == 0) {
- t = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * (lenb + 1));
- str_copy(t, b, lenb);
- return t;
- }
- else {
- int lena = str_len(a);
- t = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * (lena + lenb + 2));
- str_copy(t, a, lena);
- *(t + lena) = ' ';
- str_copy(t + lena + 1, b, lenb);
- free(a);
- return t;
- }
- }
-
- int canMatch(char *input, char *rule) { // 返回最长匹配长度 -1表示不匹配
- if (*rule == 0) { //已经到rule尾端
- return 0;
- }
- int r = -1 ,may;
- if (*rule == '*') {
- r = canMatch(input, rule + 1); // *匹配0个字符
- if (*input) {
- may = canMatch(input + 1, rule); // *匹配非0个字符
- if ((may >= 0) && (++may > r)) {
- r = may;
- }
- }
- }
- if (*input == 0) { //到尾端
- return r;
- }
- if ((*rule == '?') || (*rule == *input)) {
- may = canMatch(input + 1, rule + 1);
- if ((may >= 0) && (++may > r)) {
- r = may;
- }
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- char * my_find(char input[], char rule[]) {
- int len = str_len(input);
- int *match = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int) * len); //input第i位最多能匹配多少位 匹配不上是-1
- int i,max_pos = - 1;
- char *output = 0;
-
- for (i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
- match[i] = canMatch(input + i, rule);
- if ((max_pos < 0) || (match[i] > match[max_pos])) {
- max_pos = i;
- }
- }
- if ((max_pos < 0) || (match[max_pos] <= 0)) { //不匹配
- output = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char));
- *output = 0; // \0
- return output;
- }
- for (i = 0; i < len;) {
- if (match[i] == match[max_pos]) { //找到匹配
- output = str_join(output, input + i, match[i]);
- i += match[i];
- }
- else {
- ++i;
- }
- }
- free(match);
- return output;
- }
2、本题也可以直接写出DP方程,如下代码所示:
- //copyright@chpeih 2013/4/23
- char* my_find(char input[], char rule[])
- {
- //write your code here
- int len1,len2;
- for(len1 = 0;input[len1];len1++);
- for(len2 = 0;rule[len2];len2++);
- int MAXN = len1>len2?(len1+1):(len2+1);
- int **dp;
-
- //dp[i][j]表示字符串1和字符串2分别以i j结尾匹配的最大长度
- //记录dp[i][j]是由之前那个节点推算过来 i*MAXN+j
- dp = new int *[len1+1];
- for (int i = 0;i<=len1;i++)
- {
- dp[i] = new int[len2+1];
-
- }
-
- dp[0][0] = 0;
- for(int i = 1;i<=len2;i++)
- dp[0][i] = -1;
- for(int i = 1;i<=len1;i++)
- dp[i][0] = 0;
-
- for (int i = 1;i<=len1;i++)
- {
- for (int j = 1;j<=len2;j++)
- {
- if(rule[j-1]=='*'){
- dp[i][j] = -1;
- if (dp[i-1][j-1]!=-1)
- {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
-
- }
- if (dp[i-1][j]!=-1 && dp[i][j]
-1][j]+1) - {
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+1;
-
- }
- }else if (rule[j-1]=='?')
- {
- if(dp[i-1][j-1]!=-1){
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
-
- }else dp[i][j] = -1;
- }
- else
- {
- if(dp[i-1][j-1]!=-1 && input[i-1]==rule[j-1]){
- dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
- }else dp[i][j] = -1;
- }
- }
- }
-
- int m = -1;//记录最大字符串长度
- int *ans = new int[len1];
- int count_ans = 0;//记录答案个数
- char *returnans = new char[len1+1];
- int count = 0;
- for(int i = 1;i<=len1;i++)
- if (dp[i][len2]>m){
- m = dp[i][len2];
- count_ans = 0;
- ans[count_ans++] = i-m;
- }else if(dp[i][len2]!=-1 &&dp[i][len2]==m){
- ans[count_ans++] = i-m;
- }
-
- if (count_ans!=0)
- {
- int len = ans[0];
- for (int i = 0;i
- {
- printf("%c",input[i+ans[0]]);
- returnans[count++] = input[i+ans[0]];
- }
- for (int j = 1;j
- {
- printf(" ");
- returnans[count++] = ' ';
- len = ans[j];
- for (int i = 0;i
- {
- printf("%c",input[i+ans[j]]);
- returnans[count++] = input[i+ans[j]];
- }
- }
- printf("\n");
- returnans[count++] = '\0';
- }
-
- return returnans;
- }
欢迎于本文评论下或hero上
show your code。
参考文献及推荐阅读
- http://zhedahht.blog.163.com/blog/static/25411174200731139971/;
- http://hero.pongo.cn/,本文大部分代码都取自左边hero上参与答题者提交的代码,欢迎你也去挑战;
- 字符串转换成整数题目完整描述:http://hero.pongo.cn/Question/Details?ID=47&ExamID=45;
- 字符串匹配问题题目完整描述:http://hero.pongo.cn/Question/Details?ID=28&ExamID=28;
- linux3.8.4版本下的相关字符串整数转换函数概览:https://git.kernel.org/cgit/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git/tree/lib/vsprintf.c?id=refs/tags/v3.9.4;
- 关于linux中的likely和unlikely:http://blog.21ic.com/user1/5593/archives/2010/68193.html;
- 如果你喜欢编程挑战,除了topcoder和hero,你应该还多去leetcode上逛逛:http://leetcode.com/onlinejudge;
- atio函数的实现:http://iyenn.com/rec/1691809.html;
- atoi函数的实现: linux内核atoi函数的测试:http://iyenn.com/rec/1691810.html;
- Nut/OS中atoi函数的实现:http://www.ethernut.de/api/atoi_8c_source.html;
- 一读者写的hero上“字符串转换成整数”一题的解题报告(测试正确):http://iyenn.com/rec/1691811.html;
注:本文转载自blog.csdn.net的v_JULY_v的文章"http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/9024123"。版权归原作者所有,此博客不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。如有侵权,请联系我们删除。




评论记录:
回复评论: