CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。从某种程度上说,这项能力是它的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
CompletableFuture的继承结构如下:
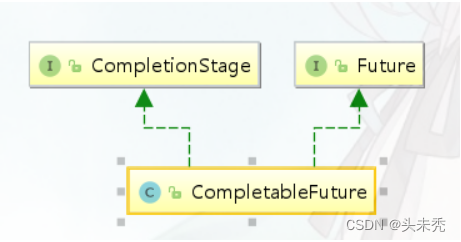
CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,执行某一阶段,可以向下执行后续阶段。异步执行的,默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),但为了业务之间互不影响,且便于定位问题,强烈推荐使用自定义线程池。
1、创建异步操作
CompletableFuture提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作:
//以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);
//以Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
这四个方法的区别:
runAsync():以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果。
supplyAsync():以Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier接口的 get()是有返回值的(会阻塞)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
使用没有指定Executor的方法时,内部使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。没有指定线程池的情况下CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是 CPU 的核数(也可以通过 JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism 来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰。
2、结果处理
方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
//当异步任务发生异常的时触发此方法,可以用来返回一个默认值
CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
//当异步任务完成(不管是正常完成还是异常完成都会触发)之后触发,可以用来进行后续操作,无法修改返回值
CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor);
//当异步任务完成(不管是正常完成还是异常完成都会触发)之后触发,如果是异常完成(异步任务的结果如果为 null则发生异常,否则为正常完成)可以用来返回默认值;如果是正常完成可以用来进行后续操作,并返回结果。
<U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
<U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
<U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
exceptionally()
一般与whenComplete()配合使用,异常捕获范围包含前面的所有异步线程
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).exceptionally(excption -> {
//可以感知异常,同时返回默认数据
System.out.println("执行发生异常,返回默认数据,异常信息为:" + excption);
return 10;
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
执行结果:
当前线程号:20
执行发生异常,返回默认数据,异常信息为:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
执行结果为:10
- 1
- 2
- 3
whenComplete()
一般与exceptionally()配合使用,获取前一个异步线程的结果和异常
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).whenCompleteAsync((res,excption) -> {
//虽然能得到异常信息,但是没法修改返回数据
System.out.println("异步任务成功执行....结果是:"+res+",异常是:"+excption);
},threadPool);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
当前线程号:20
运行结果:5
异步任务成功执行....结果是:5,异常是:null
执行结果为:5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
handle()
获取前一个异步线程的结果和异常,根据是否有异常产生执行不一样的逻辑
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
//int i = 10 / 0;
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).handle((res,excption) -> {
//异步方法执行完的后续处理
if (excption != null){
System.out.println("执行发生异常,返回默认数据,异常信息为:" + excption);
return 10;
}
System.out.println("异步任务成功执行....上一步的结果是:"+res);
return res*2;
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
执行结果:
发生异常(int i = 10 / 0)时
当前线程号:20
执行发生异常,返回默认数据,异常信息为:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
执行结果为:10
成功执行(int i = 10 / 2)时
当前线程号:20
运行结果:5
异步任务成功执行....上一步的结果是:5
执行结果为:10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3、线程穿行
方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
//不能获取上一步的执行结果,也没有自己的返回值
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable var1);
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable var1);
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable var1, Executor var2);
//能获取上一步的结果,但是没有自己返回值
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> var1);
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> var1);
ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> var1, Executor var2);
//能获取上一步的结果,而且有自己的返回值
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T, ? extends U> var1);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends U> var1);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends U> var1, Executor var2);
//能获取上一步的结果,而且有自己的返回值
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> var1);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenCompose(BiFunction<? super T, ? super Throwable, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> var1);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> var1);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> var1, Executor var2);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
thenRun()
不能获取上一步的执行结果,也没有自己的返回值
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
},threadPool);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
执行结果为:null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
thenAccept()
能获取上一步的结果,但是没有自己返回值
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("上个任务的结果:"+res);
},threadPool);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
上个任务的结果:5
执行结果为:null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
thenApply()
能获取上一步的结果,而且有自己的返回值,并且自己的返回值类型可以与上一个返回值的类型不一致
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).thenApplyAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("上个任务的结果:"+res);
return res*2+"个";
},threadPool);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
上个任务的结果:5
执行结果为:10个
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
thenCompose()
能获取上一步的结果,而且有自己的返回值,与thenApply()具有相同的功能
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool).thenComposeAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("上个任务的结果:" + res);
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return res * 2 + "个";
});
}, threadPool);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
上个任务的结果:5
执行结果为:10个
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
与thenApply()的区别:
thenApply():返回的不是CompletableFuture类型
它的功能相当于将CompletableFuture转换成CompletableFuture
thenCompose():用来连接两个CompletableFuture,返回值是新的CompletableFuture
- 1
- 2
- 3
4、两个任务组合-都要完成
有点类似于 AND。方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
//当两个任务都正常完成时,执行给定的操作
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2, Executor var3);
//当两个任务都正常完成时,使用两个结果作为参数,执行给定的操作,没有返回值
<U> ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> var2);
<U> ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> var2);
<U> ConnectionFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> var2, Executor var3);
//当两个任务都正常完成时,使用两个结果作为参数,执行给定的操作,有返回值
<U, V> ConnectionFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiFunction<? super T, ? super U, ? extends V> var2);
<U, V> ConnectionFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiFunction<? super T, ? super U, ? extends V> var2);
<U, V> ConnectionFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> var1, BiFunction<? super T, ? super U, ? extends V> var2, Executor var3);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
runAfterBoth()
两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务),没有使用前面两个任务的结果,也没有返回值
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = future1.runAfterBoth(future2, () -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,没有参数,没有返回值");
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
组合任务,当前线程号:1
执行指定操作,没有参数,没有返回值
执行结果为:null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
thenAcceptBoth()
两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAcceptBoth处理,可以使用前面两个任务的结果,但无自己的返回值
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = future1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, (res1,res2) -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,前面任务的结果为:"+res1+","+res2+"。没有自己的返回值");
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
组合任务,当前线程号:1
执行指定操作,前面任务的结果为:5,2。没有自己的返回值
执行结果为:null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
thenCombine()
两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenCombine处理,可以使用前面两个任务的结果,也有自己的返回值
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<String> future = future1.thenCombineAsync(future2, (res1, res2) -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,前面任务的结果为:"+res1+","+res2+"。有自己的返回值");
return res1 + res2 + "个";
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
组合任务,当前线程号:22
执行指定操作,前面任务的结果为:5,2。有自己的返回值
执行结果为:7个
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
5、两个任务组合-一个完成即可
有点类似于OR。方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
//两个异步任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> var1, Runnable var2, Executor var3);
//两个异步任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的消费操作。
ConnectionFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Consumer<? super T> var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Consumer<? super T> var2);
ConnectionFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Consumer<? super T> var2, Executor var3);
//两个异步任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作。
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Function<? super T, U> var2);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Function<? super T, U> var2);
<U> ConnectionFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> var1, Function<? super T, U> var2, Executor var3);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
runAfterEither()
两个异步任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = future1.runAfterEither(future2, () -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,没有参数,没有自己的返回值");
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:1
组合任务,当前线程号:21
执行指定操作,没有参数,没有自己的返回值
执行结果为:null
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
acceptEither()
两个异步任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的消费操作(即没有自己的返回值)。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = future1.acceptEither(future2, res -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,前面执行快的任务结果为:"+res+",没有自己的返回值");
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:0
组合任务,当前线程号:1
执行指定操作,前面执行快的任务结果为:0,没有自己的返回值
执行结果为:null
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
applyToEither()
两个异步任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作(即有自己的返回值)。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<String> future = future1.applyToEither(future2, res -> {
System.out.println("组合任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("执行指定操作,前面执行快的任务结果为:"+res+",有自己的返回值");
return res + "秒";
});
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
组合任务,当前线程号:20
执行指定操作,前面执行快的任务结果为:2,有自己的返回值
执行结果为:2秒
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:9
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
6、多任务组合
以下方法都为静态方法
anyOf()
在给定多个异步任务第一个完成时,就马上返回一个新的 CompletableFuture。结果与其第一个完成的异步任务相同。即第一个异常完成则最终结果为异常完成,第一个正常完成则最终结果为正常完成。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第三个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Object> future = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2, future3);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第三个任务,当前线程号:22
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:1
执行结果为:1
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
allOf()
1、当给定的多个异步任务都正常完成后,返回一个新的 CompletableFuture,给定 CompletableFuture 的结果不会反映在返回的 CompletableFuture 中,但可以通过单独检查给定任务来获得结果。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 5;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第三个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 2;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
System.out.println("future1:"+future1.get());
System.out.println("future2:"+future2.get());
System.out.println("future3:"+future3.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第三个任务,当前线程号:22
第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:7
执行结果为:null
future1:7
future2:5
future3:2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2、当任何一个异步任务异常完成,则返回的CompletableFuture 也会异常完成,并且将该异步任务的异常作为其原因。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 5;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第三个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 2;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
throw new ArithmeticException();
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第三个任务,当前线程号:22
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.reportGet(CompletableFuture.java:357)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.get(CompletableFuture.java:1908)
at com.itcxc.common.test.ThreadTest.main(ThreadTest.java:116)
Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException
at com.itcxc.common.test.ThreadTest.lambda$main$2(ThreadTest.java:113)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1604)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
3、当存在多个异常完成时,则返回排在前面的异步任务的异常信息。
具体使用:
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第一个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
return number;
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第二个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 5;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
throw new NullPointerException();
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("第三个任务,当前线程号:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int number = 2;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:" + number);
throw new ArithmeticException();
}, threadPool);
final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
System.out.println("执行结果为:"+future.get());
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
执行结果:
第一个任务,当前线程号:20
第二个任务,当前线程号:21
第三个任务,当前线程号:22
第三个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第一个任务,任务结束,运行结果:2
第二个任务,任务结束,运行结果:5
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.NullPointerException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.reportGet(CompletableFuture.java:357)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.get(CompletableFuture.java:1908)
at com.itcxc.common.test.ThreadTest.main(ThreadTest.java:116)
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.itcxc.common.test.ThreadTest.lambda$main$1(ThreadTest.java:102)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

评论记录:
回复评论: