最近聊天机器人非常火,我的微信AI助手系列,也陆续给大家分享了四种实现。
很多小伙伴问:这玩意儿有啥用?
今天突发奇想:何不给父母做个 24 小时陪伴式 AI ,接入微信呢?平时不能在他们身边,让小助理替我尽尽孝,顺便也让他们零距离感受下 AI 的力量。
说干就干!
花了一天时间,总算把这个 bot 给捏出了模样。
邀请进群,我给简单做个示范,大伙跟它聊的不亦乐乎,我反倒成了局外人…
群聊截图:
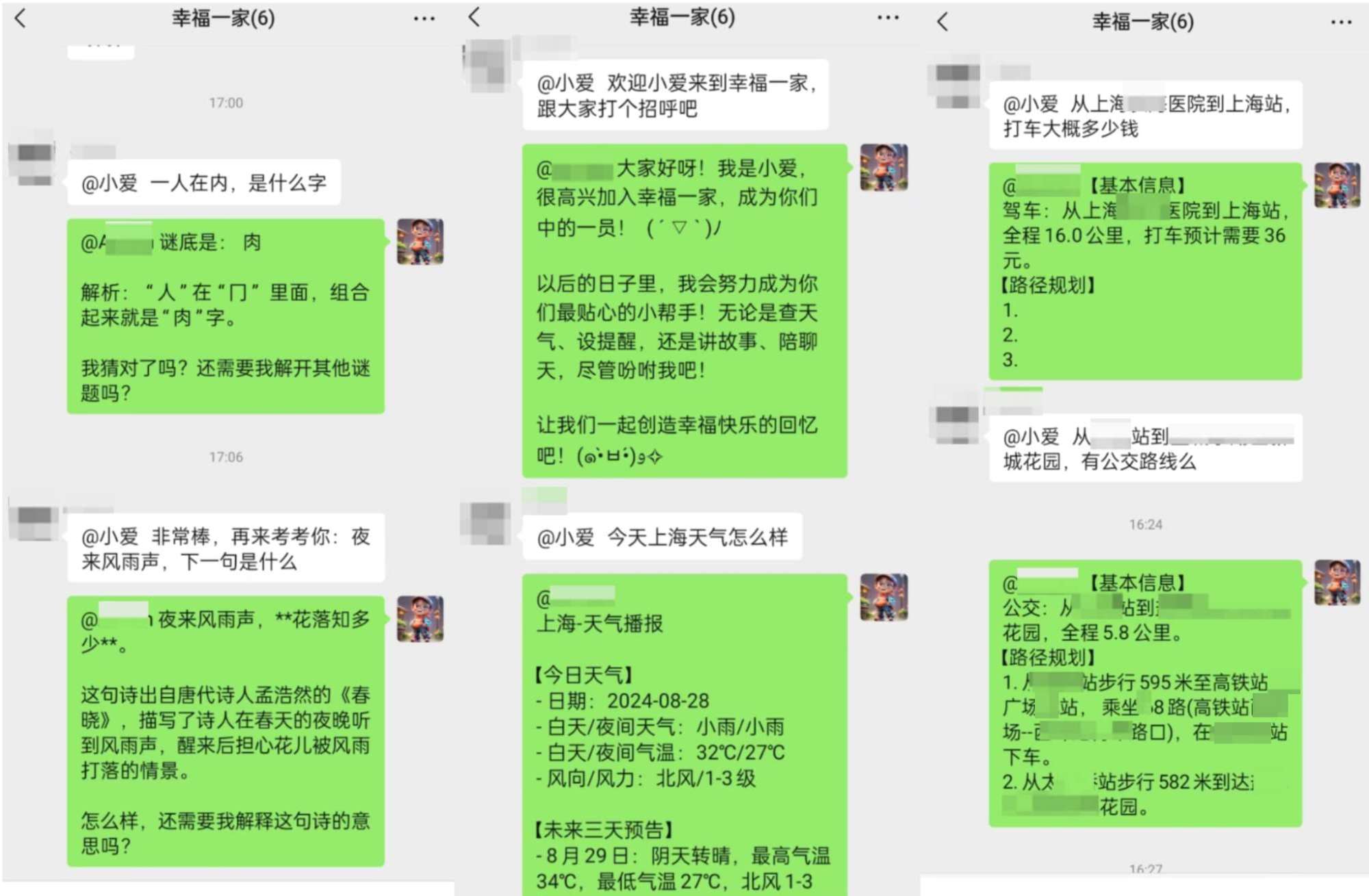
私聊截图:

今天,给大家分享下 bot 制作过程,希望对感兴趣的你有所启发。
为了大部分同学能快速上手,基于全程零风险,无费用的原则,整体技术方案主要包括三个部分:
- 本地生活服务API:为了减少大模型幻觉,同时提供和本地生活相关的可靠信息,考虑接入本地生活服务接口,这里我们采用高德开放平台提供的API,实现天气查询、路径规划、景点推荐等功能。
- 免费的大模型API:尽管免费的 API 有速率限制,不过对于个人使用而言,完全足够!之前给大家盘点了免费且靠谱的大模型 API,统一封装,任性调用,赶紧用起来!
- 微信机器人开发框架:之前分享过三种微信机器人的搭建方案,要么账号容易被封,要么需付费使用,有没有零风险,零付费的方案?有,还不了解的小伙伴,赶紧去?搭建微信机器人的第4种方式,免费开源,轻量高效.
由于篇幅较长,本教程将分为上下篇:本篇将首先介绍高德开放平台的各类API的功能和使用;下篇将介绍如何结合本地生活服务API和免费的大模型API,打造一个有学识更有温度的微信AI机器人。
友情提醒:注册小号使用,严禁用于违法用途(如发送广告/群发/诈骗、色情、政治等内容),否则封号是早晚的事哦。
1. 高德开放平台注册
首先前往控制台,创建一个应用,然后申请一个 key:
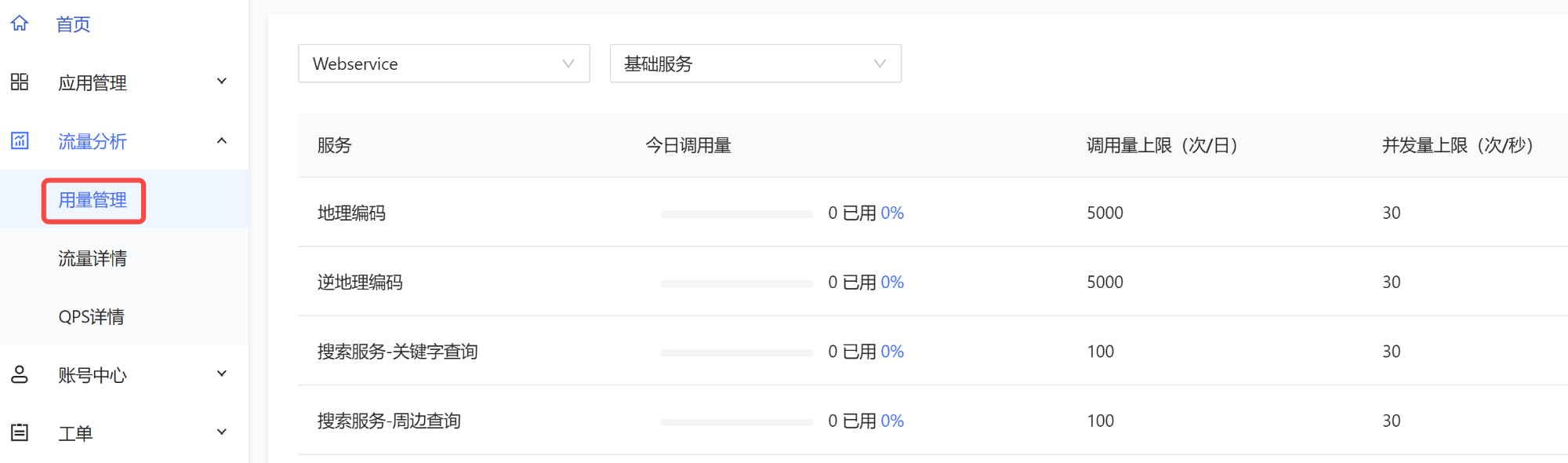
这里,可以查看各个 API 的调用量和并发量限制:
2. API 功能和调用
本节,将介绍 bot 中会使用到的各类 API。
我们首先将请求部分的代码进行封装,以便后面调用:
def get_api_response(url, params):
try:
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
data = response.json() # 解析JSON响应
return data
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求失败: {e}")
return None
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2.1 地理/逆地理编码API
由于后续功能都需要地址信息,所以首先需要了解下这个 API。
什么是地理/逆地理编码?
- 地理编码:将地址转换为经纬度坐标,支持名胜景区、建筑物名称。例:北京市朝阳区阜通东大街6号:116.480881,39.989410;
- 逆地理编码:将经纬度转换为地址,且返回附近周边的 POI 信息等。
核心请求参数介绍:
- address:结构化地址,遵循:国家、省份、城市、区县、城镇、乡村、街道、门牌号码、大厦,如:北京市朝阳区阜通东大街6号。
- city:指定查询的城市。
下面给出示例代码:
def get_adcode(address='', city=''):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/geocode/geo"
if not address:
address = city
params = {
"address": address,
"city": city,
"key": api_key
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
建议直接输入 address,会自动匹配到对应的城市,给大家看下北京海淀的请求结果:
{
"status": "1",
"info": "OK",
"infocode": "10000",
"count": "1",
"geocodes": [
{
"formatted_address": "北京市海淀区",
"country": "中国",
"province": "北京市",
"citycode": "010",
"city": "北京市",
"district": "海淀区",
"township": [],
"neighborhood": {
"name": [],
"type": []
},
"building": {
"name": [],
"type": []
},
"adcode": "110108",
"street": [],
"number": [],
"location": "116.297700,39.959893",
"level": "区县"
}
]
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
2.2 天气查询API
核心请求参数介绍:
- key:控制台申请的key;
- city:城市编码 adcode,可参考城市编码表,不过不建议将编码直接写死在程序中,而是通过地理/逆地理编码等线上服务获取adcode;
- extensions:气象类型,base:返回实况天气,all:返回预报天气(未来四天)
有了上面的地理/逆地理编码API,我们可以根据输入的地址信息,查询到 adcode。为此,天气查询的请求代码可以编写如下:
def get_weather(address='', adcode='', extensions='all'):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo"
if address:
res = get_adcode(address=address)
if res and res.get('status') == '1':
adcode = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('adcode')
if not adcode:
return None
params = {
"key": api_key,
"city": adcode,
"extensions": extensions
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
注:街道没有独有的 adcode,均继承父类(区县)的 adcode。
给大家看下天气的请求结果:
{
"status": "1",
"count": "1",
"info": "OK",
"infocode": "10000",
"lives": [
{
"province": "上海",
"city": "杨浦区",
"adcode": "310110",
"weather": "晴",
"temperature": "33",
"winddirection": "西",
"windpower": "≤3",
"humidity": "58",
"reporttime": "2024-08-26 17:01:14",
"temperature_float": "33.0",
"humidity_float": "58.0"
}
]
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
2.3 路径规划API
推荐使用路线规划接口2.0,支持驾车、公交、步行、骑行、电动车路线规划。
驾车路线规划
核心请求参数介绍:
- origin:起点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- destination:终点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- strategy:算路策略,默认同高德地图APP
因为获取地理位置信息比较通用,所以可以先把这个功能抽象出来:
def get_address(origin='', ret_city=False):
res = get_adcode(address=origin)
data = {}
if res and res.get('status') == '1':
data['location'] = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('location')
if ret_city:
data['city'] = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('city')
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
驾车路线规划的示例代码如下:
def get_driving(origin='', destination='', strategy=32):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5/direction/driving"
data_origin = get_address(origin)
data_destination = get_address(destination)
if not (data_origin and data_destination):
return None
params = {
"key": api_key,
"origin": data_origin['location'],
"destination": data_destination['location'],
"strategy": strategy
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
给大家看下请求结果:
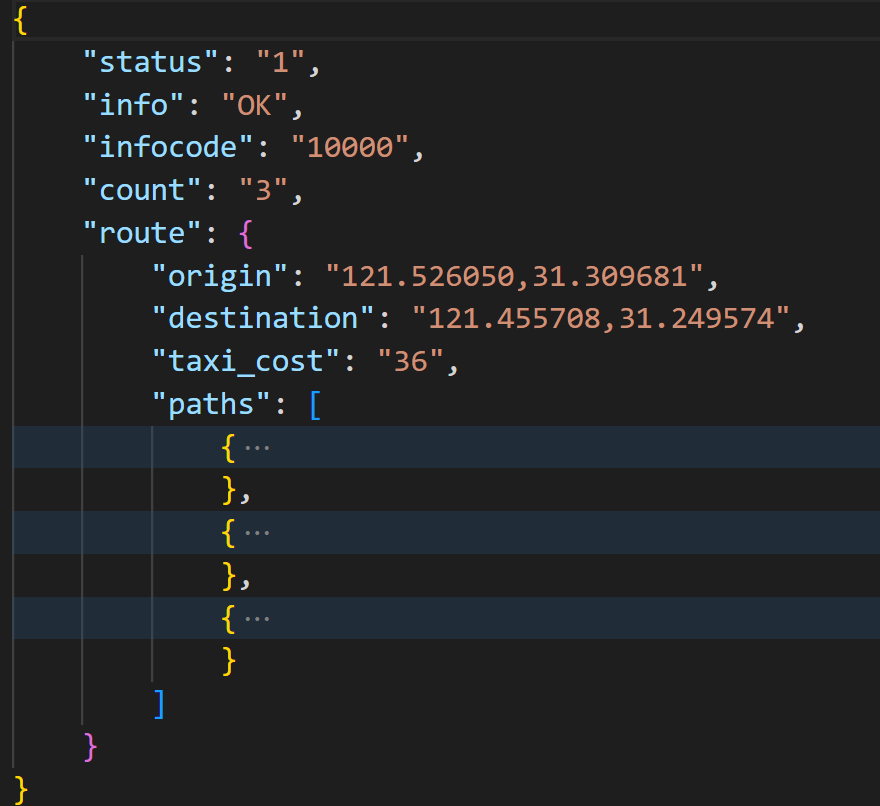
结果中,给出了预估的打车费用,并返回三条路径规划。
步行路线规划
核心请求参数介绍:
- origin:起点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- destination:终点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- alternative_route:返回路线条数,默认返回一条
步行路线规划的示例代码如下:
def get_walking(origin='', destination='', alternative_route=1):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5/direction/walking"
address = get_address(origin, destination)
if not address:
return None
params = {
"key": api_key,
"origin": address[0],
"destination": address[1],
"alternative": alternative_route
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
请求结果如下:
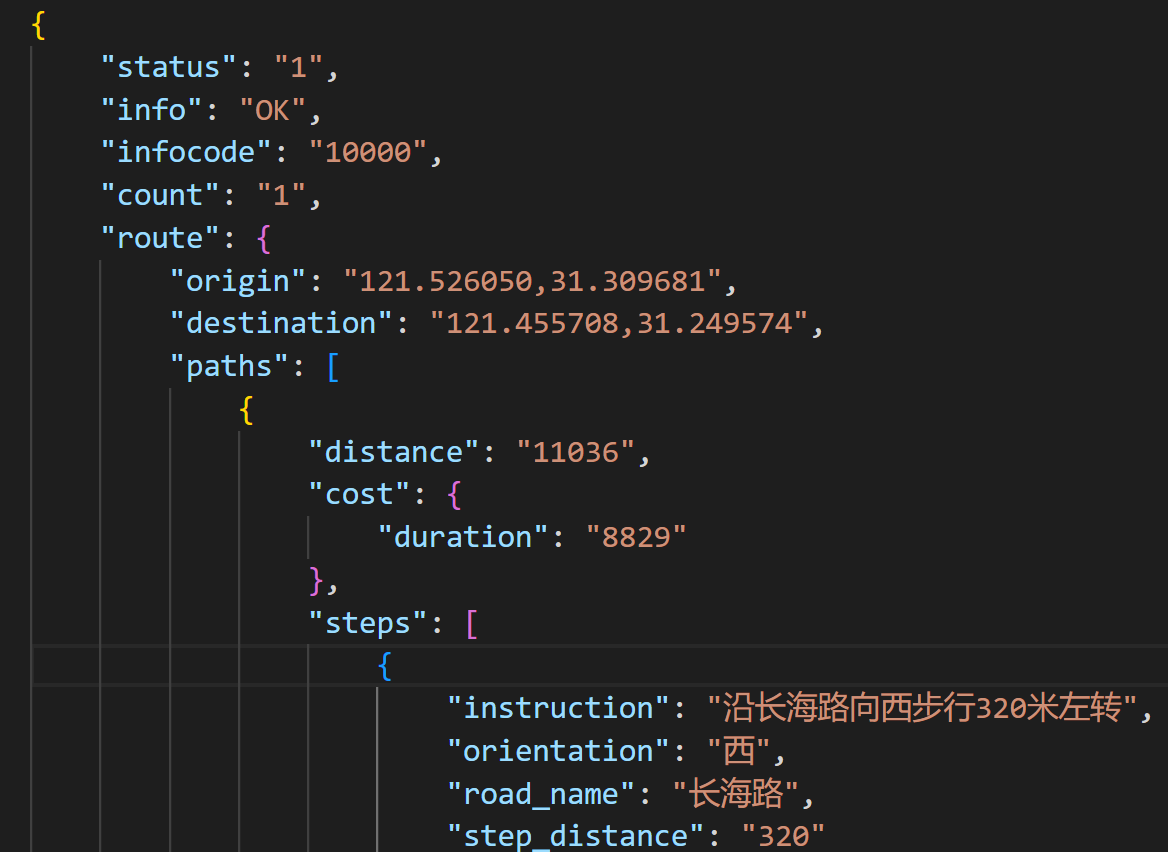
其中,distance 代表距离,单位-米;duration 代表耗时,单位-秒。
骑行路线规划
和步行路线规划的使用方式基本一致,一起看下请求结果:
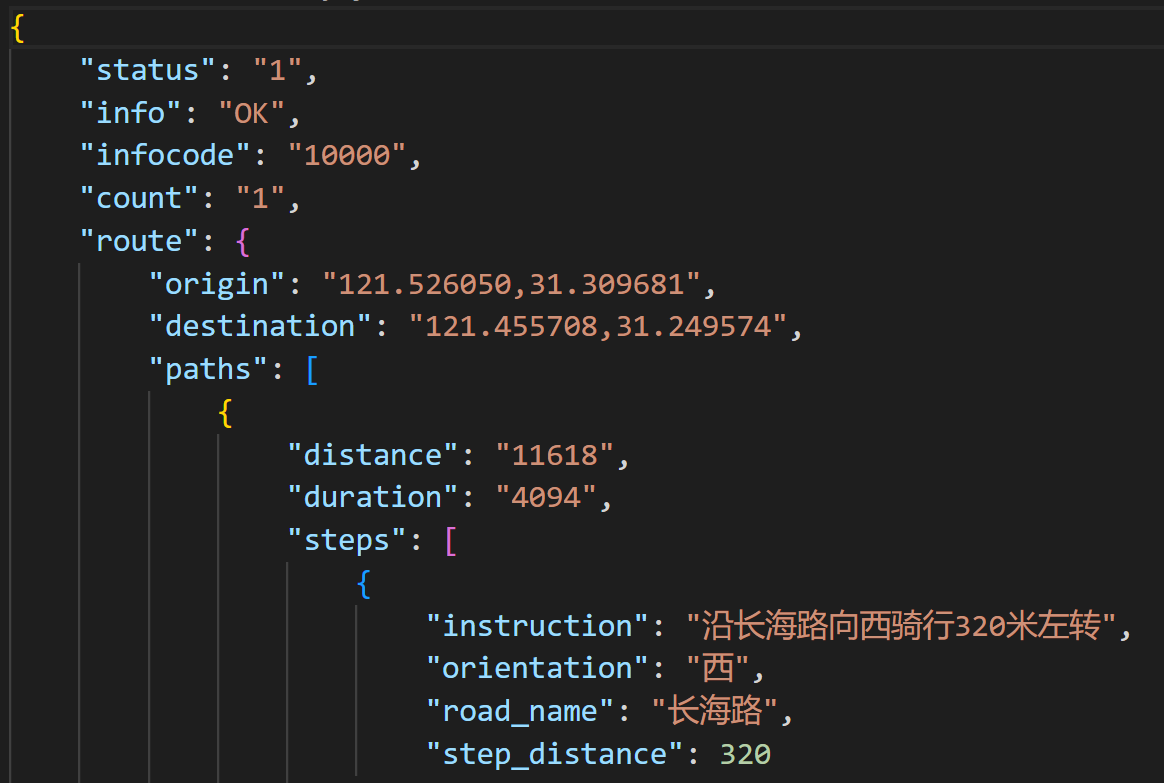
公交路线规划
核心请求参数介绍:
- origin:起点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- destination:终点经纬度,可以根据地理编码API获得
- alternative_route:返回路线条数,默认返回一条
- city1: 必填,起点所在城市
- city2: 必填,终点所在城市,二者相同代表同城,不同代表跨城
示例代码如下:
def get_bus(origin='', destination='', strategy=0, AlternativeRoute=1):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5/direction/transit/integrated"
data_origin = get_address(origin, ret_city=True)
data_destination = get_address(destination, ret_city=True)
if not (data_origin and data_destination):
return None
res = get_adcode(city=data_origin['city'])
c1_code = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('citycode') if res and res.get('status') == '1' else ''
res = get_adcode(city=data_destination['city'])
c2_code = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('citycode') if res and res.get('status') == '1' else ''
if not c1_code or not c2_code:
return None
params = {
"key": api_key,
"origin": data_origin['location'],
"destination": data_destination['location'],
"city1": c1_code,
"city2": c2_code,
"strategy": strategy,
"AlternativeRoute": AlternativeRoute
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
请求结果如下:
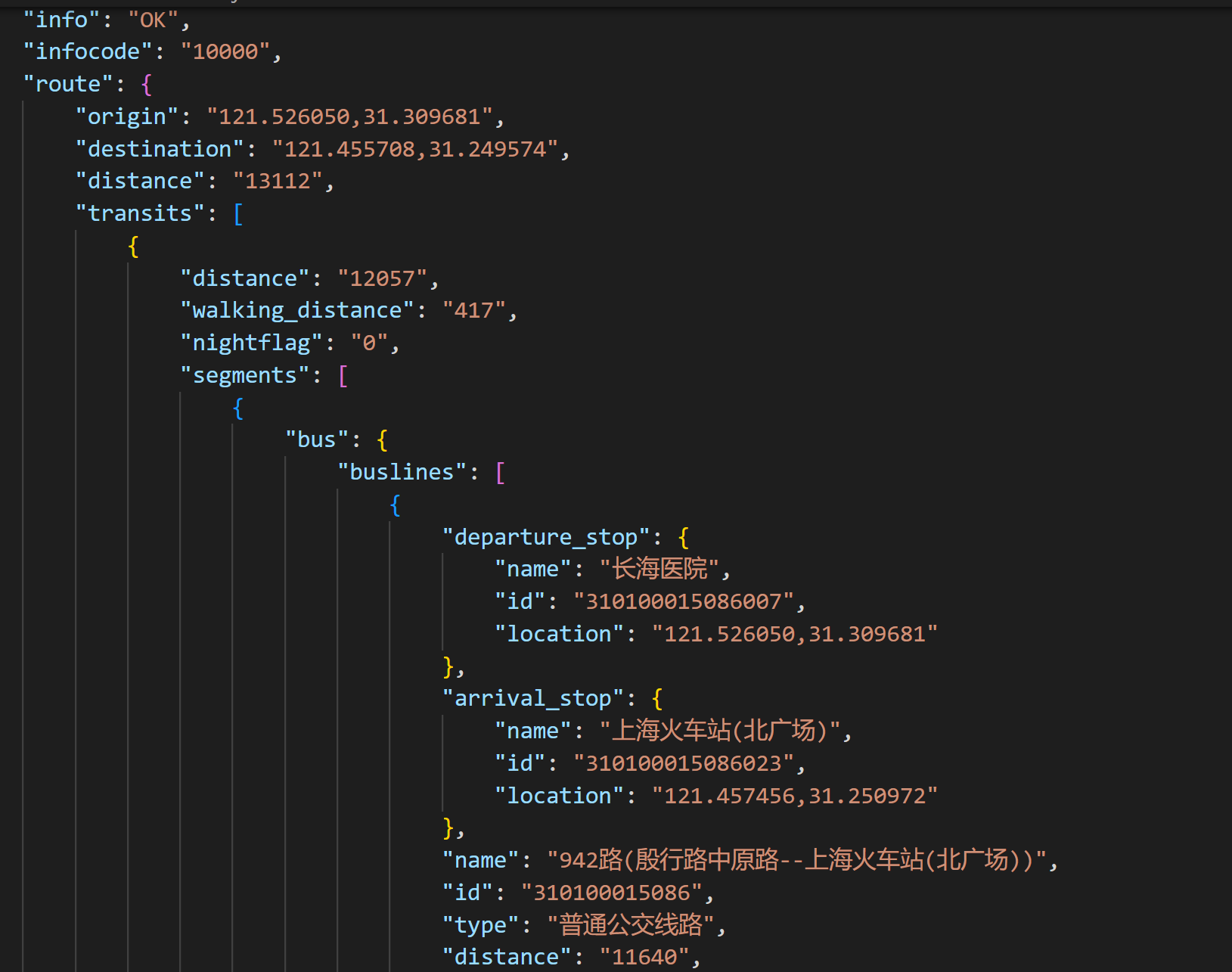
2.4 搜索POI API
搜索POI有两种方式:
- 关键词搜索;
- 基于地址的周边搜索
关键词搜索:
核心请求参数介绍:
- keywords:地点关键词,需要被检索的地点文本信息。
- region:可输入 citycode,adcode,cityname;cityname 仅支持城市级别和中文,如“北京市”
- city_limit: 为 true 时,仅召回 region 对应区域内数据;
示例代码:
def get_poi_keyword(keyword='', region='', city_limit=False):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/text"
res = get_adcode(city=region)
adcode = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('adcode') if res and res.get('status') == '1' else ''
city_limit = True if adcode else False
params = {
"key": api_key,
"keywords": keyword,
"region": adcode,
"citylimit": city_limit
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
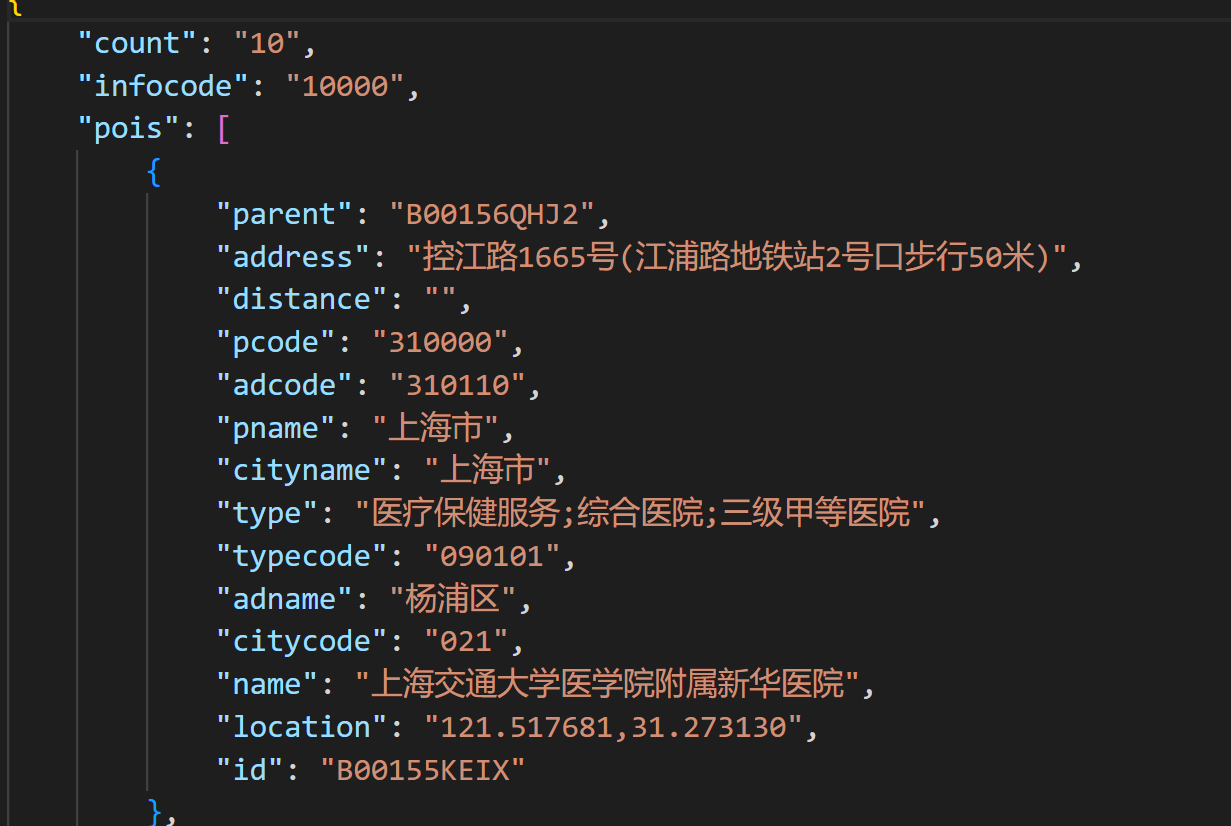
data = get_poi_keyword(keyword='医院', region='上海杨浦区')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
请求结果如下:
基于地址的周边搜索
核心请求参数介绍:
- keywords:地点关键词,需要被检索的地点文本信息。
- location:必填,中心点坐标
- region:可输入 citycode,adcode,cityname;cityname 仅支持城市级别和中文,如“北京市”
- city_limit: 为 true 时,仅召回 region 对应区域内数据;
示例代码如下:
def get_poi_around(keyword='', region='', city_limit=False):
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/around"
res = get_adcode(city=region)
adcode = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('adcode') if res and res.get('status') == '1' else ''
location = res.get('geocodes')[0].get('location') if res and res.get('status') == '1' else ''
city_limit = True if adcode else False
params = {
"key": api_key,
"keywords": keyword,
"location": location,
"region": adcode,
"citylimit": city_limit
}
data = get_api_response(url, params)
return data
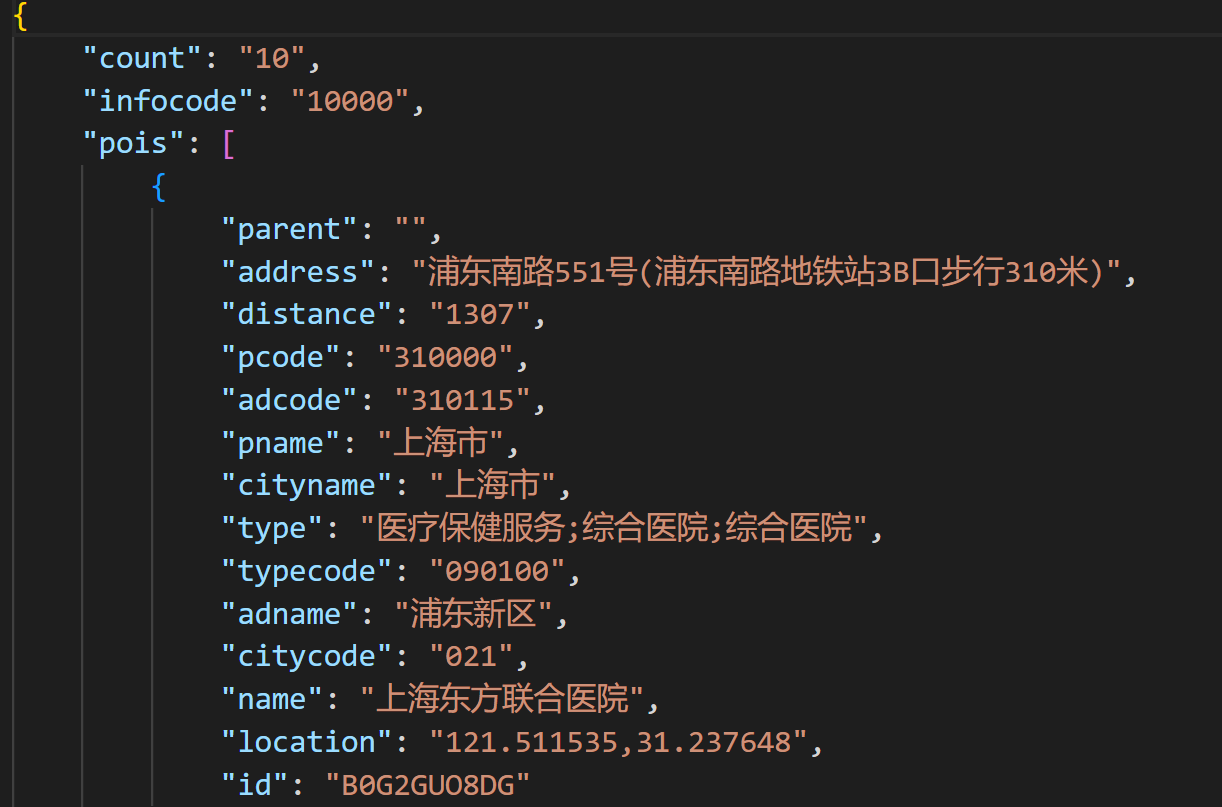
data = get_poi_around(keyword='医院', region='上海东方明珠')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
请求结果如下:
写在最后
随着小爱(AI)的加入,家庭群变得活跃起来了。爸妈和这个可爱的 bot 交流,毫无距离感。
所以,AI 不应是冰冷的代码,而应是温暖人心、传递温情的桥梁。
本文带你玩转高德开放平台 API,有了这些API加持,小助手才能不仅陪爸妈聊天解闷,还能提供各种实用的本地生活信息。
下篇,我们将结合大模型 API,让这个 bot 不仅懂得多,还要有温度。敬请期待!
如果本文对你有帮助,不妨点个免费的赞和收藏备用,转发给身边的朋友。
最后,别忘了时不时陪陪父母,毕竟再智能的AI也替代不了你的陪伴。
为了方便大家交流,新建了一个 AI 交流群,欢迎感兴趣的小伙伴加入。
小爱也在群里,想进群体验的朋友,公众号后台「联系我」即可,拉你进群。

 微信公众号
微信公众号



评论记录:
回复评论: