概述
UIAbility组件是一种包含UI的应用组件,主要用于和用户交互。
UIAbility的设计理念:
-
原生支持应用组件级的跨端迁移和多端协同。
-
支持多设备和多窗口形态。
UIAbility划分原则与建议:
UIAbility组件是系统调度的基本单元,为应用提供绘制界面的窗口。一个应用可以包含一个或多个UIAbility组件。例如,在支付应用中,可以将入口功能和收付款功能分别配置为独立的UIAbility。
每一个UIAbility组件实例都会在最近任务列表中显示一个对应的任务。
对于开发者而言,可以根据具体场景选择单个还是多个UIAbility,划分建议如下:
-
如果开发者希望在任务视图中看到一个任务,则建议使用一个UIAbility,多个页面的方式。
-
如果开发者希望在任务视图中看到多个任务,或者需要同时开启多个窗口,则建议使用多个UIAbility开发不同的模块功能。
声明配置
为使应用能够正常使用UIAbility,需要在 module.json5配置文件 的 abilities标签 中声明UIAbility的名称、入口、标签等相关信息。
{
"module": {
...
"abilities": [
{
"name": "EntryAbility", // UIAbility组件的名称
"srcEntry": "./ets/entryability/EntryAbility.ets", // UIAbility组件的代码路径
"description": "$string:EntryAbility_desc", // UIAbility组件的描述信息
"icon": "$media:icon", // UIAbility组件的图标
"label": "$string:EntryAbility_label", // UIAbility组件的标签
"startWindowIcon": "$media:icon", // UIAbility组件启动页面图标资源文件的索引
"startWindowBackground": "$color:start_window_background", // UIAbility组件启动页面背景颜色资源文件的索引
...
}
]
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
当用户打开、切换和返回到对应应用时,应用中的UIAbility实例会在其生命周期的不同状态之间转换。UIAbility类提供了一系列回调,通过这些回调可以知道当前UIAbility实例的某个状态发生改变,会经过UIAbility实例的创建和销毁,或者UIAbility实例发生了前后台的状态切换。
UIAbility的生命周期包括Create、Foreground、Background、Destroy四个状态,如下图所示。
图1 UIAbility生命周期状态

生命周期状态说明
Create状态
Create状态为在应用加载过程中,UIAbility实例创建完成时触发,系统会调用onCreate()回调。可以在该回调中进行页面初始化操作,例如变量定义资源加载等,用于后续的UI展示。
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
// 页面初始化
}
// ...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
说明
Want 是对象间信息传递的载体,可以用于应用组件间的信息传递。
WindowStageCreate和WindowStageDestroy状态
UIAbility实例创建完成之后,在进入Foreground之前,系统会创建一个WindowStage。WindowStage创建完成后会进入onWindowStageCreate()回调,可以在该回调中设置UI加载、设置WindowStage的事件订阅。
图2 WindowStageCreate和WindowStageDestroy状态

在onWindowStageCreate()回调中通过 loadContent() 方法设置应用要加载的页面,并根据需要调用 on(‘windowStageEvent’) 方法订阅WindowStage的 事件 (获焦/失焦、可见/不可见)。
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
const TAG: string = '[EntryAbility]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
// ...
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
// 设置WindowStage的事件订阅(获焦/失焦、可见/不可见)
try {
windowStage.on('windowStageEvent', (data) => {
let stageEventType: window.WindowStageEventType = data;
switch (stageEventType) {
case window.WindowStageEventType.SHOWN: // 切到前台
console.info('windowStage foreground.');
break;
case window.WindowStageEventType.ACTIVE: // 获焦状态
console.info('windowStage active.');
break;
case window.WindowStageEventType.INACTIVE: // 失焦状态
console.info('windowStage inactive.');
break;
case window.WindowStageEventType.HIDDEN: // 切到后台
console.info('windowStage background.');
break;
default:
break;
}
});
} catch (exception) {
console.error('Failed to enable the listener for window stage event changes. Cause:' + JSON.stringify(exception));
}
// 设置UI加载
windowStage.loadContent('pages/Index', (err, data) => {
// ...
});
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
说明
WindowStage的相关使用请参见 窗口开发指导 。
对应于onWindowStageCreate()回调。在UIAbility实例销毁之前,则会先进入onWindowStageDestroy()回调,可以在该回调中释放UI资源。
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[EntryAbility]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
windowStage: window.WindowStage | undefined = undefined;
// ...
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
this.windowStage = windowStage;
// ...
}
onWindowStageDestroy() {
// 释放UI资源
// 例如在onWindowStageDestroy()中注销获焦/失焦等WindowStage事件
try {
if (this.windowStage) {
this.windowStage.off('windowStageEvent');
}
} catch (err) {
let code = (err as BusinessError).code;
let message = (err as BusinessError).message;
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to disable the listener for windowStageEvent. Code is ${code}, message is ${message}`);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
WindowStageWillDestroy状态
对应onWindowStageWillDestroy()回调,在WindowStage销毁前执行,此时WindowStage可以使用。
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { window } from '@kit.ArkUI';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
windowStage: window.WindowStage | undefined = undefined;
// ...
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
this.windowStage = windowStage;
// ...
}
onWindowStageWillDestroy(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
// 释放通过windowStage对象获取的资源
}
onWindowStageDestroy() {
// 释放UI资源
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
说明
WindowStage的相关使用请参见 窗口开发指导 。
Foreground和Background状态
Foreground和Background状态分别在UIAbility实例切换至前台和切换至后台时触发,对应于onForeground()回调和onBackground()回调。
onForeground()回调,在UIAbility的UI可见之前,如UIAbility切换至前台时触发。可以在onForeground()回调中申请系统需要的资源,或者重新申请在onBackground()中释放的资源。
onBackground()回调,在UIAbility的UI完全不可见之后,如UIAbility切换至后台时候触发。可以在onBackground()回调中释放UI不可见时无用的资源,或者在此回调中执行较为耗时的操作,例如状态保存等。
例如应用在使用过程中需要使用用户定位时,假设应用已获得用户的定位权限授权。在UI显示之前,可以在onForeground()回调中开启定位功能,从而获取到当前的位置信息。
当应用切换到后台状态,可以在onBackground()回调中停止定位功能,以节省系统的资源消耗。
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
// ...
onForeground(): void {
// 申请系统需要的资源,或者重新申请在onBackground()中释放的资源
}
onBackground(): void {
// 释放UI不可见时无用的资源,或者在此回调中执行较为耗时的操作
// 例如状态保存等
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
当应用的UIAbility实例已创建,且UIAbility配置为 singleton 启动模式时,再次调用 startAbility() 方法启动该UIAbility实例时,只会进入该UIAbility的 onNewWant() 回调,不会进入其 onCreate() 和 onWindowStageCreate() 生命周期回调。应用可以在该回调中更新要加载的资源和数据等,用于后续的UI展示。
import { AbilityConstant, UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
// ...
onNewWant(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {
// 更新资源、数据
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Destroy状态
Destroy状态在UIAbility实例销毁时触发。可以在onDestroy()回调中进行系统资源的释放、数据的保存等操作。
例如调用 terminateSelf() 方法停止当前UIAbility实例,从而完成UIAbility实例的销毁;或者用户使用最近任务列表关闭该UIAbility实例,完成UIAbility的销毁。
import { UIAbility } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
// ...
onDestroy() {
// 系统资源的释放、数据的保存等
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
鸿蒙全栈开发全新学习指南
也为了积极培养鸿蒙生态人才,让大家都能学习到鸿蒙开发最新的技术,针对一些在职人员、0基础小白、应届生/计算机专业、鸿蒙爱好者等人群,整理了一套纯血版鸿蒙(HarmonyOS Next)全栈开发技术的学习路线【包含了大厂APP实战项目开发】。
本路线共分为四个阶段:
第一阶段:鸿蒙初中级开发必备技能
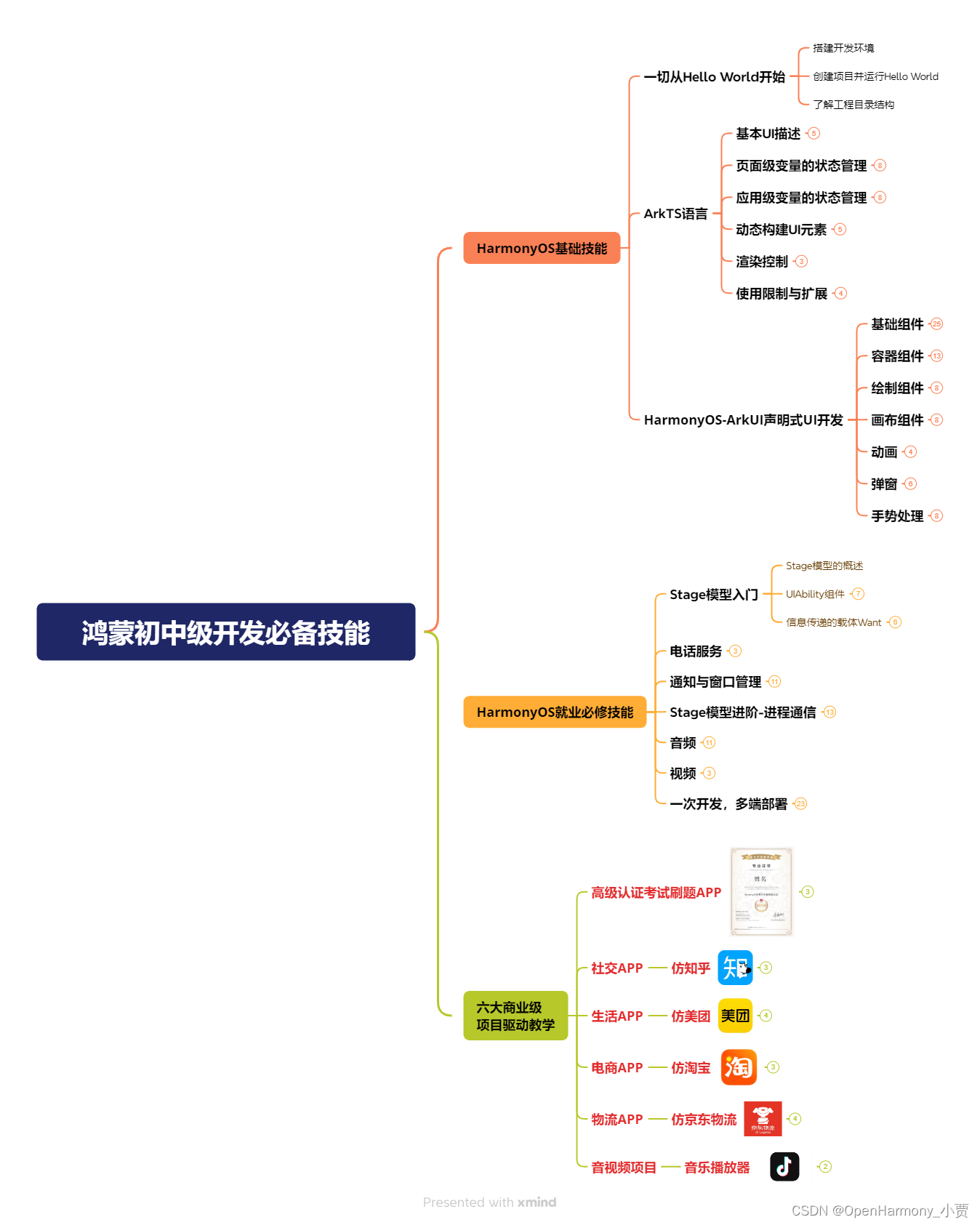
第二阶段:鸿蒙南北双向高工技能基础:gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH

第三阶段:应用开发中高级就业技术
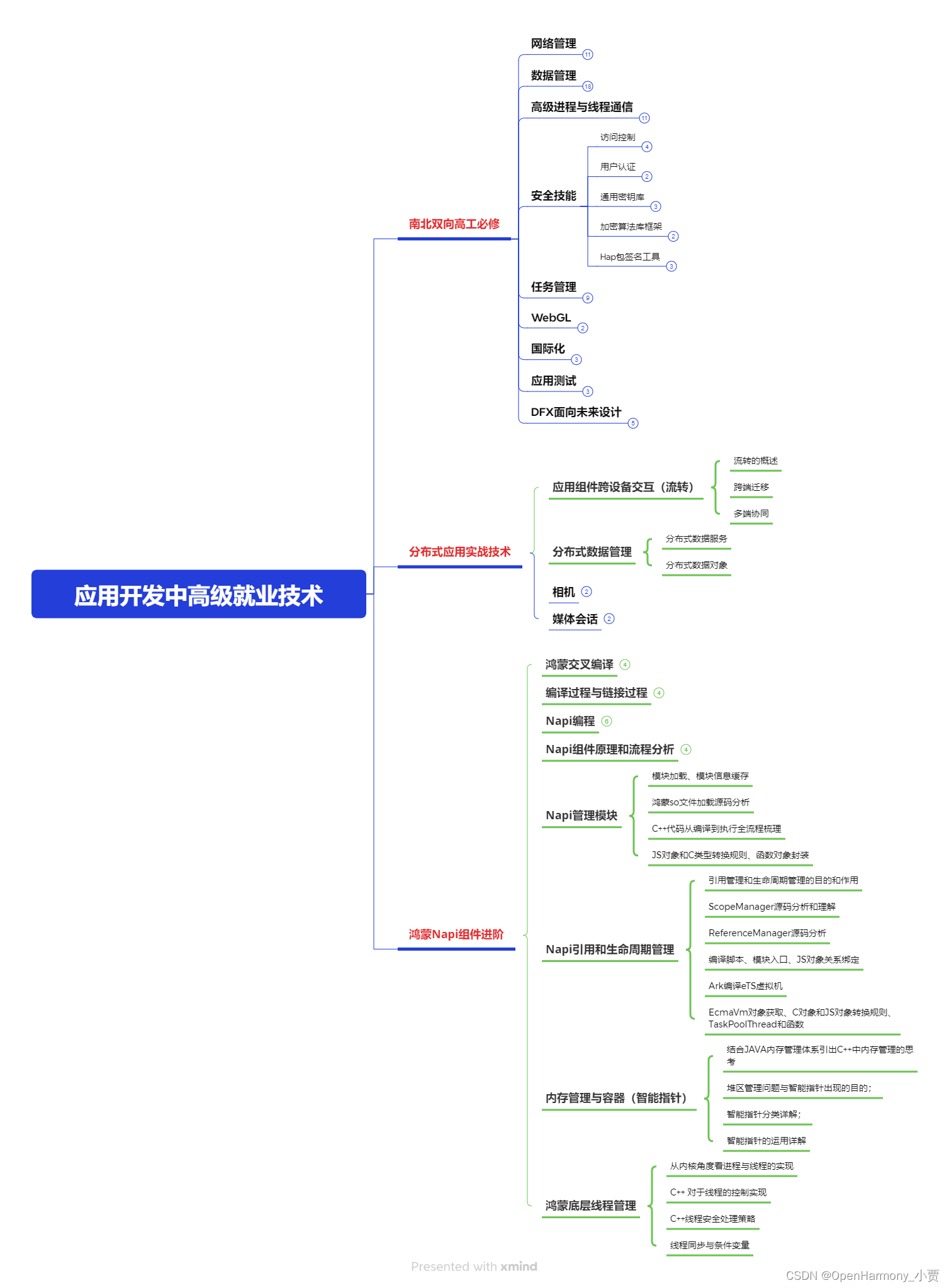
第四阶段:全网首发-工业级南向设备开发就业技术:gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH
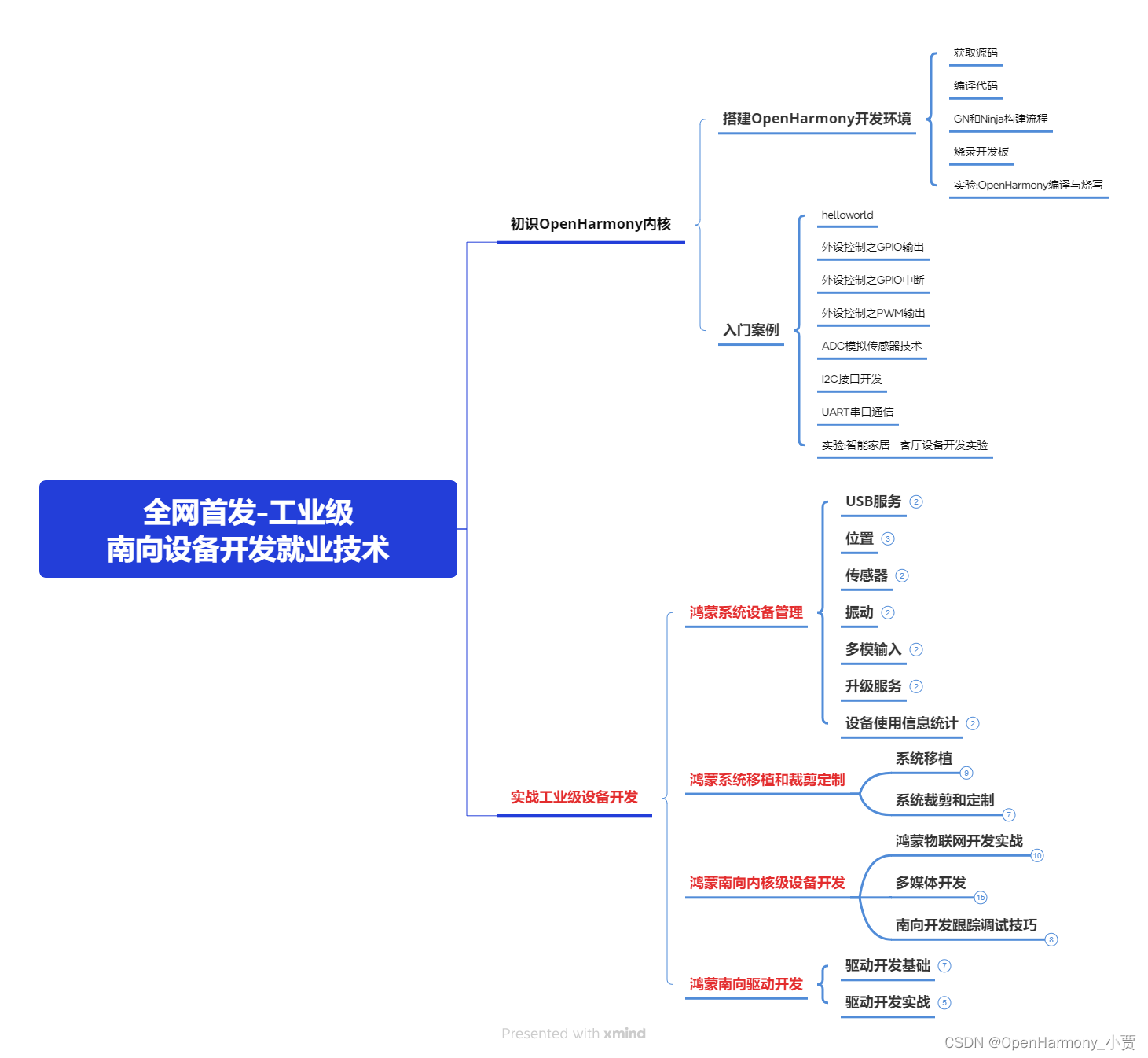
写在最后
- 如果你觉得这篇内容对你还蛮有帮助,我想邀请你帮我三个小忙:
- 点赞,转发,有你们的 『点赞和评论』,才是我创造的动力。
- 关注小编,同时可以期待后续文章ing?,不定期分享原创知识。
- 想要获取更多完整鸿蒙最新学习资源,请移步前往小编:
gitee.com/MNxiaona/733GH


 微信名片
微信名片



评论记录:
回复评论: