目录
0 环境配置
如果你在开始本节前遇到了环境配置方面的一些问题,欢迎阅读我之前写的一篇很详细文章:
⭐⭐[ pytorch+tensorflow ]⭐⭐配置两大框架下的GPU训练环境
1 前言
本文为2021吴恩达学习笔记deeplearning.ai《深度学习专项课程》篇——“第五课——Week1”章节的课后练习,完整内容参见:
深度学习入门指南——2021吴恩达学习笔记deeplearning.ai《深度学习专项课程》篇
2 一步步构建你的递归神经网络
欢迎来到课程5的第一份作业,在这里你将在NumPy中实现递归神经网络(RNN)的关键组件!
2.0 导包
- import numpy as np
- from rnn_utils import *
- from public_tests import *
2.1 基本RNN的正向传播
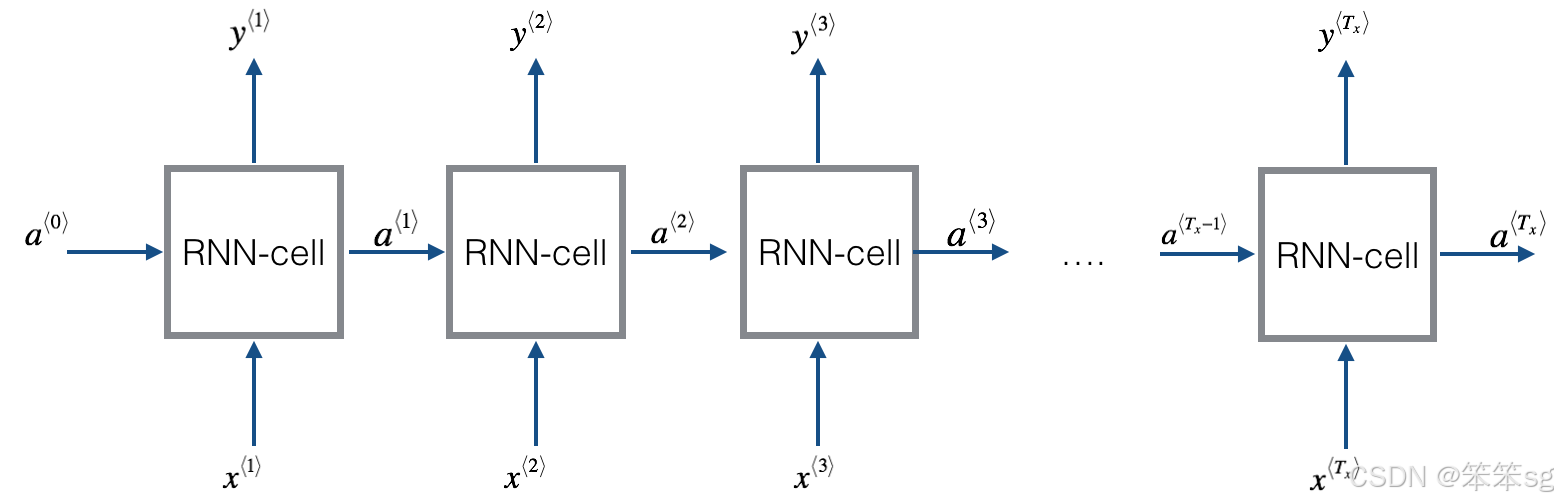
下面是实现RNN的方法,步骤:
1. 实现RNN一个时间步长所需的计算。
2. 在 时间步上实现一个循环,以便处理所有输入,一次一个。
时间步上实现一个循环,以便处理所有输入,一次一个。
RNN Cell
你可以把循环神经网络看作是对单个细胞的重复使用。首先,您将实现单个时间步长的计算。下图描述了RNN单元的单个时间步的操作:
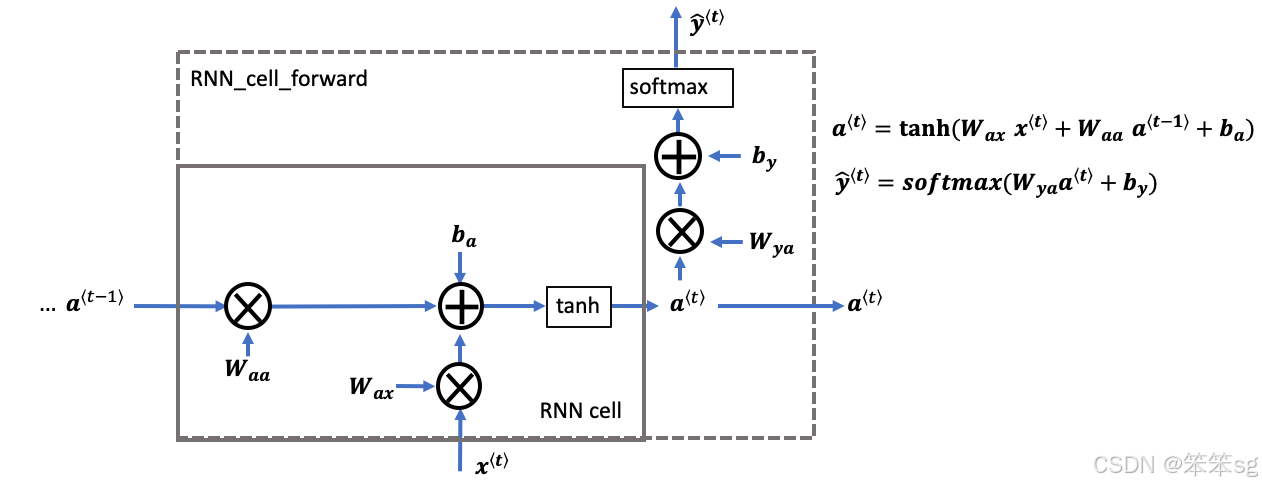
- # UNQ_C1 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: rnn_cell_forward
-
- def rnn_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, parameters):
-
- # Retrieve parameters from "parameters"
- Wax = parameters["Wax"]
- Waa = parameters["Waa"]
- Wya = parameters["Wya"]
- ba = parameters["ba"]
- by = parameters["by"]
-
- # compute next activation state using the formula given above
- a_next = np.tanh(np.dot(Waa,a_prev) + np.dot(Wax,xt) + ba)
- # compute output of the current cell using the formula given above
- yt_pred = softmax( np.dot(Wya,a_next) + by)
-
- # store values you need for backward propagation in cache
- cache = (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters)
-
- return a_next, yt_pred, cache
- np.random.seed(1)
- xt_tmp = np.random.randn(3, 10)
- a_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Waa'] = np.random.randn(5, 5)
- parameters_tmp['Wax'] = np.random.randn(5, 3)
- parameters_tmp['Wya'] = np.random.randn(2, 5)
- parameters_tmp['ba'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2, 1)
-
- a_next_tmp, yt_pred_tmp, cache_tmp = rnn_cell_forward(xt_tmp, a_prev_tmp, parameters_tmp)
- print("a_next[4] = \n", a_next_tmp[4])
- print("a_next.shape = \n", a_next_tmp.shape)
- print("yt_pred[1] =\n", yt_pred_tmp[1])
- print("yt_pred.shape = \n", yt_pred_tmp.shape)
-
- # UNIT TESTS
- rnn_cell_forward_tests(rnn_cell_forward)
a_next[4] =
[ 0.59584544 0.18141802 0.61311866 0.99808218 0.85016201 0.99980978
-0.18887155 0.99815551 0.6531151 0.82872037]
a_next.shape =
(5, 10)
yt_pred[1] =
[0.9888161 0.01682021 0.21140899 0.36817467 0.98988387 0.88945212
0.36920224 0.9966312 0.9982559 0.17746526]
yt_pred.shape =
(2, 10)
All tests passed
RNN前向传播
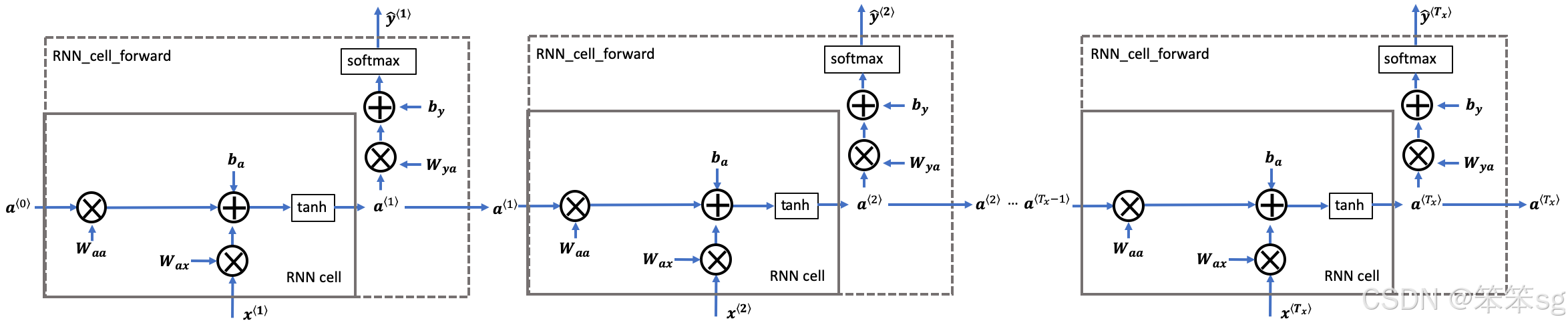
- # UNQ_C2 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: rnn_forward
-
- def rnn_forward(x, a0, parameters):
-
- # Initialize "caches" which will contain the list of all caches
- caches = []
-
- # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of x and parameters["Wya"]
- n_x, m, T_x = x.shape
- n_y, n_a = parameters["Wya"].shape
-
- # initialize "a" and "y_pred" with zeros (≈2 lines)
- a = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
- y_pred = np.zeros((n_y, m, T_x))
-
- # Initialize a_next (≈1 line)
- a_next = a0
-
- # loop over all time-steps
- for t in range(T_x):
- # Update next hidden state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line)
- a_next, yt_pred, cache = rnn_cell_forward(x[:,:,t], a_next, parameters)
- # Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line)
- a[:,:,t] = a_next
- # Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line)
- y_pred[:,:,t] = yt_pred
- # Append "cache" to "caches" (≈1 line)
- caches.append(cache)
-
- # store values needed for backward propagation in cache
- caches = (caches, x)
-
- return a, y_pred, caches
- np.random.seed(1)
- x_tmp = np.random.randn(3, 10, 4)
- a0_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Waa'] = np.random.randn(5, 5)
- parameters_tmp['Wax'] = np.random.randn(5, 3)
- parameters_tmp['Wya'] = np.random.randn(2, 5)
- parameters_tmp['ba'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2, 1)
-
- a_tmp, y_pred_tmp, caches_tmp = rnn_forward(x_tmp, a0_tmp, parameters_tmp)
- print("a[4][1] = \n", a_tmp[4][1])
- print("a.shape = \n", a_tmp.shape)
- print("y_pred[1][3] =\n", y_pred_tmp[1][3])
- print("y_pred.shape = \n", y_pred_tmp.shape)
- print("caches[1][1][3] =\n", caches_tmp[1][1][3])
- print("len(caches) = \n", len(caches_tmp))
-
- #UNIT TEST
- rnn_forward_test(rnn_forward)
a[4][1] =
[-0.99999375 0.77911235 -0.99861469 -0.99833267]
a.shape =
(5, 10, 4)
y_pred[1][3] =
[0.79560373 0.86224861 0.11118257 0.81515947]
y_pred.shape =
(2, 10, 4)
caches[1][1][3] =
[-1.1425182 -0.34934272 -0.20889423 0.58662319]
len(caches) =
2
All tests passed
恭喜! 您已经成功地从头开始构建了递归神经网络的前向传播。不错的工作!
这种RNN表现更好的情况:
- - 这对某些应用程序来说足够好了,但它会受到渐变消失的影响。
- - 当每个输出
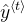 可以使用“本地”上下文估计时,RNN工作得最好。
可以使用“本地”上下文估计时,RNN工作得最好。 - - “本地”上下文指的是接近预测时间步长$t$的信息。
- - 更正式地说,本地上下文指的是输入
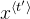 和预测
和预测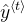 ,其中
,其中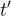 接近
接近 。
。
在下一节中,您将构建一个更复杂的模型LSTM,它更擅长处理逐渐消失的梯度。LSTM能够更好地记住一条信息并将其保存许多时间步。
2.2 LSTM的前向传播
LSTM单元的操作如下图所示:
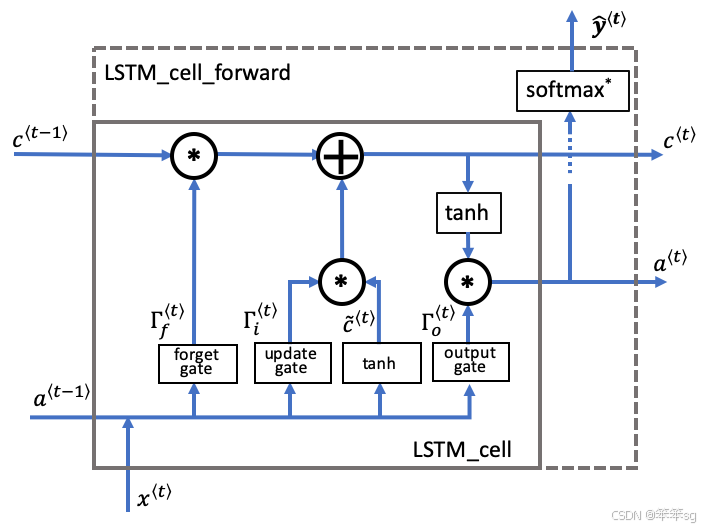
与上面的RNN示例类似,您将首先为单个时间步实现LSTM单元。然后,您将在“for循环”中迭代地调用它,以使它处理具有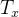 时间步长的输入。
时间步长的输入。
LSTM Cell
- # UNQ_C3 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: lstm_cell_forward
-
- def lstm_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, c_prev, parameters):
-
- # Retrieve parameters from "parameters"
- Wf = parameters["Wf"] # forget gate weight
- bf = parameters["bf"]
- Wi = parameters["Wi"] # update gate weight (notice the variable name)
- bi = parameters["bi"] # (notice the variable name)
- Wc = parameters["Wc"] # candidate value weight
- bc = parameters["bc"]
- Wo = parameters["Wo"] # output gate weight
- bo = parameters["bo"]
- Wy = parameters["Wy"] # prediction weight
- by = parameters["by"]
-
- # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of xt and Wy
- n_x, m = xt.shape
- n_y, n_a = Wy.shape
-
- # Concatenate a_prev and xt (≈1 line)
- concat = np.concatenate([a_prev,xt])
-
- # Compute values for ft, it, cct, c_next, ot, a_next using the formulas given figure (4) (≈6 lines)
- ft = sigmoid(np.dot(Wf,concat) + bf) # Forget Gate
- it = sigmoid(np.dot(Wi,concat) + bi) # Update Gate
- cct = np.tanh(np.dot(Wc,concat) + bc) # Candidate Value
- c_next = c_prev*ft + cct*it # C_t
- ot = sigmoid(np.dot(Wo,concat) + bo) # output gate
- a_next = ot*(np.tanh(c_next)) #a_t
-
- # Compute prediction of the LSTM cell (≈1 line)
- yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wy,a_next) + by)
-
- # store values needed for backward propagation in cache
- cache = (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters)
-
- return a_next, c_next, yt_pred, cache
- np.random.seed(1)
- xt_tmp = np.random.randn(3, 10)
- a_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10)
- c_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wf'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bf'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wi'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bi'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wo'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bo'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wc'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bc'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wy'] = np.random.randn(2, 5)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2, 1)
-
- a_next_tmp, c_next_tmp, yt_tmp, cache_tmp = lstm_cell_forward(xt_tmp, a_prev_tmp, c_prev_tmp, parameters_tmp)
-
- print("a_next[4] = \n", a_next_tmp[4])
- print("a_next.shape = ", a_next_tmp.shape)
- print("c_next[2] = \n", c_next_tmp[2])
- print("c_next.shape = ", c_next_tmp.shape)
- print("yt[1] =", yt_tmp[1])
- print("yt.shape = ", yt_tmp.shape)
- print("cache[1][3] =\n", cache_tmp[1][3])
- print("len(cache) = ", len(cache_tmp))
-
- # UNIT TEST
- lstm_cell_forward_test(lstm_cell_forward)
a_next[4] =
[-0.66408471 0.0036921 0.02088357 0.22834167 -0.85575339 0.00138482
0.76566531 0.34631421 -0.00215674 0.43827275]
a_next.shape = (5, 10)
c_next[2] =
[ 0.63267805 1.00570849 0.35504474 0.20690913 -1.64566718 0.11832942
0.76449811 -0.0981561 -0.74348425 -0.26810932]
c_next.shape = (5, 10)
yt[1] = [0.79913913 0.15986619 0.22412122 0.15606108 0.97057211 0.31146381
0.00943007 0.12666353 0.39380172 0.07828381]
yt.shape = (2, 10)
cache[1][3] =
[-0.16263996 1.03729328 0.72938082 -0.54101719 0.02752074 -0.30821874
0.07651101 -1.03752894 1.41219977 -0.37647422]
len(cache) = 10
All tests passed
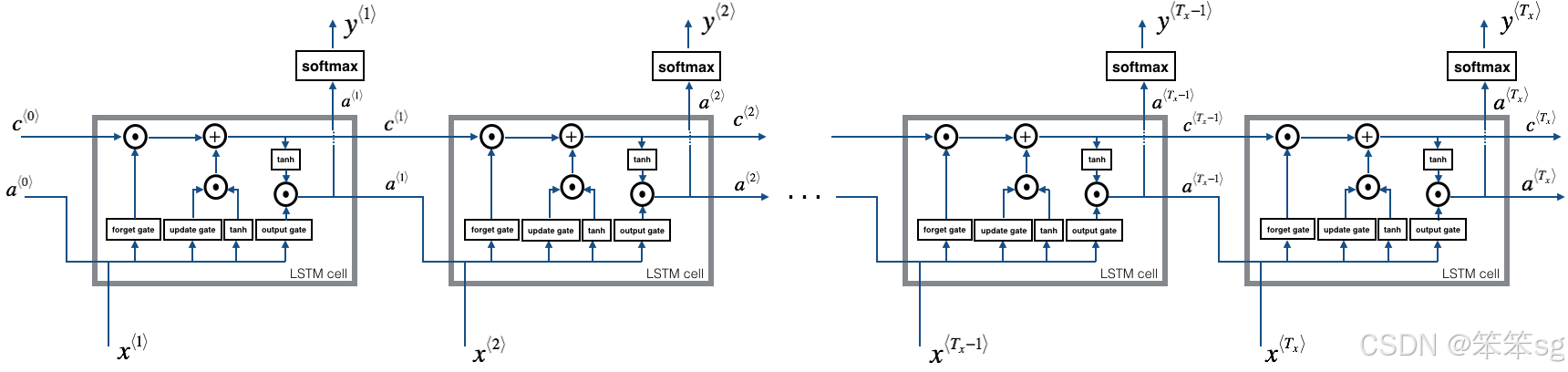
LSTM前向传播
现在您已经实现了LSTM的一个步骤,您可以使用for循环对它进行迭代,以处理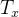 输入序列。
输入序列。
- # UNQ_C4 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: lstm_forward
-
- def lstm_forward(x, a0, parameters):
-
- # Initialize "caches", which will track the list of all the caches
- caches = []
-
- #Wy = parameters['Wy'] # Save parameters in local variables in case you want to use Wy instead of parameters['Wy']
- # Retrieve dimensions from shapes of x and parameters['Wy'] (≈2 lines)
- n_x, m, T_x = x.shape
- n_y, n_a = parameters['Wy'].shape
-
- # initialize "a", "c" and "y" with zeros (≈3 lines)
- a = np.zeros((n_a,m,T_x))
- c = np.zeros((n_a,m,T_x))
- y = np.zeros((n_y,m,T_x))
-
- # Initialize a_next and c_next (≈2 lines)
- a_next = a0
- c_next = np.zeros((n_a,m))
-
- # loop over all time-steps
- for t in range(T_x):
- # Get the 2D slice 'xt' from the 3D input 'x' at time step 't'
- xt = x[:,:,t]
- # Update next hidden state, next memory state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line)
- a_next, c_next, yt, cache = lstm_cell_forward(xt, a_next, c_next, parameters)
- # Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line)
- a[:,:,t] = a_next
- # Save the value of the next cell state (≈1 line)
- c[:,:,t] = c_next
- # Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line)
- y[:,:,t] = yt
- # Append the cache into caches (≈1 line)
- caches.append(cache)
-
- # store values needed for backward propagation in cache
- caches = (caches, x)
-
- return a, y, c, caches
- np.random.seed(1)
- x_tmp = np.random.randn(3, 10, 7)
- a0_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wf'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bf'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wi'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bi']= np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wo'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bo'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wc'] = np.random.randn(5, 5 + 3)
- parameters_tmp['bc'] = np.random.randn(5, 1)
- parameters_tmp['Wy'] = np.random.randn(2, 5)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2, 1)
-
- a_tmp, y_tmp, c_tmp, caches_tmp = lstm_forward(x_tmp, a0_tmp, parameters_tmp)
- print("a[4][3][6] = ", a_tmp[4][3][6])
- print("a.shape = ", a_tmp.shape)
- print("y[1][4][3] =", y_tmp[1][4][3])
- print("y.shape = ", y_tmp.shape)
- print("caches[1][1][1] =\n", caches_tmp[1][1][1])
- print("c[1][2][1]", c_tmp[1][2][1])
- print("len(caches) = ", len(caches_tmp))
-
- # UNIT TEST
- lstm_forward_test(lstm_forward)
a[4][3][6] = 0.17211776753291672
a.shape = (5, 10, 7)
y[1][4][3] = 0.9508734618501101
y.shape = (2, 10, 7)
caches[1][1][1] =
[ 0.82797464 0.23009474 0.76201118 -0.22232814 -0.20075807 0.18656139
0.41005165]
c[1][2][1] -0.8555449167181981
len(caches) = 2
All tests passed
恭喜你!
现在,您已经为基本RNN和LSTM实现了正向传递。当使用深度学习框架时,实现前向传递足以构建实现出色性能的系统。框架会处理好剩下的事情。
2.3 RNN的反向传播
在现代深度学习框架中,你只需要实现前向传递,框架负责后向传递,所以大多数深度学习工程师不需要为后向传递的细节而烦恼。但是,如果您是微积分专家(或者只是好奇),并且希望了解rnn中的反向反向的详细信息,您可以完成接下来的内容
RNN Cell反向传播
首先计算基本RNN单元的反向传递。然后,在下面的部分中,遍历单元格。
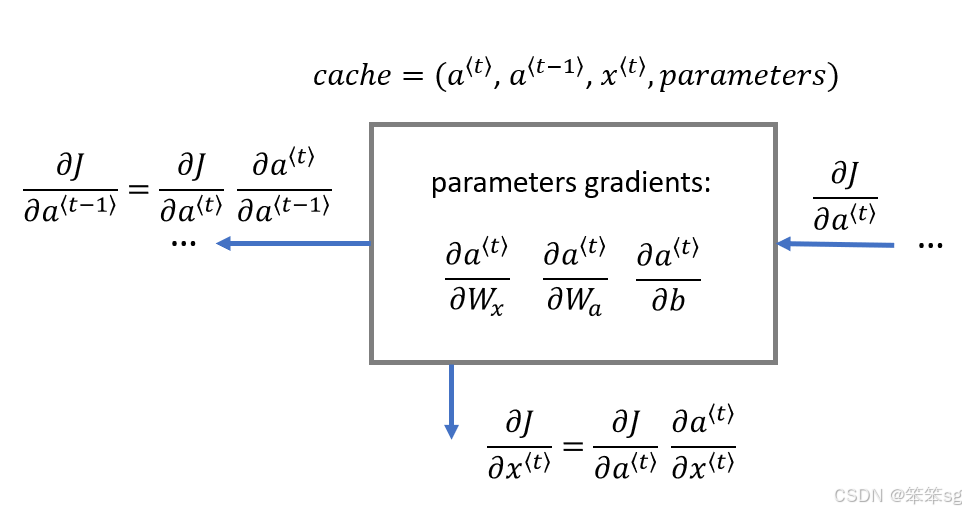
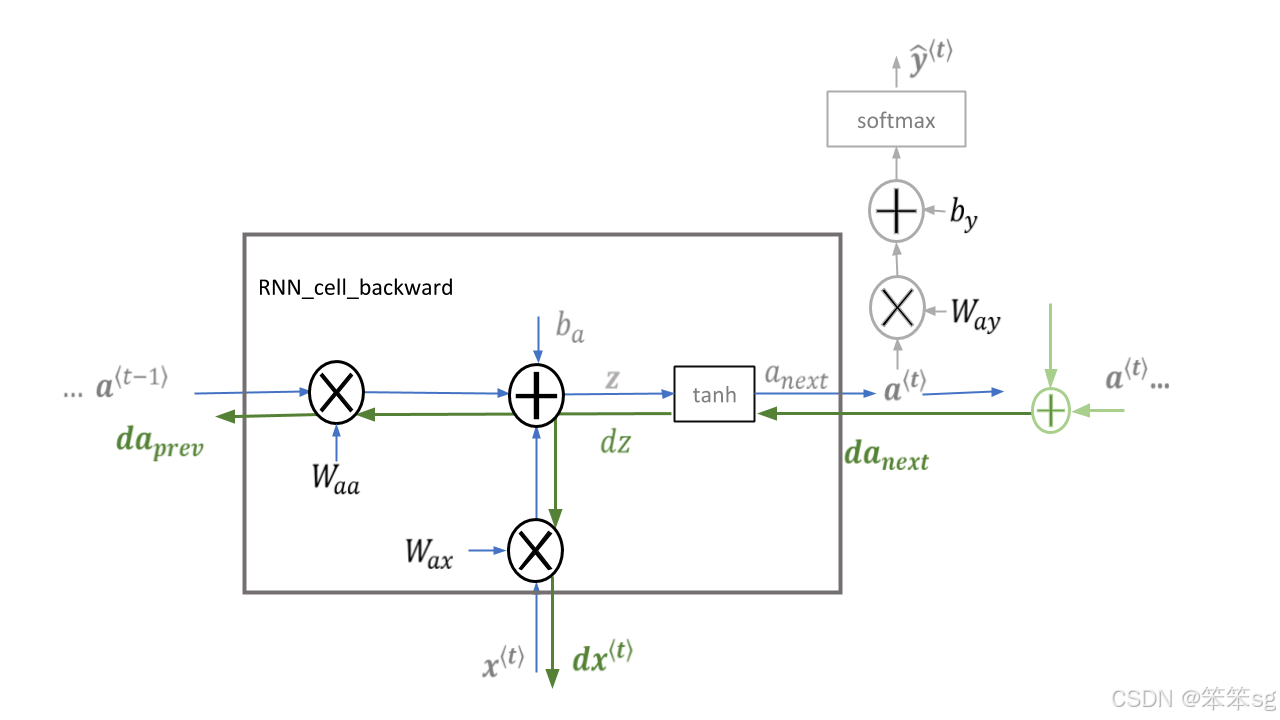
- # UNGRADED FUNCTION: rnn_cell_backward
-
- def rnn_cell_backward(da_next, cache):
-
- # Retrieve values from cache
- (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters) = cache
-
- # Retrieve values from parameters
- Wax = parameters["Wax"]
- Waa = parameters["Waa"]
- Wya = parameters["Wya"]
- ba = parameters["ba"]
- by = parameters["by"]
-
- # compute the gradient of tanh with respect to a_next (≈1 line)
- dtanh = da_next * (
- 1 - np.square(np.tanh(np.dot(Wax, xt) + np.dot(Waa, a_prev) + ba))
- )
-
- # compute the gradient of the loss with respect to Wax (≈2 lines)
- dxt = np.dot(Wax.T, dtanh)
- dWax = np.dot(dtanh, xt.T)
-
- # compute the gradient with respect to Waa (≈2 lines)
- da_prev = np.dot(Waa.T, dtanh)
- dWaa = np.dot(dtanh, a_prev.T)
-
- # compute the gradient with respect to b (≈1 line)
- dba = np.sum(dtanh, axis=1, keepdims=True)
-
- # Store the gradients in a python dictionary
- gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_prev": da_prev, "dWax": dWax, "dWaa": dWaa, "dba": dba}
-
- return gradients
- np.random.seed(1)
- xt_tmp = np.random.randn(3,10)
- a_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wax'] = np.random.randn(5,3)
- parameters_tmp['Waa'] = np.random.randn(5,5)
- parameters_tmp['Wya'] = np.random.randn(2,5)
- parameters_tmp['ba'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2,1)
-
- a_next_tmp, yt_tmp, cache_tmp = rnn_cell_forward(xt_tmp, a_prev_tmp, parameters_tmp)
-
- da_next_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- gradients_tmp = rnn_cell_backward(da_next_tmp, cache_tmp)
- print("gradients[\"dxt\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dxt"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dxt\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dxt"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"da_prev\"][2][3] =", gradients_tmp["da_prev"][2][3])
- print("gradients[\"da_prev\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["da_prev"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWax\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWax"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWax\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWax"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWaa"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWaa"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dba\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dba"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dba\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dba"].shape)
gradients["dxt"][1][2] = -1.3872130506020928
gradients["dxt"].shape = (3, 10)
gradients["da_prev"][2][3] = -0.15239949377395473
gradients["da_prev"].shape = (5, 10)
gradients["dWax"][3][1] = 0.41077282493545836
gradients["dWax"].shape = (5, 3)
gradients["dWaa"][1][2] = 1.1503450668497135
gradients["dWaa"].shape = (5, 5)
gradients["dba"][4] = [0.20023491]
gradients["dba"].shape = (5, 1)
基本RNN反向传播
- # UNGRADED FUNCTION: rnn_backward
-
- def rnn_backward(da, caches):
-
- # Retrieve values from the first cache (t=1) of caches (≈2 lines)
- (caches, x) = caches
- (a1, a0, x1, parameters) = caches[0]
-
- # Retrieve dimensions from da's and x1's shapes (≈2 lines)
- n_a, m, T_x = da.shape
- n_x, m = x1.shape
-
- # initialize the gradients with the right sizes (≈6 lines)
- dx = np.zeros((n_x, m, T_x))
- dWax = np.zeros((n_a, n_x))
- dWaa = np.zeros((n_a, n_a))
- dba = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
- da0 = np.zeros((n_a, m))
- da_prevt = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
-
- # Loop through all the time steps
- for t in reversed(range(T_x)):
- # Compute gradients at time step t. Choose wisely the "da_next" and the "cache" to use in the backward propagation step. (≈1 line)
- gradients = rnn_cell_backward(da[:, :, t] + da_prevt, caches[t])
- # Retrieve derivatives from gradients (≈ 1 line)
- dxt, da_prevt, dWaxt, dWaat, dbat = (
- gradients["dxt"],
- gradients["da_prev"],
- gradients["dWax"],
- gradients["dWaa"],
- gradients["dba"],
- )
- # Increment global derivatives w.r.t parameters by adding their derivative at time-step t (≈4 lines)
- dx[:, :, t] = dxt
- dWax += dWaxt
- dWaa += dWaat
- dba += dbat
-
- # Set da0 to the gradient of a which has been backpropagated through all time-steps (≈1 line)
- da0 = da_prevt
-
- # Store the gradients in a python dictionary
- gradients = {"dx": dx, "da0": da0, "dWax": dWax, "dWaa": dWaa,"dba": dba}
-
- return gradients
- np.random.seed(1)
- x_tmp = np.random.randn(3,10,4)
- a0_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wax'] = np.random.randn(5,3)
- parameters_tmp['Waa'] = np.random.randn(5,5)
- parameters_tmp['Wya'] = np.random.randn(2,5)
- parameters_tmp['ba'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2,1)
-
- a_tmp, y_tmp, caches_tmp = rnn_forward(x_tmp, a0_tmp, parameters_tmp)
- da_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10, 4)
- gradients_tmp = rnn_backward(da_tmp, caches_tmp)
-
- print("gradients[\"dx\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dx"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dx\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dx"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"da0\"][2][3] =", gradients_tmp["da0"][2][3])
- print("gradients[\"da0\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["da0"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWax\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWax"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWax\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWax"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWaa"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWaa"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dba\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dba"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dba\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dba"].shape)
gradients["dx"][1][2] = [-2.07101689 -0.59255627 0.02466855 0.01483317]
gradients["dx"].shape = (3, 10, 4)
gradients["da0"][2][3] = -0.31494237512664996
gradients["da0"].shape = (5, 10)
gradients["dWax"][3][1] = 11.264104496527777
gradients["dWax"].shape = (5, 3)
gradients["dWaa"][1][2] = 2.3033331265798935
gradients["dWaa"].shape = (5, 5)
gradients["dba"][4] = [-0.74747722]
gradients["dba"].shape = (5, 1)
LSTM Cell反向传播
LSTM向后传递比向前传递稍微复杂一些。
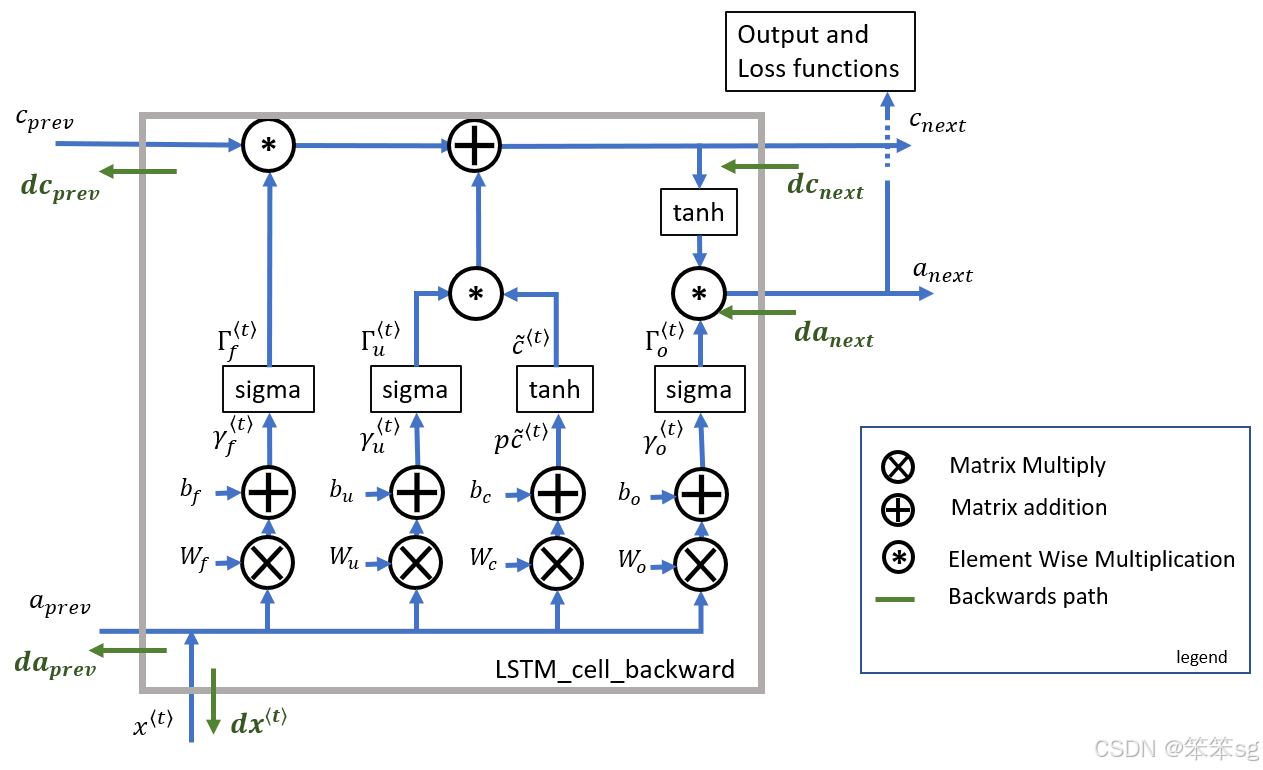
- # UNGRADED FUNCTION: lstm_cell_backward
-
- def lstm_cell_backward(da_next, dc_next, cache):
-
- # Retrieve information from "cache"
- (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters) = cache
-
- # Retrieve information from "cache"
- (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters) = cache
-
- ### START CODE HERE ###
- # Retrieve dimensions from xt's and a_next's shape (≈2 lines)
- n_x, m = xt.shape
- n_a, m = a_next.shape
-
- # Compute gates related derivatives, you can find their values can be found by looking carefully at equations (7) to (10) (≈4 lines)
- dot = da_next * np.tanh(c_next) * ot * (1-ot)
- dcct = (dc_next * it + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * it * da_next) * (1 - np.square(cct))
- dit = (dc_next * cct + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * cct * da_next) * it * (1 - it)
- dft = (dc_next * c_prev + ot * (1 - np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * c_prev * da_next) * ft * (1 - ft)
-
- # Compute parameters related derivatives. Use equations (11)-(14) (≈8 lines)
- concat = np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0).T
- dWf = np.dot(dft, concat)
- dWi = np.dot(dit, concat)
- dWc = np.dot(dcct, concat)
- dWo = np.dot(dot, concat)
- dbf = np.sum(dft, axis=1, keepdims=True)
- dbi = np.sum(dit, axis=1, keepdims=True)
- dbc = np.sum(dcct, axis=1, keepdims=True)
- dbo = np.sum(dot, axis=1, keepdims=True)
-
- # Compute derivatives w.r.t previous hidden state, previous memory state and input. Use equations (15)-(17). (≈3 lines)
- da_prev = np.dot(parameters['Wf'][:,:n_a].T, dft) + np.dot(parameters["Wi"][:, :n_a].T, dit) + np.dot(parameters['Wc'][:,:n_a].T, dcct) + np.dot(parameters['Wo'][:,:n_a].T, dot)
- dc_prev = dc_next * ft + ot * (1-np.square(np.tanh(c_next))) * ft * da_next
- dxt = np.dot(parameters['Wf'][:, n_a:].T, dft) + np.dot(parameters["Wi"][:, n_a:].T, dit)+ np.dot(parameters['Wc'][:,n_a:].T,dcct) + np.dot(parameters['Wo'][:,n_a:].T, dot)
-
- # Save gradients in dictionary
- gradients = {"dxt": dxt, "da_prev": da_prev, "dc_prev": dc_prev, "dWf": dWf,"dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi,"dbi": dbi,
- "dWc": dWc,"dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo,"dbo": dbo}
-
- return gradients
- np.random.seed(1)
- xt_tmp = np.random.randn(3,10)
- a_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- c_prev_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wf'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bf'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wi'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bi'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wo'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bo'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wc'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bc'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wy'] = np.random.randn(2,5)
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.random.randn(2,1)
-
- a_next_tmp, c_next_tmp, yt_tmp, cache_tmp = lstm_cell_forward(xt_tmp, a_prev_tmp, c_prev_tmp, parameters_tmp)
-
- da_next_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- dc_next_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
- gradients_tmp = lstm_cell_backward(da_next_tmp, dc_next_tmp, cache_tmp)
- print("gradients[\"dxt\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dxt"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dxt\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dxt"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"da_prev\"][2][3] =", gradients_tmp["da_prev"][2][3])
- print("gradients[\"da_prev\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["da_prev"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dc_prev\"][2][3] =", gradients_tmp["dc_prev"][2][3])
- print("gradients[\"dc_prev\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dc_prev"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWf\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWf"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWf\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWf"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWi\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWi"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWi\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWi"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWc\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWc"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWc\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWc"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWo\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWo"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWo\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWo"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbf\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbf"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbf\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbf"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbi\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbi"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbi\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbi"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbc\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbc"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbc\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbc"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbo\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbo"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbo\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbo"].shape)
gradients["dxt"][1][2] = 3.2305591151091875
gradients["dxt"].shape = (3, 10)
gradients["da_prev"][2][3] = -0.06396214197109236
gradients["da_prev"].shape = (5, 10)
gradients["dc_prev"][2][3] = 0.7975220387970015
gradients["dc_prev"].shape = (5, 10)
gradients["dWf"][3][1] = -0.1479548381644968
gradients["dWf"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWi"][1][2] = 1.0574980552259903
gradients["dWi"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWc"][3][1] = 2.3045621636876668
gradients["dWc"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWo"][1][2] = 0.3313115952892109
gradients["dWo"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dbf"][4] = [0.18864637]
gradients["dbf"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbi"][4] = [-0.40142491]
gradients["dbi"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbc"][4] = [0.25587763]
gradients["dbc"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbo"][4] = [0.13893342]
gradients["dbo"].shape = (5, 1)
LSTM反向传播
- # UNGRADED FUNCTION: lstm_backward
-
- def lstm_backward(da, caches):
-
- # Retrieve values from the first cache (t=1) of caches.
- (caches, x) = caches
- (a1, c1, a0, c0, f1, i1, cc1, o1, x1, parameters) = caches[0]
-
- # Retrieve dimensions from da's and x1's shapes (≈2 lines)
- n_a, m, T_x = da.shape
- n_x, m = x1.shape
-
- # initialize the gradients with the right sizes (≈12 lines)
- dx = np.zeros([n_x, m, T_x])
- da0 = np.zeros([n_a, m])
- da_prevt = np.zeros([n_a, m])
- dc_prevt = np.zeros([n_a, m])
- dWf = np.zeros([n_a, n_a + n_x])
- dWi = np.zeros([n_a, n_a + n_x])
- dWc = np.zeros([n_a, n_a + n_x])
- dWo = np.zeros([n_a, n_a + n_x])
- dbf = np.zeros([n_a, 1])
- dbi = np.zeros([n_a, 1])
- dbc = np.zeros([n_a, 1])
- dbo = np.zeros([n_a, 1])
-
- # loop back over the whole sequence
- for t in reversed(range(T_x)):
- # Compute all gradients using lstm_cell_backward
- gradients = lstm_cell_backward(da[:, :, t] + da_prevt, dc_prevt, caches[t])
- # Store or add the gradient to the parameters' previous step's gradient
- da_prevt = gradients["da_prev"]
- dc_prevt = gradients["dc_prev"]
- dx[:, :, t] = gradients["dxt"]
- dWf = dWf + gradients["dWf"]
- dWi = dWi + gradients["dWi"]
- dWc = dWc + gradients["dWc"]
- dWo = dWo + gradients["dWo"]
- dbf = dbf + gradients["dbf"]
- dbi = dbi + gradients["dbi"]
- dbc = dbc + gradients["dbc"]
- dbo = dbo + gradients["dbo"]
- # Set the first activation's gradient to the backpropagated gradient da_prev.
- da0 = gradients["da_prev"]
-
- # Store the gradients in a python dictionary
- gradients = {"dx": dx, "da0": da0, "dWf": dWf,"dbf": dbf, "dWi": dWi,"dbi": dbi,
- "dWc": dWc,"dbc": dbc, "dWo": dWo,"dbo": dbo}
-
- return gradients
- np.random.seed(1)
- x_tmp = np.random.randn(3,10,7)
- a0_tmp = np.random.randn(5,10)
-
- parameters_tmp = {}
- parameters_tmp['Wf'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bf'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wi'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bi'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wo'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bo'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wc'] = np.random.randn(5, 5+3)
- parameters_tmp['bc'] = np.random.randn(5,1)
- parameters_tmp['Wy'] = np.zeros((2,5)) # unused, but needed for lstm_forward
- parameters_tmp['by'] = np.zeros((2,1)) # unused, but needed for lstm_forward
-
- a_tmp, y_tmp, c_tmp, caches_tmp = lstm_forward(x_tmp, a0_tmp, parameters_tmp)
-
- da_tmp = np.random.randn(5, 10, 4)
- gradients_tmp = lstm_backward(da_tmp, caches_tmp)
-
- print("gradients[\"dx\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dx"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dx\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dx"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"da0\"][2][3] =", gradients_tmp["da0"][2][3])
- print("gradients[\"da0\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["da0"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWf\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWf"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWf\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWf"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWi\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWi"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWi\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWi"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWc\"][3][1] =", gradients_tmp["dWc"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWc\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWc"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dWo\"][1][2] =", gradients_tmp["dWo"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWo\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dWo"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbf\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbf"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbf\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbf"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbi\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbi"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbi\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbi"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbc\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbc"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbc\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbc"].shape)
- print("gradients[\"dbo\"][4] =", gradients_tmp["dbo"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dbo\"].shape =", gradients_tmp["dbo"].shape)
gradients["dx"][1][2] = [ 0.00218254 0.28205375 -0.48292508 -0.43281115]
gradients["dx"].shape = (3, 10, 4)
gradients["da0"][2][3] = 0.31277031025726026
gradients["da0"].shape = (5, 10)
gradients["dWf"][3][1] = -0.08098023109383463
gradients["dWf"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWi"][1][2] = 0.40512433092981837
gradients["dWi"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWc"][3][1] = -0.07937467355121491
gradients["dWc"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dWo"][1][2] = 0.038948775762986956
gradients["dWo"].shape = (5, 8)
gradients["dbf"][4] = [-0.15745657]
gradients["dbf"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbi"][4] = [-0.50848333]
gradients["dbi"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbc"][4] = [-0.42510818]
gradients["dbc"].shape = (5, 1)
gradients["dbo"][4] = [-0.17958196]
gradients["dbo"].shape = (5, 1)
祝贺你完成了这个作业!
现在你明白了循环神经网络是如何工作的!在下一个练习中,您将使用RNN来构建字符级语言模型。到时见!
3 字符级语言模型-恐龙岛
欢迎来到恐龙岛!六千五百万年前,恐龙就存在了,在这次任务中,它们又回来了。
你负责一项特殊的任务:领先的生物学研究人员正在创造新的恐龙品种,并将它们带到地球上,而你的工作是为这些恐龙命名。如果恐龙不喜欢自己的名字,它可能会发狂。所以要明智地选择!

幸运的是,你现在已经具备了一些深度学习能力,你将用它来拯救世界!你的助手收集了他们能找到的所有恐龙名字的列表,并将它们汇编成这个[数据集](dinosaur .txt)。(请点击前面的链接查看。)要创建新的恐龙名称,您将构建一个字符级语言模型来生成新的名称。您的算法将学习不同的名称模式,并随机生成新名称。希望这个算法能让你和你的团队远离恐龙的愤怒!
当你完成这个作业时,你将能够:
- * 存储文本数据,使用RNN进行处理
- * 使用RNN构建字符级文本生成模型
- * RNN中的新序列样本
- * 解释rnn中的梯度消失/爆炸问题
- * 应用梯度裁剪作为爆炸梯度的解决方案
首先加载‘ rn_utils ’中为您提供的一些函数。具体来说,你可以访问像‘ rnn_forward ’和‘ rnn_backward ’这样的函数,它们相当于你在前面的赋值中实现的函数。
3.0 导包
- import numpy as np
- from utils import *
- import random
- import pprint
- import copy
3.1 问题重述
数据集与预处理
运行下面的单元格读取恐龙名称数据集,创建唯一字符列表(如a-z),并计算数据集和词汇表大小。
- data = open('dinos.txt', 'r').read()
- data= data.lower()
- chars = list(set(data))
- data_size, vocab_size = len(data), len(chars)
- print('There are %d total characters and %d unique characters in your data.' % (data_size, vocab_size))
There are 19909 total characters and 27 unique characters in your data.
- * 字符是a-z(26个字符)加上“\n”(或换行字符)。
- * 在此作业中,换行字符“\n”的作用类似于讲座中讨论的“
”(或“句子结束”)标记。 - 在这里,“\n”表示恐龙名字的结尾,而不是句子的结尾。
- * ' char_to_ix ':在下面的单元格中,您将创建一个Python字典(即哈希表),将每个字符映射到从0-26的索引。
- * ' ix_to_char ':然后,创建第二个Python字典,将每个索引映射回相应的字符。
- - 这将帮助您找出哪个索引对应于softmax层的概率分布输出中的哪个字符。
- chars = sorted(chars)
- print(chars)
['\n', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
- char_to_ix = { ch:i for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
- ix_to_char = { i:ch for i,ch in enumerate(chars) }
- pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=4)
- pp.pprint(ix_to_char)
{ 0: '\n',
1: 'a',
2: 'b',
3: 'c',
4: 'd',
5: 'e',
6: 'f',
7: 'g',
8: 'h',
9: 'i',
10: 'j',
11: 'k',
12: 'l',
13: 'm',
14: 'n',
15: 'o',
16: 'p',
17: 'q',
18: 'r',
19: 's',
20: 't',
21: 'u',
22: 'v',
23: 'w',
24: 'x',
25: 'y',
26: 'z'}
模型概述
您的模型将具有以下结构:
- - 初始化参数
- - 执行优化循环
- - 前向传播,计算损失函数
- - 反向传播计算梯度相对于损失函数
- - 剪辑梯度,以避免爆炸梯度
- - 使用梯度,用梯度下降更新规则更新参数。
- - 返回学习到的参数
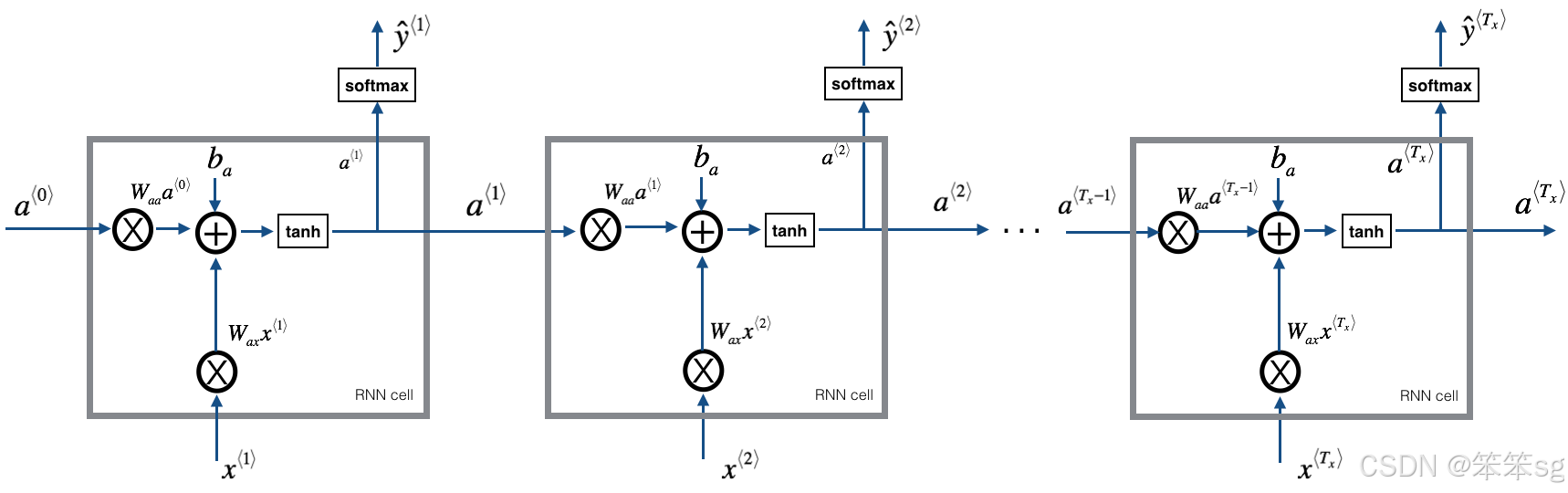
3.2 构建模型的小块
在这一部分中,您将构建整个模型的两个重要模块:
1. 渐变裁剪: 避免渐变爆炸
2. 采样:一种用来生成字符的技术
然后,您将应用这两个函数来构建模型。
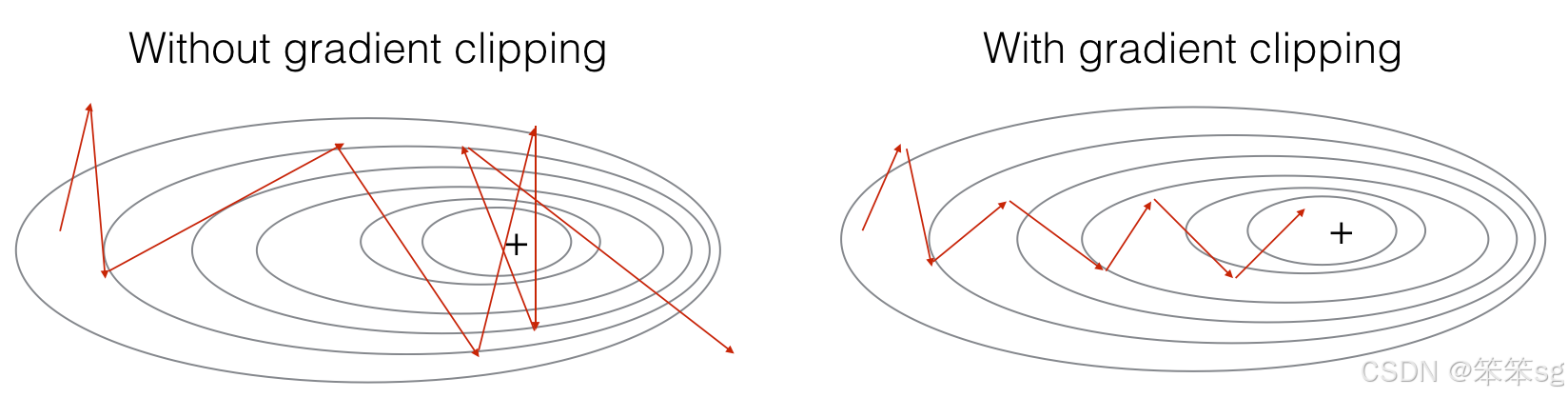
裁剪优化循环中的梯度
在本节中,您将实现在优化循环中调用的“clip”函数。
- * 有不同的方法来剪辑渐变。
- * 你将使用一个简单的元素裁剪过程,在这个过程中,梯度向量的每个元素都被裁剪到某个范围[-N, N]之间。
- * 例如,如果N=10,则范围为[- 10,10]
- - 如果梯度向量的任何分量大于10,则设置为10。
- - 如果梯度向量的任何分量小于-10,则设置为-10。
- - 如果组件值在-10 ~ 10之间,则保持原值。
- # UNQ_C1 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- ### GRADED FUNCTION: clip
-
- def clip(gradients, maxValue):
-
- gradients = copy.deepcopy(gradients)
-
- dWaa, dWax, dWya, db, dby = gradients['dWaa'], gradients['dWax'], gradients['dWya'], gradients['db'], gradients['dby']
-
- # Clip to mitigate exploding gradients, loop over [dWax, dWaa, dWya, db, dby]. (≈2 lines)
- for gradient in gradients:
- np.clip(gradients[gradient], -maxValue, maxValue, out = gradients[gradient])
-
- gradients = {"dWaa": dWaa, "dWax": dWax, "dWya": dWya, "db": db, "dby": dby}
-
- return gradients
- # Test with a max value of 10
- def clip_test(target, mValue):
- print(f"\nGradients for mValue={mValue}")
- np.random.seed(3)
- dWax = np.random.randn(5, 3) * 10
- dWaa = np.random.randn(5, 5) * 10
- dWya = np.random.randn(2, 5) * 10
- db = np.random.randn(5, 1) * 10
- dby = np.random.randn(2, 1) * 10
- gradients = {"dWax": dWax, "dWaa": dWaa, "dWya": dWya, "db": db, "dby": dby}
-
- gradients2 = target(gradients, mValue)
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"][1][2] =", gradients2["dWaa"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"dWax\"][3][1] =", gradients2["dWax"][3][1])
- print("gradients[\"dWya\"][1][2] =", gradients2["dWya"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"db\"][4] =", gradients2["db"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dby\"][1] =", gradients2["dby"][1])
-
- for grad in gradients2.keys():
- valuei = gradients[grad]
- valuef = gradients2[grad]
- mink = np.min(valuef)
- maxk = np.max(valuef)
- assert mink >= -abs(mValue), f"Problem with {grad}. Set a_min to -mValue in the np.clip call"
- assert maxk <= abs(mValue), f"Problem with {grad}.Set a_max to mValue in the np.clip call"
- index_not_clipped = np.logical_and(valuei <= mValue, valuei >= -mValue)
- assert np.all(valuei[index_not_clipped] == valuef[index_not_clipped]), f" Problem with {grad}. Some values that should not have changed, changed during the clipping process."
-
- print("\033[92mAll tests passed!\x1b[0m")
-
- clip_test(clip, 10)
- clip_test(clip, 5)
Gradients for mValue=10
gradients["dWaa"][1][2] = 10.0
gradients["dWax"][3][1] = -10.0
gradients["dWya"][1][2] = 0.2971381536101662
gradients["db"][4] = [10.]
gradients["dby"][1] = [8.45833407]
All tests passed!Gradients for mValue=5
gradients["dWaa"][1][2] = 5.0
gradients["dWax"][3][1] = -5.0
gradients["dWya"][1][2] = 0.2971381536101662
gradients["db"][4] = [5.]
gradients["dby"][1] = [5.]
All tests passed!
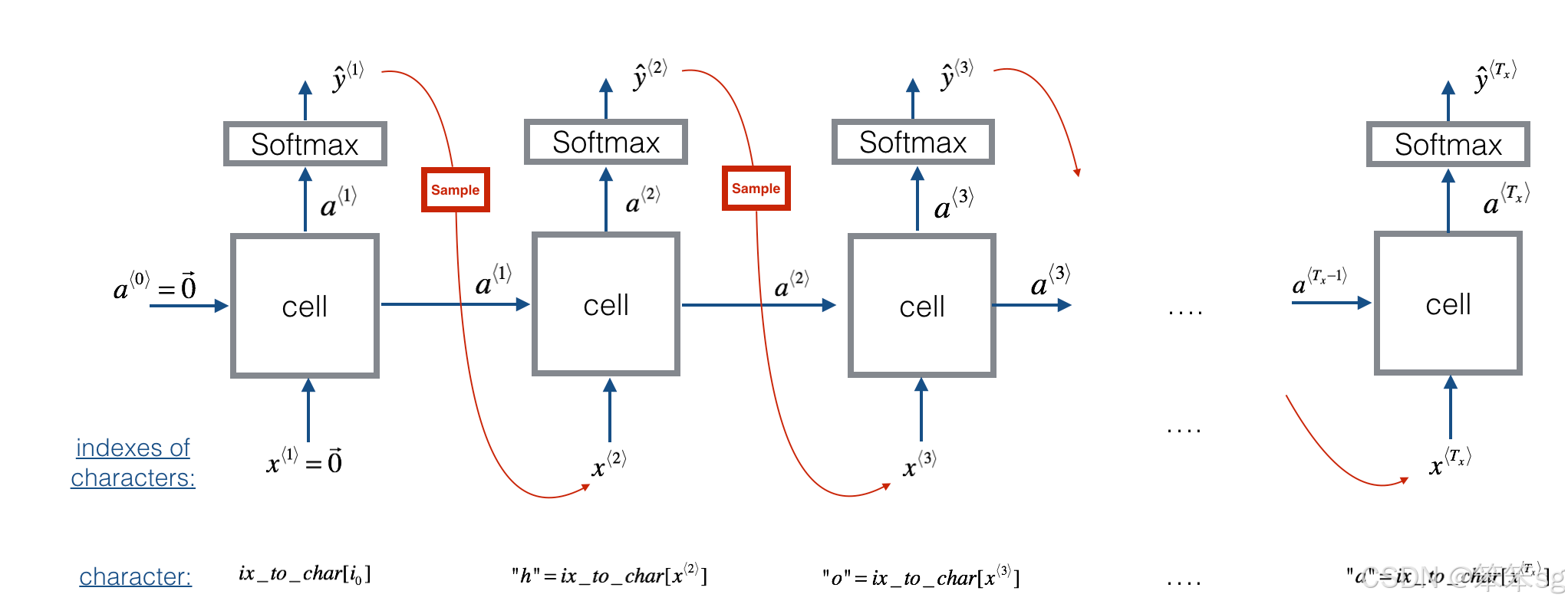
采样
现在,假设您的模型已经过训练,并且希望生成新的文本(字符)。生成过程如下图所示:
- # UNQ_C2 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: sample
-
- def sample(parameters, char_to_ix, seed):
-
- # Retrieve parameters and relevant shapes from "parameters" dictionary
- Waa, Wax, Wya, by, b = parameters['Waa'], parameters['Wax'], parameters['Wya'], parameters['by'], parameters['b']
- vocab_size = by.shape[0]
- n_a = Waa.shape[1]
-
- # Step 1: Create the a zero vector x that can be used as the one-hot vector
- # Representing the first character (initializing the sequence generation). (≈1 line)
- x = np.zeros((vocab_size,1))
- # Step 1': Initialize a_prev as zeros (≈1 line)
- a_prev = np.zeros((n_a ,1))
-
- # Create an empty list of indices. This is the list which will contain the list of indices of the characters to generate (≈1 line)
- indices = []
-
- # idx is the index of the one-hot vector x that is set to 1
- # All other positions in x are zero.
- # Initialize idx to -1
- idx = -1
-
- # Loop over time-steps t. At each time-step:
- # Sample a character from a probability distribution
- # And append its index (`idx`) to the list "indices".
- # You'll stop if you reach 50 characters
- # (which should be very unlikely with a well-trained model).
- # Setting the maximum number of characters helps with debugging and prevents infinite loops.
- counter = 0
- newline_character = char_to_ix['\n']
-
- while (idx != newline_character and counter != 50):
-
- # Step 2: Forward propagate x using the equations (1), (2) and (3)
- a = np.tanh(np.dot(Wax,x) + np.dot(Waa,a_prev) + b)
- z = np.dot(Wya,a) + by
- y = softmax(z)
-
- # For grading purposes
- np.random.seed(counter + seed)
-
- # Step 3: Sample the index of a character within the vocabulary from the probability distribution y
- # (see additional hints above)
- idx = np.random.choice(range(len(y)), p = np.squeeze(y) )
-
- # Append the index to "indices"
- indices.append(idx)
-
- # Step 4: Overwrite the input x with one that corresponds to the sampled index `idx`.
- # (see additional hints above)
- x = np.zeros((vocab_size,1))
- x[idx] = 1
-
- # Update "a_prev" to be "a"
- a_prev = a
-
- # for grading purposes
- seed += 1
-
- counter +=1
-
- if (counter == 50):
- indices.append(char_to_ix['\n'])
-
- return indices
- def sample_test(target):
- np.random.seed(24)
- _, n_a = 20, 100
- Wax, Waa, Wya = np.random.randn(n_a, vocab_size), np.random.randn(n_a, n_a), np.random.randn(vocab_size, n_a)
- b, by = np.random.randn(n_a, 1), np.random.randn(vocab_size, 1)
- parameters = {"Wax": Wax, "Waa": Waa, "Wya": Wya, "b": b, "by": by}
-
-
- indices = target(parameters, char_to_ix, 0)
- print("Sampling:")
- print("list of sampled indices:\n", indices)
- print("list of sampled characters:\n", [ix_to_char[i] for i in indices])
-
- assert len(indices) < 52, "Indices lenght must be smaller than 52"
- assert indices[-1] == char_to_ix['\n'], "All samples must end with \\n"
- assert min(indices) >= 0 and max(indices) < len(char_to_ix), f"Sampled indexes must be between 0 and len(char_to_ix)={len(char_to_ix)}"
- assert np.allclose(indices[0:6], [23, 16, 26, 26, 24, 3]), "Wrong values"
-
- print("\033[92mAll tests passed!")
-
- sample_test(sample)
Sampling:
list of sampled indices:
[23, 16, 26, 26, 24, 3, 21, 1, 7, 24, 15, 3, 25, 20, 6, 13, 10, 8, 20, 12, 2, 0]
list of sampled characters:
['w', 'p', 'z', 'z', 'x', 'c', 'u', 'a', 'g', 'x', 'o', 'c', 'y', 't', 'f', 'm', 'j', 'h', 't', 'l', 'b', '\n']
All tests passed!
你应该记住的:
- * 非常大或“爆炸”的梯度更新可能太大,以至于它们在反向支撑期间“超调”了最优值——使训练变得困难
- * 剪辑梯度之前更新参数,以避免爆炸梯度
- * 抽样是一种可以用来根据概率分布选择下一个字符的索引的技术。
- * 开始字符级采样:
- * 输入一个零的“虚拟”向量作为默认输入
- * 运行一步前向传播以获得?〈1〉(您的第一个字符)和expes〈1〉(以下字符的概率分布)
- * 在抽样时,通过使用‘ np.random.choice ’来避免每次给定起始字母都产生相同的结果(并使您的名字更有趣!)
3.3 构建语言模型
是时候构建用于文本生成的字符级语言模型了!
梯度下降法
在本节中,您将实现一个函数,执行随机梯度下降的一步(带有剪切梯度)。你会一次看一个训练样例,所以优化算法是随机梯度下降。
提醒一下,以下是RNN常见优化循环的步骤:
- - 通过RNN前向传播,计算损失
- - 通过时间反向传播,计算损失相对于参数的梯度
- - 剪辑渐变
- - 使用梯度下降法更新参数
- # UNQ_C3 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: optimize
-
- def optimize(X, Y, a_prev, parameters, learning_rate = 0.01):
-
- # Forward propagate through time (≈1 line)
- loss, cache = rnn_forward(X, Y, a_prev, parameters)
-
- # Backpropagate through time (≈1 line)
- gradients, a = rnn_backward(X, Y, parameters, cache)
-
- # Clip your gradients between -5 (min) and 5 (max) (≈1 line)
- gradients = clip(gradients, 5)
-
- # Update parameters (≈1 line)
- parameters = update_parameters(parameters, gradients, learning_rate)
-
- return loss, gradients, a[len(X)-1]
- def optimize_test(target):
- np.random.seed(1)
- vocab_size, n_a = 27, 100
- a_prev = np.random.randn(n_a, 1)
- Wax, Waa, Wya = np.random.randn(n_a, vocab_size), np.random.randn(n_a, n_a), np.random.randn(vocab_size, n_a)
- b, by = np.random.randn(n_a, 1), np.random.randn(vocab_size, 1)
- parameters = {"Wax": Wax, "Waa": Waa, "Wya": Wya, "b": b, "by": by}
- X = [12, 3, 5, 11, 22, 3]
- Y = [4, 14, 11, 22, 25, 26]
- old_parameters = copy.deepcopy(parameters)
- loss, gradients, a_last = target(X, Y, a_prev, parameters, learning_rate = 0.01)
- print("Loss =", loss)
- print("gradients[\"dWaa\"][1][2] =", gradients["dWaa"][1][2])
- print("np.argmax(gradients[\"dWax\"]) =", np.argmax(gradients["dWax"]))
- print("gradients[\"dWya\"][1][2] =", gradients["dWya"][1][2])
- print("gradients[\"db\"][4] =", gradients["db"][4])
- print("gradients[\"dby\"][1] =", gradients["dby"][1])
- print("a_last[4] =", a_last[4])
-
- assert np.isclose(loss, 126.5039757), "Problems with the call of the rnn_forward function"
- for grad in gradients.values():
- assert np.min(grad) >= -5, "Problems in the clip function call"
- assert np.max(grad) <= 5, "Problems in the clip function call"
- assert np.allclose(gradients['dWaa'][1, 2], 0.1947093), "Unexpected gradients. Check the rnn_backward call"
- assert np.allclose(gradients['dWya'][1, 2], -0.007773876), "Unexpected gradients. Check the rnn_backward call"
- assert not np.allclose(parameters['Wya'], old_parameters['Wya']), "parameters were not updated"
-
- print("\033[92mAll tests passed!")
-
- optimize_test(optimize)
Loss = 126.50397572165382
gradients["dWaa"][1][2] = 0.19470931534716163
np.argmax(gradients["dWax"]) = 93
gradients["dWya"][1][2] = -0.007773876032002922
gradients["db"][4] = [-0.06809825]
gradients["dby"][1] = [0.01538192]
a_last[4] = [-1.]
All tests passed!
模型训练
* 给定恐龙名称数据集,您将使用数据集的每一行(一个名称)作为一个训练示例。
* 每2000步的随机梯度下降,你将抽样几个随机选择的名字,看看算法是如何做的。
- # UNQ_C4 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: model
-
- def model(data_x, ix_to_char, char_to_ix, num_iterations = 35000, n_a = 50, dino_names = 7, vocab_size = 27, verbose = False):
-
- # Retrieve n_x and n_y from vocab_size
- n_x, n_y = vocab_size, vocab_size
-
- # Initialize parameters
- parameters = initialize_parameters(n_a, n_x, n_y)
-
- # Initialize loss (this is required because we want to smooth our loss)
- loss = get_initial_loss(vocab_size, dino_names)
-
- # Build list of all dinosaur names (training examples).
- examples = [x.strip() for x in data_x]
-
- # Shuffle list of all dinosaur names
- np.random.seed(0)
- np.random.shuffle(examples)
-
- # Initialize the hidden state of your LSTM
- a_prev = np.zeros((n_a, 1))
-
- # for grading purposes
- last_dino_name = "abc"
-
- # Optimization loop
- for j in range(num_iterations):
-
- # Set the index `idx` (see instructions above)
- idx = j%len(examples)
-
- # Set the input X (see instructions above)
- single_example_chars = examples[idx]
- single_example_ix = [char_to_ix[c] for c in single_example_chars]
-
- # if X[t] == None, we just have x[t]=0. This is used to set the input for the first timestep to the zero vector.
- X = [None] + single_example_ix
-
- # Set the labels Y (see instructions above)
- # The goal is to train the RNN to predict the next letter in the name
- # So the labels are the list of characters that are one time-step ahead of the characters in the input X
- Y = X[1:]
- # The RNN should predict a newline at the last letter, so add ix_newline to the end of the labels
- ix_newline = [char_to_ix["\n"]]
- Y = Y + ix_newline
-
- # Perform one optimization step: Forward-prop -> Backward-prop -> Clip -> Update parameters
- # Choose a learning rate of 0.01
- curr_loss, gradients, a_prev = optimize(X, Y, a_prev, parameters, learning_rate = 0.01)
-
- # debug statements to aid in correctly forming X, Y
- if verbose and j in [0, len(examples) -1, len(examples)]:
- print("j = " , j, "idx = ", idx,)
- if verbose and j in [0]:
- #print("single_example =", single_example)
- print("single_example_chars", single_example_chars)
- print("single_example_ix", single_example_ix)
- print(" X = ", X, "\n", "Y = ", Y, "\n")
-
- # Use a latency trick to keep the loss smooth. It happens here to accelerate the training.
- loss = smooth(loss, curr_loss)
-
- # Every 1000 Iteration, generate "n" characters thanks to sample() to check if the model is learning properly
- if j % 1000 == 0:
-
- print('Iteration: %d, Loss: %f' % (j, loss) + '\n')
-
- # The number of dinosaur names to print
- seed = 0
- for name in range(dino_names):
-
- # Sample indices and print them
- sampled_indices = sample(parameters, char_to_ix, seed)
- last_dino_name = get_sample(sampled_indices, ix_to_char)
- print(last_dino_name.replace('\n', ''))
-
- seed += 1 # To get the same result (for grading purposes), increment the seed by one.
-
- print('\n')
-
- return parameters, last_dino_name
当您运行下面的单元格时,您应该看到您的模型在第一次迭代时输出看起来随机的字符。经过几千次迭代后,您的模型应该学会生成看起来合理的名称。
- parameters, last_name = model(data.split("\n"), ix_to_char, char_to_ix, 22001, verbose = True)
-
- assert last_name == 'Trodonosaurus\n', "Wrong expected output"
- print("\033[92mAll tests passed!")
- j = 0 idx = 0
- single_example_chars turiasaurus
- single_example_ix [20, 21, 18, 9, 1, 19, 1, 21, 18, 21, 19]
- X = [None, 20, 21, 18, 9, 1, 19, 1, 21, 18, 21, 19]
- Y = [20, 21, 18, 9, 1, 19, 1, 21, 18, 21, 19, 0]
-
- Iteration: 0, Loss: 23.087336
-
- Nkzxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu
- Kneb
- Kzxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu
- Neb
- Zxwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu
- Eb
- Xwtdmfqoeyhsqwasjkjvu
-
-
- Iteration: 1000, Loss: 28.712699
-
- Nivusahidoraveros
- Ioia
- Iwtroeoirtaurusabrngeseaosawgeanaitafeaolaeratohop
- Nac
- Xtroeoirtaurusabrngeseaosawgeanaitafeaolaeratohopr
- Ca
- Tseeohnnaveros
-
-
- j = 1535 idx = 1535
- j = 1536 idx = 0
- Iteration: 2000, Loss: 27.884160
-
- Liusskeomnolxeros
- Hmdaairus
- Hytroligoraurus
- Lecalosapaus
- Xusicikoraurus
- Abalpsamantisaurus
- Tpraneronxeros
-
-
- Iteration: 3000, Loss: 26.863598
-
- Niusos
- Infa
- Iusrtendor
- Nda
- Wtrololos
- Ca
- Tps
-
-
- Iteration: 4000, Loss: 25.901815
-
- Mivrosaurus
- Inee
- Ivtroplisaurus
- Mbaaisaurus
- Wusichisaurus
- Cabaselachus
- Toraperlethosdarenitochusthiamamumamaon
-
-
- Iteration: 5000, Loss: 25.290275
-
- Ngyusedonis
- Klecagropechus
- Lytosaurus
- Necagropechusangotmeeycerum
- Xuskangosaurus
- Da
- Tosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 6000, Loss: 24.608779
-
- Onwusceomosaurus
- Lieeaerosaurus
- Lxussaurus
- Oma
- Xusteonosaurus
- Eeahosaurus
- Toreonosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 7000, Loss: 24.425330
-
- Ngytromiasaurus
- Ingabcosaurus
- Kyusichiropurusanrasauraptous
- Necamithachusidinysaus
- Yusodon
- Caaesaurus
- Tosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 8000, Loss: 24.070350
-
- Onxusichepriuon
- Kilabersaurus
- Lutrodon
- Omaaerosaurus
- Xutrcheps
- Edaksoje
- Trodiktonus
-
-
- Iteration: 9000, Loss: 23.730944
-
- Onyusaurus
- Klecanotal
- Kyuspang
- Ogaacosaurus
- Xutrasaurus
- Dabcosaurus
- Troching
-
-
- Iteration: 10000, Loss: 23.844446
-
- Onyusaurus
- Klecalosaurus
- Lustodon
- Ola
- Xusodonia
- Eeaeosaurus
- Troceosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 11000, Loss: 23.581901
-
- Leutosaurus
- Inda
- Itrtoplerosherotarangos
- Lecalosaurus
- Xutogolosaurus
- Babator
- Trodonosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 12000, Loss: 23.291971
-
- Onyxosaurus
- Kica
- Lustrepiosaurus
- Olaagrraiansaurus
- Yuspangosaurus
- Eealosaurus
- Trognesaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 13000, Loss: 23.547611
-
- Nixrosaurus
- Indabcosaurus
- Jystolong
- Necalosaurus
- Yuspangosaurus
- Daagosaurus
- Usndicirax
-
-
- Iteration: 14000, Loss: 23.382338
-
- Meutromodromurus
- Inda
- Iutroinatorsaurus
- Maca
- Yusteratoptititan
- Ca
- Troclosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 15000, Loss: 23.049756
-
- Phyusaurus
- Lidaa
- Lustraodon
- Padaeron
- Yuspchinnaugus
- Edalosaurus
- Trodon
-
-
- Iteration: 16000, Loss: 23.282946
-
- Mdyusaurus
- Indaacosaupisaurus
- Justolong
- Maca
- Yuspandosaurus
- Cabaspadantes
- Trodon
-
-
- Iteration: 17000, Loss: 23.156690
-
- Ootstrethosaurus
- Jica
- Kustonagor
- Ola
- Yustanchohugrosaurus
- Eeagosaurus
- Trpenesaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 18000, Loss: 22.850813
-
- Phyusaurus
- Meja
- Mystoosaurus
- Pegamosaurus
- Yusmaphosaurus
- Eiahosaurus
- Trolonosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 19000, Loss: 23.046266
-
- Opusaurus
- Kola
- Lustolonis
- Ola
- Yustanisaurus
- Eiahosaurus
- Trofonosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 20000, Loss: 22.929326
-
- Nlyusaurus
- Logbalosaurus
- Lvuslangosaurus
- Necalosaurus
- Ytrrangosaurus
- Ekairus
- Troenesaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 21000, Loss: 22.672015
-
- Phyusaurus
- Loeia
- Lyutorosaurus
- Pacalosaurus
- Yusodon
- Egaerosaurus
- Troholosaurus
-
-
- Iteration: 22000, Loss: 22.760728
-
- Onvusaroglolonoshareimus
- Llecaerona
- Myrrocephoeurus
- Pedacosaurus
- Ytrodonosaurus
- Eiadosaurus
- Trodonosaurus
-
-
- All tests passed!
3.4 结论
你可以看到,在训练结束时,你的算法已经开始生成合理的恐龙名称。一开始,它是随机生成角色,但到最后,你可以开始看到恐龙的名字有很酷的结尾。请随意运行算法更长时间,并使用超参数,看看是否可以获得更好的结果!我们的实现生成了一些非常酷的名字,比如“maconucon”、“marloralus”和“macingsersaurus”。希望你的模型也了解到恐龙的名字往往以“saurus”、“don”、“aura”、“tor”等结尾。
如果你的模型产生了一些不酷的名字,不要完全责怪模型——并不是所有真正的恐龙名字听起来都很酷。(例如,“dromaeosauroides”是一个真实的恐龙名称,并且在训练集中。)但这个模型应该会给你一组候选对象,你可以从中选择最酷的!
这个任务使用了一个相对较小的数据集,这样你就可以在CPU上快速训练一个RNN。训练一个英语语言模型需要更大的数据集,通常需要更多的计算,并且可以在gpu上运行几个小时。我们用了很长一段时间的恐龙名字,到目前为止我们最喜欢的名字是伟大的,凶猛的,不败的:**芒果龙**!
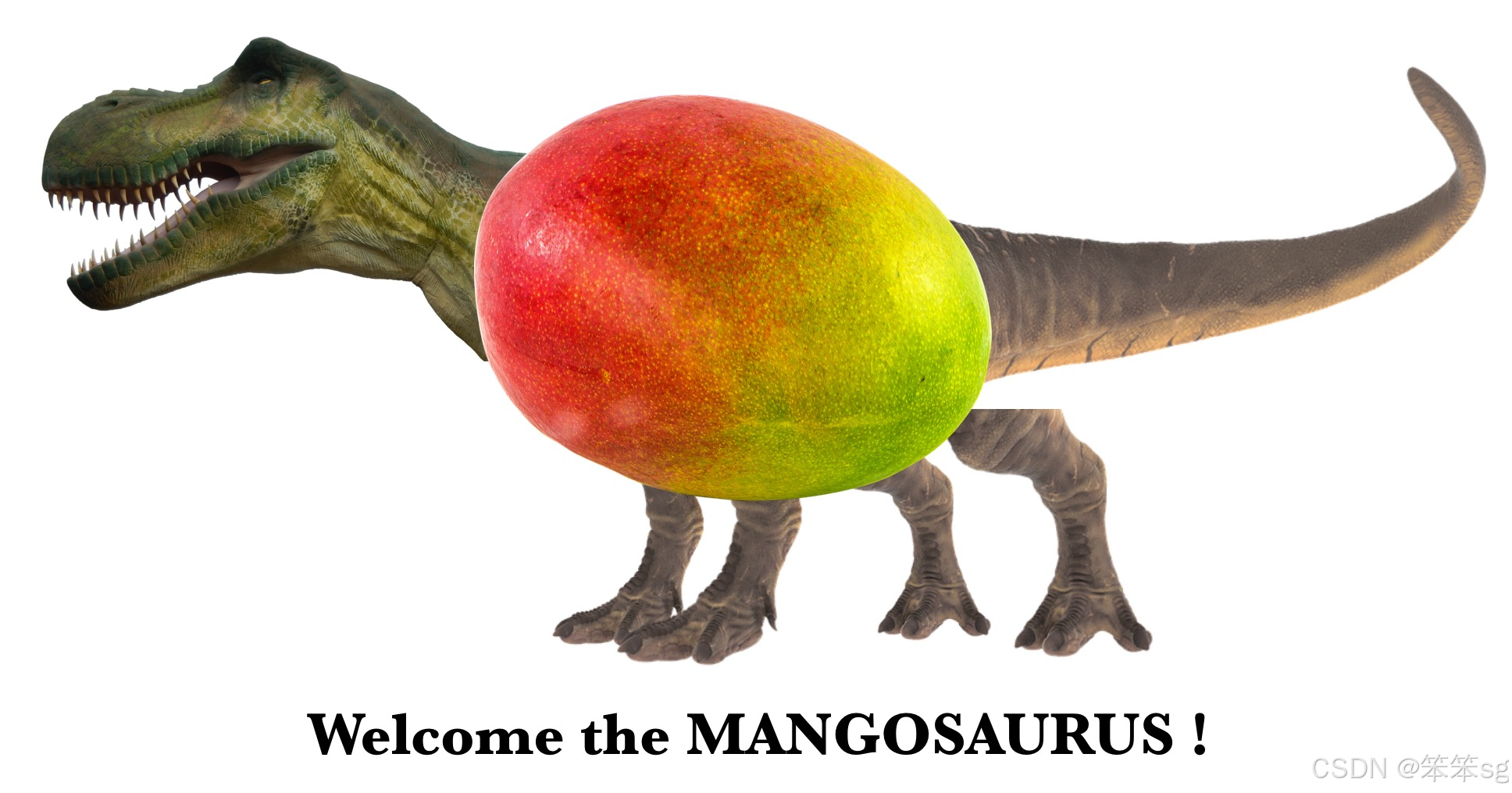

您已经完成了本笔记本的分级部分,并创建了一个工作语言模型!很棒的工作。
到目前为止,你已经:
- * 使用RNN存储文本数据进行处理
- * 建立字符级文本生成模型
- * 探索了rnn中的梯度消失/爆炸问题
- * 应用梯度裁剪,以避免爆炸梯度
你也有希望生成一些足够酷的恐龙名字,既能取悦你,又能避免恐龙的愤怒。
3.5 像莎士比亚一样写作
与字符级文本生成类似(但更复杂)的任务是生成莎士比亚诗歌。你可以使用莎士比亚的诗集,而不是从恐龙名字的数据集中学习。使用LSTM单元,您可以学习跨越文本中许多字符的长期依赖关系。,一个角色出现在序列的某个地方,可能会影响到序列后面应该出现的不同角色。这些长期的依赖关系对于恐龙的名字来说就不那么重要了,因为恐龙的名字都很短。

下面,您可以使用Keras实现莎士比亚诗歌生成器。运行下面的单元格来加载所需的包和模型。这可能需要几分钟。
- from __future__ import print_function
- from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import LambdaCallback
- from tensorflow.keras.models import Model, load_model, Sequential
- from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout, Input, Masking
- from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM
- from tensorflow.keras.utils import get_file
- from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
- from shakespeare_utils import *
- import sys
- import io
- print("\nModel & Data Loaded\n")
为了节省您的时间,我们已经对一个名为“[十四行诗](shakespeare.txt)”的莎士比亚诗歌集进行了约1000个epoch的模型训练。
让我们再训练一个epoch的模型。当它完成epoch的训练时(这也需要几分钟),您可以运行‘ generate_output ’,它将提示您输入(' < ' 40个字符)。这首诗将从你的句子开始,你的RNN莎士比亚将为你完成这首诗的其余部分!例如,试试“Forsooth this maketh no sense”(没有引号!)。根据您是否在末尾包含空格,您的结果也可能有所不同,因此请尝试两种方式,并尝试其他输入。
- print_callback = LambdaCallback(on_epoch_end=on_epoch_end)
-
- model.fit(x, y, batch_size=128, epochs=1, callbacks=[print_callback])
246/246 [==============================] - 128s 505ms/step - loss: 2.5351
- # Run this cell to try with different inputs without having to re-train the model
- generate_output()
Input:Forsooth this maketh no sense
Here is your poem:
Forsooth this maketh no sense,
live of love mased beeuted liot poftery,
which espunty eye but my didelven heart.
'owt thos eyes maimed woeds inled and to dele.
to all i sane eye table me,
thin eid the styout befooe with muting,
and one, ar the kthat than on bother bate things lofe,
a difl a live convedamed, will hif daker,
of love onti swast, fore hath unhir storsed,
assange i primacan defeding be iy more,
who show both is hi
祝贺你完成了这本笔记本!
RNN莎士比亚模型和你为恐龙命名建立的模型非常相似。唯一的主要区别是:
- - lstm代替基本RNN来捕获更远距离的依赖关系
- - 模型是一个更深的,堆叠的LSTM模型(2层)
- - 使用Keras代替Python来简化代码
4 用LSTM网络即兴演奏爵士独奏
欢迎来到本周最后的编程作业!在本笔记本中,您将实现一个使用LSTM生成音乐的模型。最后,你甚至可以听自己的音乐!

在本次作业结束时,你将能够:
- 将LSTM应用于音乐生成任务
- 用深度学习生成你自己的爵士音乐
- 使用灵活的Functional API来创建复杂的模型
这会很有趣的。我们开始吧!
4.0 导包
- import IPython
- import sys
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- import tensorflow as tf
-
- from music21 import *
- from grammar import *
- from qa import *
- from preprocess import *
- from music_utils import *
- from data_utils import *
- from outputs import *
- from test_utils import *
-
- from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout, Input, LSTM, Reshape, Lambda, RepeatVector
- from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
- from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
- from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
- physical_gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
- tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_gpus[0], True)
- logical_gpus = tf.config.list_logical_devices("GPU")
4.1 问题重述
你想为朋友的生日特别创作一首爵士音乐。然而,你不知道如何演奏乐器,也不知道如何作曲。幸运的是,您了解深度学习,并将使用LSTM网络解决这个问题!
你将训练一个网络来生成新的爵士独奏,其风格代表了一组已完成的作品。??
数据集
首先,您将在爵士音乐语料库上训练您的算法。运行下面的单元格来收听训练集中的音频片段:
IPython.display.Audio('./data/30s_seq.wav')
音乐数据的预处理已经处理好了,对于本笔记本来说,这意味着它已经以音乐“值”的形式呈现。
什么是音乐的“值”?
你可以把每个“值”想象成一个音符,它包括一个音高和一个持续时间。例如,如果您按下一个特定的钢琴键0.5秒,那么您刚刚演奏了一个音符。在音乐理论中,“值”实际上比这更复杂——具体来说,它还捕获了同时演奏多个音符所需的信息。例如,在演奏一段音乐时,你可能同时按下两个钢琴键(同时演奏多个音符会产生所谓的“和弦”)。但是你们不需要担心这个作业中音乐理论的细节。
音乐是一系列的价值观
* 为了这个作业的目的,你所需要知道的是你将获得一个值的数据集,并将使用RNN模型来生成值的序列。
* 你的音乐生成系统将使用90个独特的值。
- X, Y, n_values, indices_values, chords = load_music_utils("data/original_metheny.mid")
- print('number of training examples:', X.shape[0])
- print('Tx (length of sequence):', X.shape[1])
- print('total # of unique values:', n_values)
- print('shape of X:', X.shape)
- print('Shape of Y:', Y.shape)
number of training examples: 60
Tx (length of sequence): 30
total # of unique values: 90
shape of X: (60, 30, 90)
Shape of Y: (30, 60, 90)
模型概述
下面是您将使用的模型的体系结构。它类似于Dinosaurus模型,只不过您将在Keras中实现它。
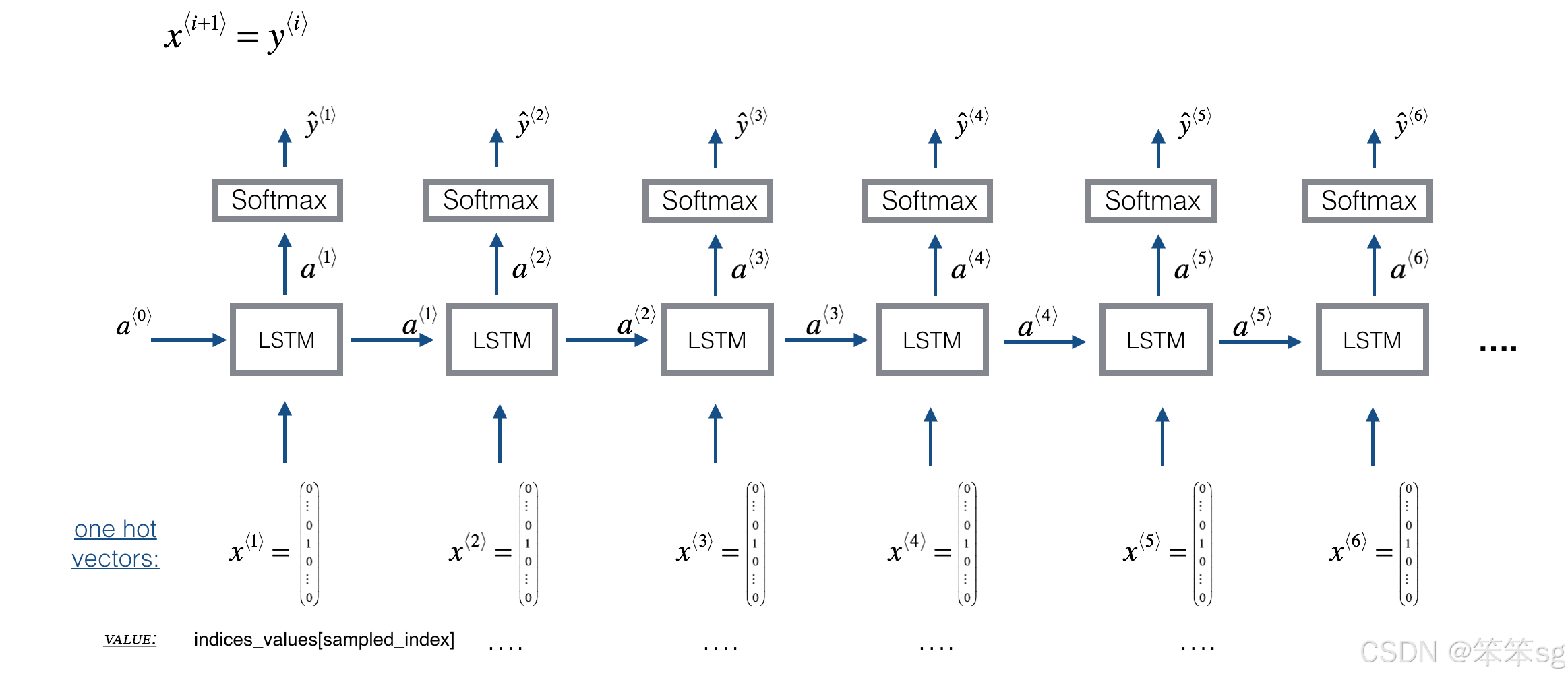
在第2部分中,您将训练一个模型,该模型预测下一个音符的风格与它所训练的爵士音乐相似。训练包含在模型的权重和偏差中。
然后,在第3节中,您将在预测一系列音符的新模型中使用这些权重和偏差,并使用前一个音符来预测下一个音符。
4.2 构造模型
现在,你将建立并训练一个学习音乐模式的模型。
* 模型接受形状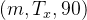 的输入X和形状
的输入X和形状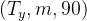 的标签Y。
的标签Y。
* 您将使用具有 维的隐藏状态的LSTM。
维的隐藏状态的LSTM。
- # number of dimensions for the hidden state of each LSTM cell.
- n_a = 64
- n_values = 90 # number of music values
- reshaper = Reshape((1, n_values)) # Used in Step 2.B of djmodel(), below
- LSTM_cell = LSTM(n_a, return_state = True) # Used in Step 2.C
- densor = Dense(n_values, activation='softmax') # Used in Step 2.D
- # UNQ_C1 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: djmodel
-
- def djmodel(Tx, LSTM_cell, densor, reshaper):
- # Get the shape of input values
- n_values = densor.units
-
- # Get the number of the hidden state vector
- n_a = LSTM_cell.units
-
- # Define the input layer and specify the shape
- X = Input(shape=(Tx, n_values))
-
- # Define the initial hidden state a0 and initial cell state c0
- # using `Input`
- a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')
- c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')
- a = a0
- c = c0
- # Step 1: Create empty list to append the outputs while you iterate (≈1 line)
- outputs = []
-
- # Step 2: Loop from 0 to Tx
- for t in range(Tx):
-
- # Step 2.A: select the "t"th time step vector from X.
- x = X[:,t,:]
- # Step 2.B: Use reshaper to reshape x to be (1, n_values) (≈1 line)
- x = reshaper(x)
- # Step 2.C: Perform one step of the LSTM_cell
- a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a, c])
- # Step 2.D: Apply densor to the hidden state output of LSTM_Cell
- out = densor(a)
- # Step 2.E: add the output to "outputs"
- outputs.append(out)
-
- # Step 3: Create model instance
- model = Model(inputs=[X, a0, c0], outputs=outputs)
-
- return model
创建模型对象
* 运行以下单元格来定义您的模型。
* 我们将使用“Tx=30”。
* 此单元格可能需要几秒钟才能运行。
model = djmodel(Tx=30, LSTM_cell=LSTM_cell, densor=densor, reshaper=reshaper)- # UNIT TEST
- output = summary(model)
- # Check your model
- model.summary()
- Model: "model"
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
- ==================================================================================================
- input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 30, 90)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem (Slici (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- reshape (Reshape) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.__operators__.getitem[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_1[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_2[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_3[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_4[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_5[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_6[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_7[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_8[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_9[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_10[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_11[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_12[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_13[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_14[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_15[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_16[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_17[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_18[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_19[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_20[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_21[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_22[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_23[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_24[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_25[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_26[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_27[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_28[0][0]
- tf.__operators__.getitem_29[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- a0 (InputLayer) [(None, 64)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- c0 (InputLayer) [(None, 64)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_1 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- lstm (LSTM) [(None, 64), (None, 39680 reshape[0][0]
- a0[0][0]
- c0[0][0]
- reshape[1][0]
- lstm[0][0]
- lstm[0][2]
- reshape[2][0]
- lstm[1][0]
- lstm[1][2]
- reshape[3][0]
- lstm[2][0]
- lstm[2][2]
- reshape[4][0]
- lstm[3][0]
- lstm[3][2]
- reshape[5][0]
- lstm[4][0]
- lstm[4][2]
- reshape[6][0]
- lstm[5][0]
- lstm[5][2]
- reshape[7][0]
- lstm[6][0]
- lstm[6][2]
- reshape[8][0]
- lstm[7][0]
- lstm[7][2]
- reshape[9][0]
- lstm[8][0]
- lstm[8][2]
- reshape[10][0]
- lstm[9][0]
- lstm[9][2]
- reshape[11][0]
- lstm[10][0]
- lstm[10][2]
- reshape[12][0]
- lstm[11][0]
- lstm[11][2]
- reshape[13][0]
- lstm[12][0]
- lstm[12][2]
- reshape[14][0]
- lstm[13][0]
- lstm[13][2]
- reshape[15][0]
- lstm[14][0]
- lstm[14][2]
- reshape[16][0]
- lstm[15][0]
- lstm[15][2]
- reshape[17][0]
- lstm[16][0]
- lstm[16][2]
- reshape[18][0]
- lstm[17][0]
- lstm[17][2]
- reshape[19][0]
- lstm[18][0]
- lstm[18][2]
- reshape[20][0]
- lstm[19][0]
- lstm[19][2]
- reshape[21][0]
- lstm[20][0]
- lstm[20][2]
- reshape[22][0]
- lstm[21][0]
- lstm[21][2]
- reshape[23][0]
- lstm[22][0]
- lstm[22][2]
- reshape[24][0]
- lstm[23][0]
- lstm[23][2]
- reshape[25][0]
- lstm[24][0]
- lstm[24][2]
- reshape[26][0]
- lstm[25][0]
- lstm[25][2]
- reshape[27][0]
- lstm[26][0]
- lstm[26][2]
- reshape[28][0]
- lstm[27][0]
- lstm[27][2]
- reshape[29][0]
- lstm[28][0]
- lstm[28][2]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_2 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_3 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_4 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_5 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_6 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_7 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_8 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_9 (Sli (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_10 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_11 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_12 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_13 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_14 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_15 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_16 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_17 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_18 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_19 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_20 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_21 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_22 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_23 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_24 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_25 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_26 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_27 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_28 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.__operators__.getitem_29 (Sl (None, 90) 0 input_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- dense (Dense) (None, 90) 5850 lstm[0][0]
- lstm[1][0]
- lstm[2][0]
- lstm[3][0]
- lstm[4][0]
- lstm[5][0]
- lstm[6][0]
- lstm[7][0]
- lstm[8][0]
- lstm[9][0]
- lstm[10][0]
- lstm[11][0]
- lstm[12][0]
- lstm[13][0]
- lstm[14][0]
- lstm[15][0]
- lstm[16][0]
- lstm[17][0]
- lstm[18][0]
- lstm[19][0]
- lstm[20][0]
- lstm[21][0]
- lstm[22][0]
- lstm[23][0]
- lstm[24][0]
- lstm[25][0]
- lstm[26][0]
- lstm[27][0]
- lstm[28][0]
- lstm[29][0]
- ==================================================================================================
- Total params: 45,530
- Trainable params: 45,530
- Non-trainable params: 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
编译模型
- * 你现在需要编译你的模型进行训练。
- * 我们将使用:
- - optimizer:亚当优化器
- - 损失函数:分类交叉熵(多类分类)
- opt = Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01)
-
- model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
初始化隐藏状态和单元状态
最后,让我们初始化‘ a0 ’和‘ c0 ’,使LSTM的初始状态为零。
- m = 60
- a0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
- c0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
训练模型
history = model.fit([X, a0, c0], list(Y), epochs=100, verbose = 0)- print(f"loss at epoch 1: {history.history['loss'][0]}")
- print(f"loss at epoch 100: {history.history['loss'][99]}")
- plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
loss at epoch 1: 129.90142822265625
loss at epoch 100: 9.128642082214355
预测输出
模型损失一开始会很高(100次左右),100次之后,应该是个位数。由于权重的随机初始化,这些不会是你将看到的确切数字。
现在您已经训练了一个模型,让我们进入最后一节,实现一个推理算法,并生成一些音乐!
4.3 生成音乐
你现在有了一个训练有素的模型,它已经学会了爵士独奏家的模式。你现在可以使用这个模型来合成新的音乐!
预测与采样
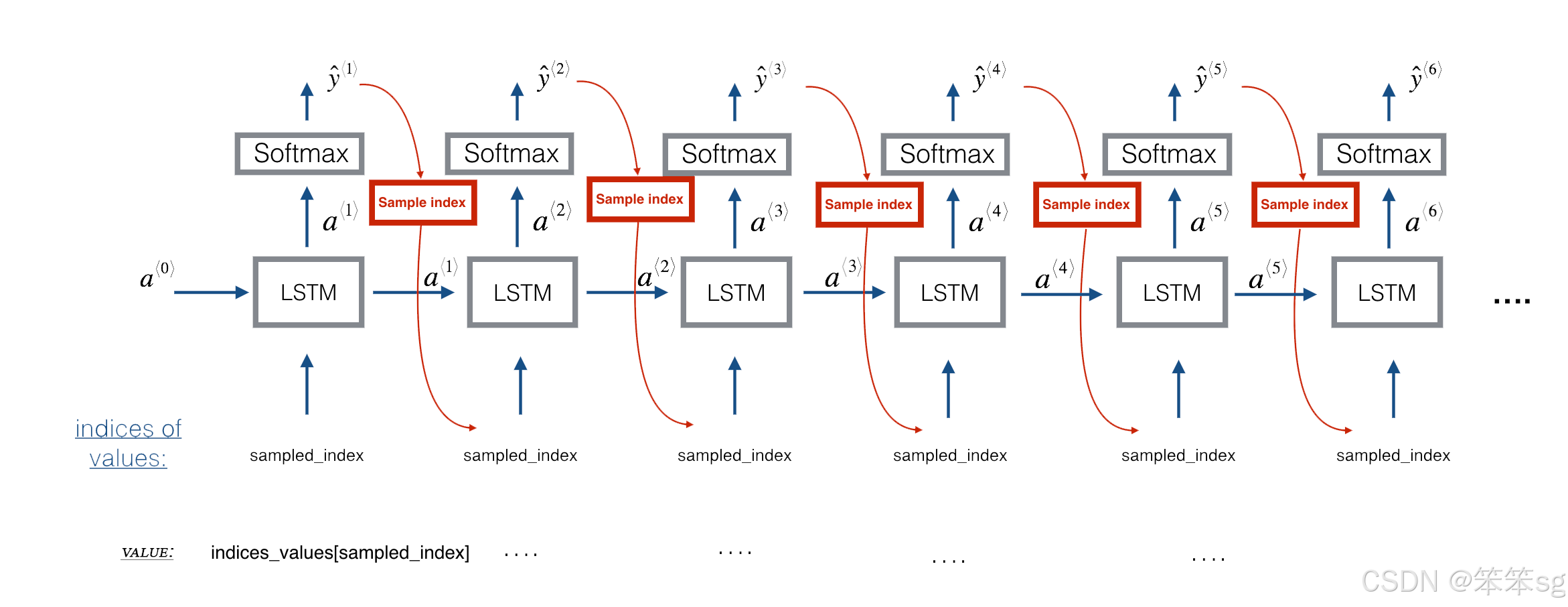
- # UNQ_C2 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: music_inference_model
-
- def music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, Ty=100):
-
- # Get the shape of input values
- n_values = densor.units
- # Get the number of the hidden state vector
- n_a = LSTM_cell.units
-
- # Define the input of your model with a shape
- x0 = Input(shape=(1, n_values))
-
-
- # Define s0, initial hidden state for the decoder LSTM
- a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')
- c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')
- a = a0
- c = c0
- x = x0
-
- # Step 1: Create an empty list of "outputs" to later store your predicted values (≈1 line)
- outputs = []
-
- # Step 2: Loop over Ty and generate a value at every time step
- for t in range(Ty):
- # Step 2.A: Perform one step of LSTM_cell. Use "x", not "x0" (≈1 line)
- a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a, c])
-
- # Step 2.B: Apply Dense layer to the hidden state output of the LSTM_cell (≈1 line)
- out = densor(a)
- # Step 2.C: Append the prediction "out" to "outputs". out.shape = (None, 90) (≈1 line)
- outputs.append(out)
-
-
- # Step 2.D:
- # Select the next value according to "out",
- # Set "x" to be the one-hot representation of the selected value
- # See instructions above.
- x = tf.math.argmax(out, axis=-1)
- x = tf.one_hot(x, n_values)
- # Step 2.E:
- # Use RepeatVector(1) to convert x into a tensor with shape=(None, 1, 90)
- x = RepeatVector(1)(x)
-
- # Step 3: Create model instance with the correct "inputs" and "outputs" (≈1 line)
- inference_model = Model(inputs=[x0, a0, c0], outputs=outputs)
-
- return inference_model
该模型被硬编码为生成50个值。
inference_model = music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, Ty = 50)- # UNIT TEST
- inference_summary = summary(inference_model)
- # comparator(inference_summary, music_inference_model_out)
- # Check the inference model
- inference_model.summary()
- Model: "model_1"
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
- ==================================================================================================
- input_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 1, 90)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- a0 (InputLayer) [(None, 64)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- c0 (InputLayer) [(None, 64)] 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- lstm (LSTM) [(None, 64), (None, 39680 input_2[0][0]
- a0[0][0]
- c0[0][0]
- repeat_vector[0][0]
- lstm[30][0]
- lstm[30][2]
- repeat_vector_1[0][0]
- lstm[31][0]
- lstm[31][2]
- repeat_vector_2[0][0]
- lstm[32][0]
- lstm[32][2]
- repeat_vector_3[0][0]
- lstm[33][0]
- lstm[33][2]
- repeat_vector_4[0][0]
- lstm[34][0]
- lstm[34][2]
- repeat_vector_5[0][0]
- lstm[35][0]
- lstm[35][2]
- repeat_vector_6[0][0]
- lstm[36][0]
- lstm[36][2]
- repeat_vector_7[0][0]
- lstm[37][0]
- lstm[37][2]
- repeat_vector_8[0][0]
- lstm[38][0]
- lstm[38][2]
- repeat_vector_9[0][0]
- lstm[39][0]
- lstm[39][2]
- repeat_vector_10[0][0]
- lstm[40][0]
- lstm[40][2]
- repeat_vector_11[0][0]
- lstm[41][0]
- lstm[41][2]
- repeat_vector_12[0][0]
- lstm[42][0]
- lstm[42][2]
- repeat_vector_13[0][0]
- lstm[43][0]
- lstm[43][2]
- repeat_vector_14[0][0]
- lstm[44][0]
- lstm[44][2]
- repeat_vector_15[0][0]
- lstm[45][0]
- lstm[45][2]
- repeat_vector_16[0][0]
- lstm[46][0]
- lstm[46][2]
- repeat_vector_17[0][0]
- lstm[47][0]
- lstm[47][2]
- repeat_vector_18[0][0]
- lstm[48][0]
- lstm[48][2]
- repeat_vector_19[0][0]
- lstm[49][0]
- lstm[49][2]
- repeat_vector_20[0][0]
- lstm[50][0]
- lstm[50][2]
- repeat_vector_21[0][0]
- lstm[51][0]
- lstm[51][2]
- repeat_vector_22[0][0]
- lstm[52][0]
- lstm[52][2]
- repeat_vector_23[0][0]
- lstm[53][0]
- lstm[53][2]
- repeat_vector_24[0][0]
- lstm[54][0]
- lstm[54][2]
- repeat_vector_25[0][0]
- lstm[55][0]
- lstm[55][2]
- repeat_vector_26[0][0]
- lstm[56][0]
- lstm[56][2]
- repeat_vector_27[0][0]
- lstm[57][0]
- lstm[57][2]
- repeat_vector_28[0][0]
- lstm[58][0]
- lstm[58][2]
- repeat_vector_29[0][0]
- lstm[59][0]
- lstm[59][2]
- repeat_vector_30[0][0]
- lstm[60][0]
- lstm[60][2]
- repeat_vector_31[0][0]
- lstm[61][0]
- lstm[61][2]
- repeat_vector_32[0][0]
- lstm[62][0]
- lstm[62][2]
- repeat_vector_33[0][0]
- lstm[63][0]
- lstm[63][2]
- repeat_vector_34[0][0]
- lstm[64][0]
- lstm[64][2]
- repeat_vector_35[0][0]
- lstm[65][0]
- lstm[65][2]
- repeat_vector_36[0][0]
- lstm[66][0]
- lstm[66][2]
- repeat_vector_37[0][0]
- lstm[67][0]
- lstm[67][2]
- repeat_vector_38[0][0]
- lstm[68][0]
- lstm[68][2]
- repeat_vector_39[0][0]
- lstm[69][0]
- lstm[69][2]
- repeat_vector_40[0][0]
- lstm[70][0]
- lstm[70][2]
- repeat_vector_41[0][0]
- lstm[71][0]
- lstm[71][2]
- repeat_vector_42[0][0]
- lstm[72][0]
- lstm[72][2]
- repeat_vector_43[0][0]
- lstm[73][0]
- lstm[73][2]
- repeat_vector_44[0][0]
- lstm[74][0]
- lstm[74][2]
- repeat_vector_45[0][0]
- lstm[75][0]
- lstm[75][2]
- repeat_vector_46[0][0]
- lstm[76][0]
- lstm[76][2]
- repeat_vector_47[0][0]
- lstm[77][0]
- lstm[77][2]
- repeat_vector_48[0][0]
- lstm[78][0]
- lstm[78][2]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- dense (Dense) (None, 90) 5850 lstm[30][0]
- lstm[31][0]
- lstm[32][0]
- lstm[33][0]
- lstm[34][0]
- lstm[35][0]
- lstm[36][0]
- lstm[37][0]
- lstm[38][0]
- lstm[39][0]
- lstm[40][0]
- lstm[41][0]
- lstm[42][0]
- lstm[43][0]
- lstm[44][0]
- lstm[45][0]
- lstm[46][0]
- lstm[47][0]
- lstm[48][0]
- lstm[49][0]
- lstm[50][0]
- lstm[51][0]
- lstm[52][0]
- lstm[53][0]
- lstm[54][0]
- lstm[55][0]
- lstm[56][0]
- lstm[57][0]
- lstm[58][0]
- lstm[59][0]
- lstm[60][0]
- lstm[61][0]
- lstm[62][0]
- lstm[63][0]
- lstm[64][0]
- lstm[65][0]
- lstm[66][0]
- lstm[67][0]
- lstm[68][0]
- lstm[69][0]
- lstm[70][0]
- lstm[71][0]
- lstm[72][0]
- lstm[73][0]
- lstm[74][0]
- lstm[75][0]
- lstm[76][0]
- lstm[77][0]
- lstm[78][0]
- lstm[79][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[30][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_1 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[31][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_1 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_1[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_2 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[32][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_2 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_2[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_2 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_2[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_3 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[33][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_3 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_3[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_3 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_3[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_4 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[34][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_4 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_4[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_4 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_4[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_5 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[35][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_5 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_5[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_5 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_5[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_6 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[36][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_6 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_6[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_6 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_6[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_7 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[37][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_7 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_7[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_7 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_7[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_8 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[38][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_8 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_8[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_8 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_8[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_9 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[39][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_9 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_9[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_9 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_9[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_10 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[40][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_10 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_10[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_10 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_10[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_11 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[41][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_11 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_11[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_11 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_11[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_12 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[42][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_12 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_12[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_12 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_12[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_13 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[43][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_13 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_13[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_13 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_13[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_14 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[44][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_14 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_14[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_14 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_14[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_15 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[45][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_15 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_15[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_15 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_15[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_16 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[46][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_16 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_16[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_16 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_16[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_17 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[47][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_17 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_17[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_17 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_17[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_18 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[48][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_18 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_18[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_18 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_18[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_19 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[49][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_19 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_19[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_19 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_19[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_20 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[50][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_20 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_20[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_20 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_20[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_21 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[51][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_21 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_21[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_21 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_21[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_22 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[52][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_22 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_22[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_22 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_22[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_23 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[53][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_23 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_23[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_23 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_23[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_24 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[54][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_24 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_24[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_24 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_24[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_25 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[55][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_25 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_25[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_25 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_25[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_26 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[56][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_26 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_26[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_26 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_26[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_27 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[57][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_27 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_27[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_27 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_27[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_28 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[58][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_28 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_28[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_28 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_28[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_29 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[59][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_29 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_29[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_29 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_29[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_30 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[60][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_30 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_30[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_30 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_30[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_31 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[61][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_31 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_31[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_31 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_31[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_32 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[62][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_32 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_32[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_32 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_32[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_33 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[63][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_33 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_33[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_33 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_33[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_34 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[64][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_34 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_34[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_34 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_34[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_35 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[65][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_35 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_35[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_35 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_35[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_36 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[66][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_36 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_36[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_36 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_36[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_37 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[67][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_37 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_37[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_37 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_37[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_38 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[68][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_38 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_38[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_38 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_38[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_39 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[69][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_39 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_39[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_39 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_39[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_40 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[70][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_40 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_40[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_40 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_40[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_41 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[71][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_41 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_41[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_41 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_41[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_42 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[72][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_42 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_42[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_42 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_42[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_43 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[73][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_43 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_43[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_43 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_43[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_44 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[74][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_44 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_44[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_44 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_44[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_45 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[75][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_45 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_45[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_45 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_45[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_46 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[76][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_46 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_46[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_46 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_46[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_47 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[77][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_47 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_47[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_47 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_47[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.math.argmax_48 (TFOpLambda) (None,) 0 dense[78][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- tf.one_hot_48 (TFOpLambda) (None, 90) 0 tf.math.argmax_48[0][0]
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
- repeat_vector_48 (RepeatVector) (None, 1, 90) 0 tf.one_hot_48[0][0]
- ==================================================================================================
- Total params: 45,530
- Trainable params: 45,530
- Non-trainable params: 0
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
下面的代码创建了将用于初始化‘ x ’和LSTM状态变量‘ a ’和‘ c ’的零值向量。
- x_initializer = np.zeros((1, 1, n_values))
- a_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
- c_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
- # UNQ_C3 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)
- # GRADED FUNCTION: predict_and_sample
-
- def predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer = x_initializer, a_initializer = a_initializer,
- c_initializer = c_initializer):
-
- n_values = x_initializer.shape[2]
-
- # Step 1: Use your inference model to predict an output sequence given x_initializer, a_initializer and c_initializer.
- pred = inference_model.predict([x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer])
- # Step 2: Convert "pred" into an np.array() of indices with the maximum probabilities
- indices = np.argmax(pred, axis = -1)
- # Step 3: Convert indices to one-hot vectors, the shape of the results should be (Ty, n_values)
- results = to_categorical(indices, num_classes=n_values)
-
- return results, indices
- results, indices = predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer)
-
- print("np.argmax(results[12]) =", np.argmax(results[12]))
- print("np.argmax(results[17]) =", np.argmax(results[17]))
- print("list(indices[12:18]) =", list(indices[12:18]))
np.argmax(results[12]) = 31
np.argmax(results[17]) = 44
list(indices[12:18]) = [array([31], dtype=int64), array([76], dtype=int64), array([50], dtype=int64), array([9], dtype=int64), array([34], dtype=int64), array([44], dtype=int64)]
生成音乐
你的RNN生成一个值序列。下面的代码通过首先调用‘ predict_and_sample() ’函数来生成音乐。然后将这些值后处理成和弦(意味着可以同时播放多个值或音符)。
大多数计算音乐算法使用一些后处理,因为没有后处理就很难生成好听的音乐。后期处理的工作包括清理生成的音频,确保相同的声音不会重复太多次,或者两个连续的音符在音高上不会相差太远,等等。
有人可能会说,许多这些后期处理步骤是hack;此外,许多音乐生成文献也专注于手工制作后处理器,许多输出质量取决于后处理的质量,而不仅仅是模型的质量。但是这种后处理确实会产生巨大的差异,因此您也应该在实现中使用它。
让我们做点音乐吧!
运行以下单元格生成音乐并将其记录到您的‘ out_stream ’中。这可能需要几分钟。
out_stream = generate_music(inference_model, indices_values, chords, "output/sghn.midi")Predicting new values for different set of chords.
Generated 37 sounds using the predicted values for the set of chords ("1") and after pruning
Generated 37 sounds using the predicted values for the set of chords ("2") and after pruning
Generated 37 sounds using the predicted values for the set of chords ("3") and after pruning
Generated 37 sounds using the predicted values for the set of chords ("4") and after pruning
Generated 37 sounds using the predicted values for the set of chords ("5") and after pruning
Your generated music is saved in output/sghn.midi
使用基本的midi到wav解析器,您可以对该模型生成的音频剪辑有一个大致的了解。解析器非常有限。
- mid2wav('output/sghn.midi')
- IPython.display.Audio('./output/rendered.wav')
将 MIDI 文件转换为 WAV 音频文件,转换后的 WAV 文件通常保存为 rendered.wav 或指定的文件名

我觉得还蛮好听的,可惜分享不了。
恭喜你!
你已经完成了这个任务,并生成了你自己的爵士独奏!科尔特兰一家会感到骄傲的。
到目前为止,你已经:
- 将LSTM应用于音乐生成任务
- 通过深度学习生成自己的爵士音乐
- 使用灵活的Functional API创建更复杂的模型
这是一项漫长的任务。你应该为你的努力感到自豪,希望你能有一些好音乐来展示你的努力。谢谢,下次见!
注意事项:
- - 序列模型可以用来生成音乐值,然后后期处理成midi音乐。
- - 你可以使用一个相当相似的模型来完成从生成恐龙名字到生成原创音乐的任务,唯一的主要区别是输入到模型中。
- - 在Keras中,序列生成涉及定义具有共享权重的层,然后在不同的时间步长
中重复。

评论记录:
回复评论: